Hex bolts provide superior torque strength and are ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring high clamping force, featuring a hexagonal head for use with wrenches or sockets. Carriage bolts have a smooth, rounded head with a square neck that prevents spinning when tightened, making them perfect for wood and metal fastening in applications where a finished appearance is desired. Choosing between hex bolts and carriage bolts depends on the specific requirements for grip, appearance, and installation method in your project.
Table of Comparison
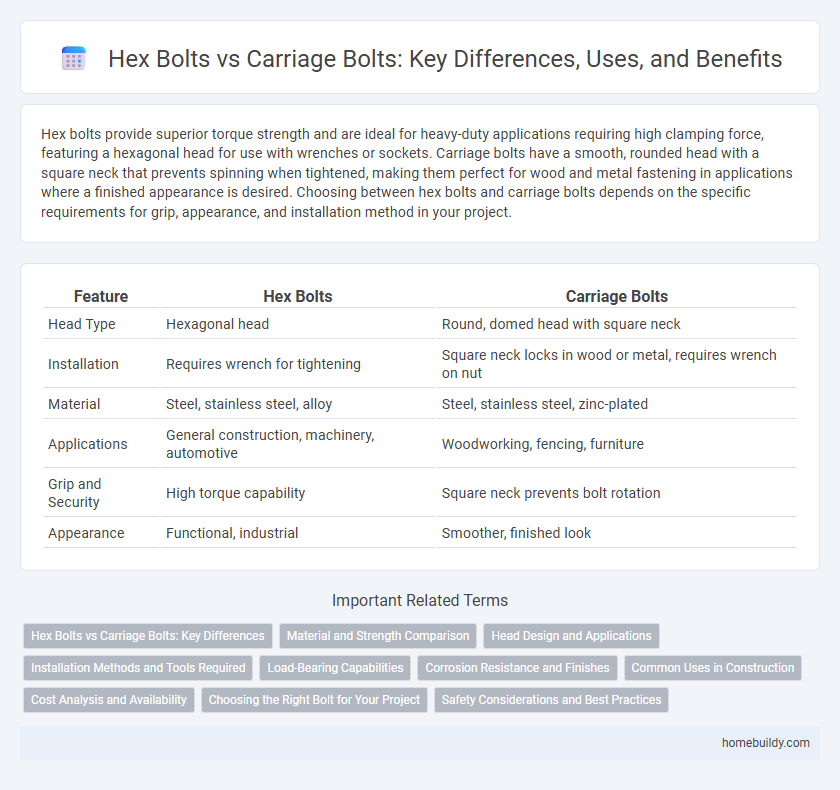
| Feature | Hex Bolts | Carriage Bolts |
|---|---|---|
| Head Type | Hexagonal head | Round, domed head with square neck |
| Installation | Requires wrench for tightening | Square neck locks in wood or metal, requires wrench on nut |
| Material | Steel, stainless steel, alloy | Steel, stainless steel, zinc-plated |
| Applications | General construction, machinery, automotive | Woodworking, fencing, furniture |
| Grip and Security | High torque capability | Square neck prevents bolt rotation |
| Appearance | Functional, industrial | Smoother, finished look |
Hex Bolts vs Carriage Bolts: Key Differences
Hex bolts feature a hexagonal head designed for wrench tightening, providing strong torque resistance ideal for heavy-duty applications. Carriage bolts have a rounded, smooth head with a square neck to prevent rotation once installed, commonly used in wood connections for a clean finish. The primary differences lie in head shape, installation method, and application suitability, with hex bolts preferred for metal and carriage bolts for wood fastening.
Material and Strength Comparison
Hex bolts typically feature a fully threaded or partially threaded shank made from high-strength carbon steel or stainless steel, offering superior tensile strength and durability for heavy-duty applications. Carriage bolts usually have a smooth, rounded head with a square neck beneath it to prevent rotation and are often manufactured from mild steel or galvanized steel, which provides moderate strength and corrosion resistance. The material composition and design differences result in hex bolts being more suitable for structural connections requiring higher load capacity, while carriage bolts are preferred for wood fastening and applications needing a finished appearance with moderate strength.
Head Design and Applications
Hex bolts feature a six-sided head designed for wrench tightening, providing strong torque and easy grip in construction and machinery assembly. Carriage bolts have a domed, smooth, rounded head with a square neck beneath that locks into wood, commonly used in woodworking and fastening metal to wood. The head design of hex bolts suits heavy-duty applications requiring high torque, while carriage bolts are ideal for aesthetic finishes and preventing bolt rotation in wooden structures.
Installation Methods and Tools Required
Hex bolts require a wrench or socket driver for installation, tightening the hexagonal head to secure materials. Carriage bolts feature a rounded head with a square neck that locks into the wood or metal, allowing installation with a wrench on the nut side while the head remains flush. Proper tool selection ensures efficient fastening and prevents bolt damage during installation.
Load-Bearing Capabilities
Hex bolts feature a hexagonal head designed for wrench tightening, providing strong clamping force and superior load-bearing capabilities in heavy-duty applications. Carriage bolts have a rounded head with a square neck that locks into wood or metal, offering moderate load capacity but limited torque resistance compared to hex bolts. The design of hex bolts supports higher tensile strength and shear forces, making them more suitable for structural and high-stress environments.
Corrosion Resistance and Finishes
Hex bolts typically feature a wider range of corrosion-resistant finishes, such as zinc plating, hot-dip galvanizing, and stainless steel options that provide superior protection in harsh environments. Carriage bolts commonly come with a smooth, rounded head and are often available in galvanized or stainless steel finishes, offering good corrosion resistance but generally less variety compared to hex bolts. Choosing between hex bolts and carriage bolts depends on the needed corrosion resistance level, environmental exposure, and the specific finish that best extends fastener longevity.
Common Uses in Construction
Hex bolts are commonly used in construction for securing heavy materials and machinery due to their strong, hexagonal heads that allow for high torque application with wrenches or sockets. Carriage bolts, featuring a smooth, rounded head and a square neck, are preferred for wood-to-metal connections and outdoor projects where a finished appearance and resistance to loosening are essential. Both fasteners play critical roles in structural applications, with hex bolts favored for steel assembly and carriage bolts for timber framing and decking.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Hex bolts generally cost less than carriage bolts due to simpler manufacturing processes and widespread use in industrial applications, making them more readily available at hardware stores and suppliers. Carriage bolts, featuring a rounded head and square neck, often incur higher costs and limited availability because of their specialized design and use in woodworking or decorative projects. For budget-conscious buyers requiring quick access, hex bolts present a more cost-effective and easily sourced fastening option.
Choosing the Right Bolt for Your Project
Hex bolts feature a hexagonal head designed for wrench tightening, offering strong clamping force and easy installation in metal or wood construction. Carriage bolts have a domed head with a square neck that locks into wood or metal, preventing rotation when tightened, ideal for woodworking and securing metal to wood. Selecting the right bolt depends on application requirements such as load, aesthetics, and material compatibility to ensure optimal strength and durability.
Safety Considerations and Best Practices
Hex bolts offer superior torque control and secure fastening due to their six-sided head design, making them ideal for high-stress applications where safety is critical. Carriage bolts feature a rounded head with a square neck that prevents rotation, enhancing safety in woodworking and metal joining by reducing loosening risks. Proper installation torque, use of washers, and regular inspections are essential best practices to ensure bolt integrity and maintain optimal safety standards.
hex bolts vs carriage bolts Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com