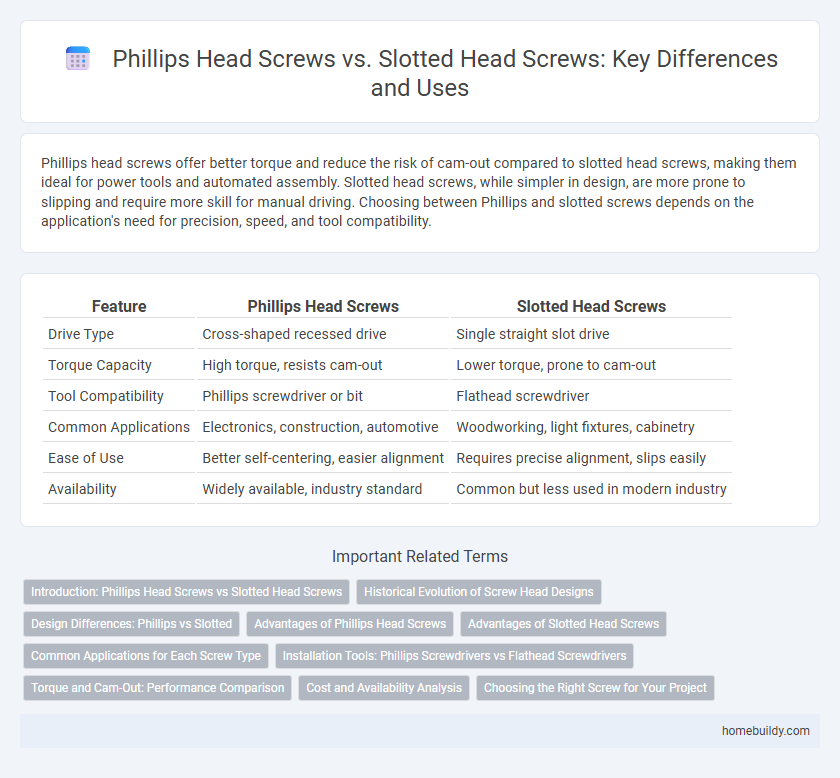
Phillips head screws offer better torque and reduce the risk of cam-out compared to slotted head screws, making them ideal for power tools and automated assembly. Slotted head screws, while simpler in design, are more prone to slipping and require more skill for manual driving. Choosing between Phillips and slotted screws depends on the application's need for precision, speed, and tool compatibility.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Phillips Head Screws | Slotted Head Screws |
|---|---|---|
| Drive Type | Cross-shaped recessed drive | Single straight slot drive |
| Torque Capacity | High torque, resists cam-out | Lower torque, prone to cam-out |
| Tool Compatibility | Phillips screwdriver or bit | Flathead screwdriver |
| Common Applications | Electronics, construction, automotive | Woodworking, light fixtures, cabinetry |
| Ease of Use | Better self-centering, easier alignment | Requires precise alignment, slips easily |
| Availability | Widely available, industry standard | Common but less used in modern industry |
Introduction: Phillips Head Screws vs Slotted Head Screws
Phillips head screws feature a cross-shaped drive that provides better grip and torque compared to the single-slot design of slotted head screws. The self-centering design of Phillips heads reduces cam-out, making them ideal for power tools, while slotted screws require more precision and are prone to slipping. These differences impact their application in construction, electronics, and woodworking, where fastening efficiency and tool compatibility are critical.
Historical Evolution of Screw Head Designs
Phillips head screws were developed in the 1930s to address the limitations of slotted head screws, offering improved torque transfer and reduced cam-out during assembly. Slotted head screws date back to the Renaissance era, characterized by a simple single slot that was prone to slipping and limited efficiency in power-driven tools. The evolution from slotted to Phillips head designs marked a significant advancement in fastening technology, enabling faster manufacturing processes and enhanced reliability in mechanical applications.
Design Differences: Phillips vs Slotted
Phillips head screws feature a cross-shaped slot designed to prevent cam-out by allowing the screwdriver to self-center, whereas slotted head screws have a single straight slot requiring precise alignment. The Phillips design permits higher torque application and faster engagement, improving efficiency in automated assembly lines. Slotted screws, while simpler in shape, offer less resistance to slipping and are better suited for manual, low-torque applications.
Advantages of Phillips Head Screws
Phillips head screws provide superior torque control, reducing the risk of cam-out during installation, which enhances efficiency and prevents damage to the fastener and work surface. Their self-centering design allows for easier alignment with the screwdriver, improving speed and accuracy in assembly processes. Widely used in manufacturing and construction, Phillips head screws are compatible with powered drivers, making them ideal for high-volume applications.
Advantages of Slotted Head Screws
Slotted head screws offer the advantage of simplicity and compatibility with a wide range of traditional tools, making them ideal for basic woodworking and light maintenance tasks. Their single-slot design reduces the risk of cam-out compared to Phillips head screws under low torque conditions, ensuring better control during manual driving. Additionally, slotted screws are easier to manufacture, often resulting in lower costs and wide availability for standard applications.
Common Applications for Each Screw Type
Phillips head screws are commonly used in electronic devices, automotive assemblies, and construction projects due to their self-centering design and resistance to cam-out, making them ideal for power tools. Slotted head screws find frequent application in woodworking, light fixtures, and historical restoration because they require simple tools like flathead screwdrivers and are easier to adjust manually. Both screw types serve distinct purposes driven by their design characteristics and the specific requirements of the task at hand.
Installation Tools: Phillips Screwdrivers vs Flathead Screwdrivers
Phillips head screws require Phillips screwdrivers with a cross-shaped tip that provides better grip and torque, reducing the risk of cam-out during installation. Slotted head screws are installed using flathead screwdrivers with a flat, straight blade, which offer less torque and are more prone to slipping or damaging the screw head. Choosing the appropriate screwdriver enhances installation efficiency and minimizes hardware wear in fastening applications.
Torque and Cam-Out: Performance Comparison
Phillips head screws offer higher torque tolerance with reduced risk of cam-out due to their cruciform design, enabling better engagement with the screwdriver. Slotted head screws typically provide lower torque capacity and are more prone to cam-out since the flat slot allows the driver to slip under high torque conditions. For applications requiring consistent torque and minimal slippage, Phillips screws deliver superior fastening performance compared to traditional slotted screws.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Phillips head screws generally offer a cost advantage due to their standardized design and widespread manufacturing, which leads to mass production economies. Slotted head screws, while often less expensive per unit in small batches, face limited availability and reduced compatibility with modern automated assembly systems, impacting overall procurement efficiency. The broader availability of Phillips head screws in various materials and sizes also enhances their cost-effectiveness for large-scale industrial use.
Choosing the Right Screw for Your Project
Phillips head screws offer better grip and torque control, making them ideal for power tools and high-torque applications, whereas slotted head screws suit simple, low-torque tasks and manual screwdrivers. Selecting the right screw depends on the required precision, tool compatibility, and the material being fastened. Consider Phillips screws for stronger, more secure fastening in woodworking or metal projects, while slotted screws work well for light-duty repairs and vintage hardware restoration.
Phillips head screws vs slotted head screws Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com