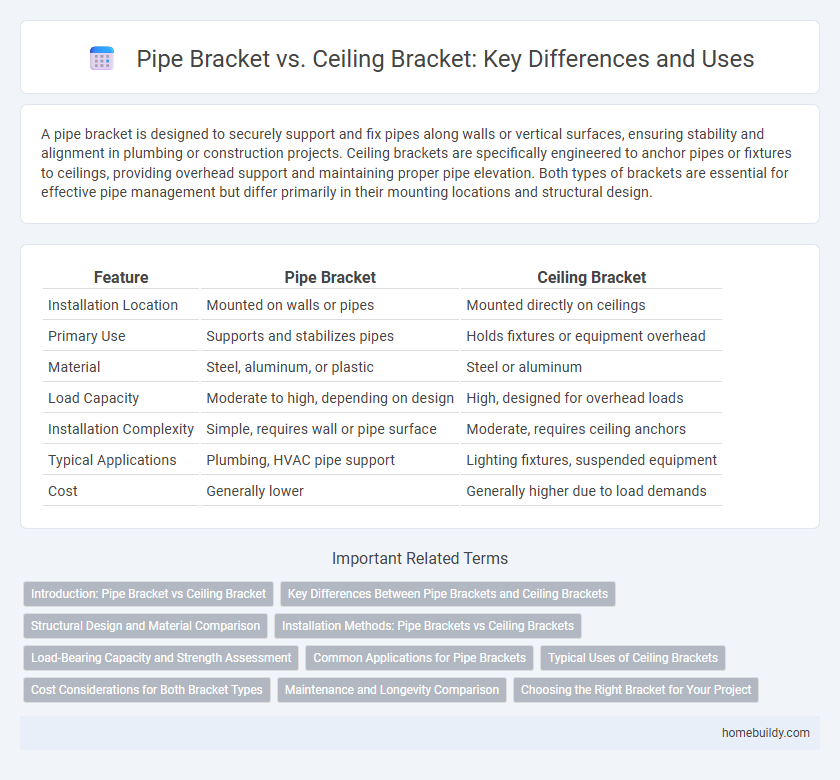
A pipe bracket is designed to securely support and fix pipes along walls or vertical surfaces, ensuring stability and alignment in plumbing or construction projects. Ceiling brackets are specifically engineered to anchor pipes or fixtures to ceilings, providing overhead support and maintaining proper pipe elevation. Both types of brackets are essential for effective pipe management but differ primarily in their mounting locations and structural design.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pipe Bracket | Ceiling Bracket |
|---|---|---|
| Installation Location | Mounted on walls or pipes | Mounted directly on ceilings |
| Primary Use | Supports and stabilizes pipes | Holds fixtures or equipment overhead |
| Material | Steel, aluminum, or plastic | Steel or aluminum |
| Load Capacity | Moderate to high, depending on design | High, designed for overhead loads |
| Installation Complexity | Simple, requires wall or pipe surface | Moderate, requires ceiling anchors |
| Typical Applications | Plumbing, HVAC pipe support | Lighting fixtures, suspended equipment |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher due to load demands |
Introduction: Pipe Bracket vs Ceiling Bracket
Pipe brackets provide strong lateral support for horizontal pipes, ensuring stability by securing them along walls or beams. Ceiling brackets, designed for vertical suspension, hang pipes from overhead structures to maintain alignment and reduce stress. Choosing between pipe brackets and ceiling brackets depends on the pipe's orientation and load-bearing requirements in plumbing or HVAC installations.
Key Differences Between Pipe Brackets and Ceiling Brackets
Pipe brackets are primarily designed to secure pipes along walls or vertical surfaces, offering sturdy lateral support, whereas ceiling brackets are engineered to suspend pipes from overhead structures, providing vertical load bearing. The key difference lies in their mounting orientation and load distribution: pipe brackets anchor horizontally against walls, while ceiling brackets hang vertically from ceilings, affecting installation methods and load capacity. Material composition and size vary according to environmental exposure and pipe diameter, ensuring optimal durability and fit for their respective applications.
Structural Design and Material Comparison
Pipe brackets are typically designed with sturdy steel or galvanized iron to support vertical or horizontal pipe loads, offering high tensile strength and corrosion resistance essential for heavy-duty applications. Ceiling brackets often utilize lighter materials like aluminum or plastic composites to reduce weight while maintaining sufficient rigidity for ceiling-mounted pipes, prioritizing ease of installation and aesthetic integration. Structural design of pipe brackets emphasizes load-bearing capacity and stability under dynamic forces, whereas ceiling brackets focus on maximizing support with minimal structural intrusion.
Installation Methods: Pipe Brackets vs Ceiling Brackets
Pipe brackets are typically installed by clamping around the pipe and securing to walls or other vertical surfaces using screws or bolts, allowing for direct support of horizontal piping runs. Ceiling brackets are mounted onto overhead structures, often requiring anchors and additional hardware to suspend pipes from ceilings, which is ideal for elevating piping systems above floor level. The choice between pipe and ceiling brackets depends on the structural context and desired pipe orientation, with pipe brackets favoring vertical supports and ceiling brackets facilitating overhead suspension.
Load-Bearing Capacity and Strength Assessment
Pipe brackets are designed to securely support pipes by distributing load evenly, often exhibiting higher load-bearing capacity compared to ceiling brackets, which rely on ceiling structures that may have variable strength. Strength assessment of pipe brackets involves evaluating material durability, bracket thickness, and welding quality, ensuring optimal resistance to bending and shear forces. Ceiling brackets, however, depend largely on the ceiling's structural integrity, making their load capacity generally lower and more situational than that of pipe brackets.
Common Applications for Pipe Brackets
Pipe brackets are widely used for securely mounting and supporting pipes in plumbing, HVAC systems, and industrial installations, providing stability and reducing vibration. Compared to ceiling brackets, pipe brackets are preferred in vertical and horizontal pipe runs where wall or floor attachment is necessary. Their common applications include securing water, gas, and electrical conduit pipes in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
Typical Uses of Ceiling Brackets
Ceiling brackets are commonly used to support pipes that run parallel to the ceiling, providing strong overhead stabilization for plumbing, electrical conduits, and HVAC systems. Their design allows for secure attachment in areas with limited wall space or where floor-mounted supports are impractical. Ceiling brackets excel in environments such as commercial buildings and industrial settings, where pipes need to be elevated to prevent obstruction and ensure safety compliance.
Cost Considerations for Both Bracket Types
Pipe brackets generally incur lower material and installation costs due to their simpler design and compatibility with standard piping systems, making them a budget-friendly option for many projects. Ceiling brackets often require more robust mounting, enhanced hardware, and professional labor, resulting in higher overall expenses. Evaluating project requirements and cost implications helps determine the most economical choice between pipe brackets and ceiling brackets.
Maintenance and Longevity Comparison
Pipe brackets typically offer easier maintenance due to their simpler design, allowing quicker access for cleaning and inspections compared to ceiling brackets. Ceiling brackets, while offering a more secure fixed support, often require more frequent checks and potentially complex repairs due to their overhead positioning. Longevity of pipe brackets is generally higher in environments with low physical stress, whereas ceiling brackets demonstrate better durability in heavy load applications but may suffer from faster wear if improperly maintained.
Choosing the Right Bracket for Your Project
Pipe brackets provide sturdy support for securing pipes along walls or floors, ideal for horizontal installations. Ceiling brackets are specifically designed to suspend pipes from overhead structures, allowing for vertical clearance and space optimization. Selecting the right bracket depends on the installation environment, load requirements, and desired pipe positioning to ensure stability and ease of maintenance.
Pipe bracket vs Ceiling bracket Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com