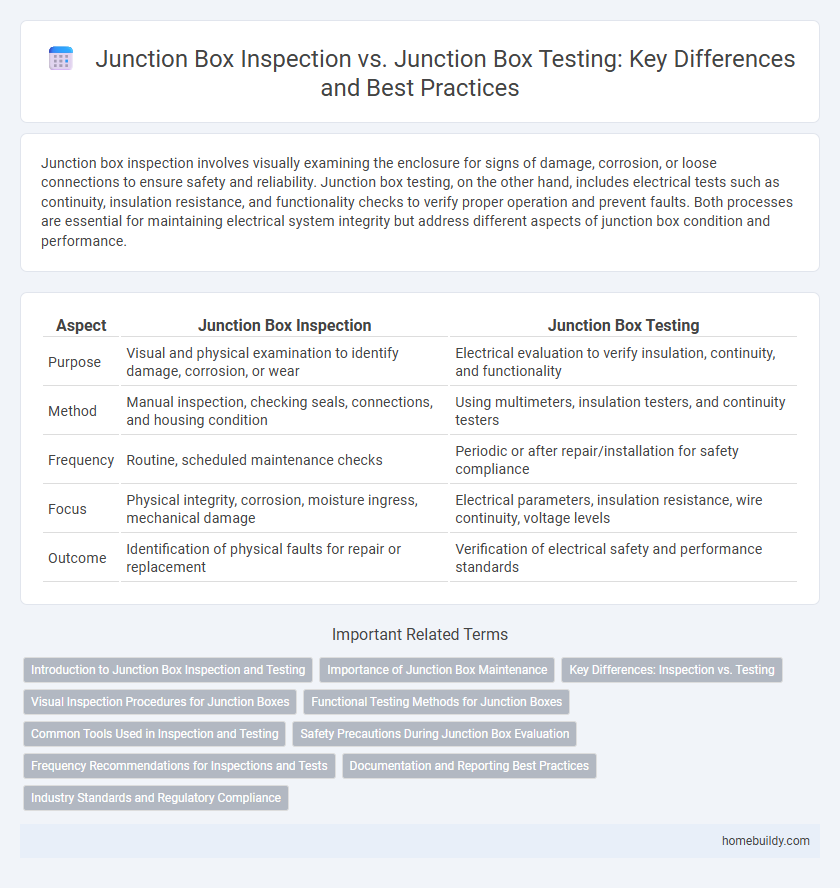
Junction box inspection involves visually examining the enclosure for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections to ensure safety and reliability. Junction box testing, on the other hand, includes electrical tests such as continuity, insulation resistance, and functionality checks to verify proper operation and prevent faults. Both processes are essential for maintaining electrical system integrity but address different aspects of junction box condition and performance.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Junction Box Inspection | Junction Box Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Visual and physical examination to identify damage, corrosion, or wear | Electrical evaluation to verify insulation, continuity, and functionality |
| Method | Manual inspection, checking seals, connections, and housing condition | Using multimeters, insulation testers, and continuity testers |
| Frequency | Routine, scheduled maintenance checks | Periodic or after repair/installation for safety compliance |
| Focus | Physical integrity, corrosion, moisture ingress, mechanical damage | Electrical parameters, insulation resistance, wire continuity, voltage levels |
| Outcome | Identification of physical faults for repair or replacement | Verification of electrical safety and performance standards |
Introduction to Junction Box Inspection and Testing
Junction box inspection involves a thorough visual and physical examination to ensure proper installation, integrity of wiring connections, and absence of damage or corrosion. Junction box testing primarily focuses on electrical assessments such as continuity, insulation resistance, and functionality of circuits within the box. Both inspection and testing are critical for maintaining safety, compliance with electrical codes, and preventing potential failures in electrical systems.
Importance of Junction Box Maintenance
Junction box inspection identifies physical damage, corrosion, and loose connections that can lead to electrical hazards, ensuring safety and compliance. Junction box testing evaluates electrical continuity, insulation resistance, and functionality to detect hidden faults and prevent system failures. Regular maintenance combining inspection and testing optimizes electrical system reliability, reduces downtime, and extends equipment lifespan.
Key Differences: Inspection vs. Testing
Junction box inspection involves a visual and physical examination of wiring, connections, and components to ensure compliance with safety standards and detect potential damage or corrosion. Junction box testing includes electrical tests such as continuity, insulation resistance, and voltage tests to verify the functionality and integrity of circuits within the box. Key differences lie in inspection focusing on identifying visible defects and adherence to installation standards, while testing evaluates electrical performance and operational safety.
Visual Inspection Procedures for Junction Boxes
Visual inspection procedures for junction boxes primarily involve checking for physical damage, corrosion, proper sealing, and secure connections to ensure electrical safety and reliability. Inspectors examine the enclosure for cracks, moisture ingress, and signs of overheating while verifying that all wiring terminals are correctly tightened and free from insulation damage. Regular visual inspections are essential to identify potential hazards before conducting electrical testing, facilitating preventive maintenance and compliance with safety standards.
Functional Testing Methods for Junction Boxes
Functional testing methods for junction boxes involve evaluating electrical continuity, insulation resistance, and circuit integrity to ensure proper operation under load conditions. Inspection focuses primarily on visual assessment, verifying correct wiring, component integrity, and enclosure sealing to prevent environmental damage. Combining both inspection and functional testing ensures the junction box meets safety standards and performs reliably in practical applications.
Common Tools Used in Inspection and Testing
Junction box inspection typically involves visual assessment tools such as flashlights, magnifying glasses, and thermal imaging cameras to identify physical damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Junction box testing, on the other hand, employs electrical testing instruments like multimeters, insulation resistance testers, and continuity testers to verify circuit integrity and ensure proper insulation resistance. Both processes rely on specialized equipment to maintain safety standards and operational reliability in electrical systems.
Safety Precautions During Junction Box Evaluation
Safety precautions during junction box evaluation emphasize the importance of both inspection and testing to prevent electrical hazards. Inspection involves visually checking for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections that could cause short circuits or fires, while testing includes verifying voltage, continuity, and insulation integrity using specialized instruments. Proper personal protective equipment (PPE), power isolation, and adherence to electrical safety standards significantly reduce the risk of electric shock and equipment failure during both inspection and testing processes.
Frequency Recommendations for Inspections and Tests
Junction box inspection frequency typically ranges from every 6 to 12 months, ensuring visual checks for corrosion, loose connections, and physical damage. Testing, including insulation resistance and continuity tests, is generally recommended annually to verify electrical integrity and safety compliance. Adhering to these intervals minimizes the risk of electrical failures and extends equipment lifespan.
Documentation and Reporting Best Practices
Junction box inspection involves visual and physical assessment to verify proper installation, continuity, and absence of damage, with documentation focusing on detailed checklists and photographic records. Junction box testing includes electrical measurements such as insulation resistance and continuity tests, requiring precise recording of test values, date, and tester information for compliance and troubleshooting. Comprehensive reporting combines both inspection and testing data, ensuring traceability and facilitating maintenance through standardized forms and digital logging systems.
Industry Standards and Regulatory Compliance
Junction box inspection involves a thorough visual and physical examination to ensure structural integrity, proper sealing, and correct wiring as per industry standards such as NEC (National Electrical Code) and IEC regulations. Junction box testing emphasizes verifying electrical continuity, insulation resistance, and grounding effectiveness to comply with regulatory requirements like UL certification and OSHA safety standards. Both inspection and testing are critical for maintaining compliance, preventing hazards, and ensuring reliable operation in industrial environments.
Junction box inspection vs Junction box testing Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com