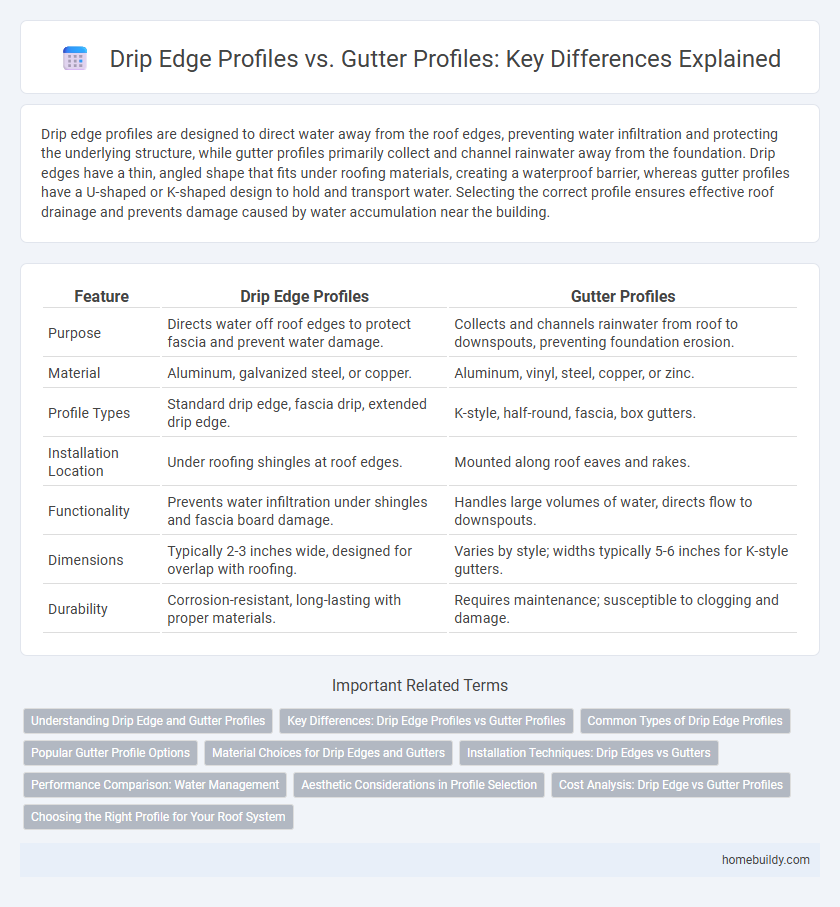
Drip edge profiles are designed to direct water away from the roof edges, preventing water infiltration and protecting the underlying structure, while gutter profiles primarily collect and channel rainwater away from the foundation. Drip edges have a thin, angled shape that fits under roofing materials, creating a waterproof barrier, whereas gutter profiles have a U-shaped or K-shaped design to hold and transport water. Selecting the correct profile ensures effective roof drainage and prevents damage caused by water accumulation near the building.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Drip Edge Profiles | Gutter Profiles |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Directs water off roof edges to protect fascia and prevent water damage. | Collects and channels rainwater from roof to downspouts, preventing foundation erosion. |
| Material | Aluminum, galvanized steel, or copper. | Aluminum, vinyl, steel, copper, or zinc. |
| Profile Types | Standard drip edge, fascia drip, extended drip edge. | K-style, half-round, fascia, box gutters. |
| Installation Location | Under roofing shingles at roof edges. | Mounted along roof eaves and rakes. |
| Functionality | Prevents water infiltration under shingles and fascia board damage. | Handles large volumes of water, directs flow to downspouts. |
| Dimensions | Typically 2-3 inches wide, designed for overlap with roofing. | Varies by style; widths typically 5-6 inches for K-style gutters. |
| Durability | Corrosion-resistant, long-lasting with proper materials. | Requires maintenance; susceptible to clogging and damage. |
Understanding Drip Edge and Gutter Profiles
Drip edge profiles feature a bent metal flange designed to direct water away from the roof edge, preventing water damage to underlying structures and fascia. Gutter profiles, on the other hand, are designed to channel and collect rainwater, typically shaped to fit seamlessly under the drip edge and direct flow into downspouts. Understanding the specific shape and function of each profile ensures effective water management and longevity of roofing systems.
Key Differences: Drip Edge Profiles vs Gutter Profiles
Drip edge profiles are designed to direct water away from the roof edge, preventing water damage and protecting underlying roofing components, while gutter profiles focus on channeling rainwater from the roof to the downspouts for controlled drainage. Drip edges typically have a thin, angled metal design that extends slightly beyond the roof deck to ensure proper water runoff. Gutter profiles come in various shapes such as K-style or half-round, which are optimized to maximize water flow capacity and debris resistance.
Common Types of Drip Edge Profiles
Drip edge profiles primarily include L-shaped, W-shaped, and T-shaped designs that effectively direct water away from roof edges to prevent damage to the fascia and underlying structure. Common gutter profiles such as K-style and half-round differ by their function, mainly focusing on collecting and channeling water away from the foundation. Understanding the distinct purposes and shapes of drip edge profiles helps optimize roof water management and protect building integrity.
Popular Gutter Profile Options
Drip edge profiles are designed to direct water away from the roof edge, preventing water damage, while gutter profiles focus on effectively collecting and channeling rainwater. Popular gutter profile options include K-style, half-round, and box gutters, each varying in capacity and aesthetic appeal to suit different architectural styles. K-style gutters are the most common due to their high capacity and decorative appearance, while half-round gutters offer a traditional look, and box gutters provide a seamless integration with the roofline.
Material Choices for Drip Edges and Gutters
Drip edge profiles are typically made from durable materials such as aluminum, galvanized steel, or copper to resist corrosion and direct water away from roofing edges efficiently. Gutter profiles often utilize similar materials but are designed with thicker gauges or specialized coatings to withstand heavier water flow and debris impact. Material selection for both drip edges and gutters directly influences longevity, maintenance requirements, and overall performance in various climate conditions.
Installation Techniques: Drip Edges vs Gutters
Drip edge installation involves securing metal flashing along roof edges to direct water away from fascia and underlayment, using nails placed 12-16 inches apart and ensuring overlap at seams for effective water shedding. Gutter installation requires attaching gutters with brackets spaced about 24 inches apart, sloped slightly to direct water toward downspouts, with precise alignment to roof edges for optimal water collection. Proper installation of both components is critical for preventing water damage, but drip edges primarily protect roofing materials, while gutters focus on managing water runoff below the roofline.
Performance Comparison: Water Management
Drip edge profiles are designed to direct water away from the fascia and underlying roofing components, preventing water infiltration and damage. Gutter profiles primarily collect and channel water from the roof to the drainage system but offer limited protection against water seeping under shingles or roof edges. In water management performance, drip edges provide enhanced defense against water intrusion, while gutter profiles focus on efficient water conveyance off the roof.
Aesthetic Considerations in Profile Selection
Drip edge profiles and gutter profiles differ significantly in their aesthetic impact, with drip edges offering a sleek, low-profile finish that seamlessly integrates with rooflines, enhancing the roof's visual appeal. Gutter profiles, on the other hand, tend to be bulkier and more visible, potentially disrupting clean architectural lines but providing a distinct accent to exterior design. Selecting between drip edge and gutter profiles involves balancing the desired aesthetic outcome with functional needs, ensuring the roofing system complements the overall building style.
Cost Analysis: Drip Edge vs Gutter Profiles
Drip edge profiles typically cost less per linear foot than gutter profiles due to simpler manufacturing and installation requirements, making them a budget-friendly option for roof edge protection. Gutter profiles, while more expensive, provide essential rainwater management and help prevent foundation damage, potentially saving on costly repairs over time. Analyzing upfront material and labor costs against long-term benefits reveals that drip edges offer affordable protection whereas gutters represent a more significant investment with added functional value.
Choosing the Right Profile for Your Roof System
Selecting the appropriate profile between drip edge and gutter depends on your roof's design and water management needs; drip edge profiles primarily focus on redirecting water away from fascia and underlying roof components to prevent water damage, while gutter profiles are designed to collect and channel rainwater effectively along the eaves. Drip edge profiles typically feature a metal flange angled outward to extend beyond the fascia, enhancing roof edge protection, whereas gutter profiles are shaped to maximize water flow capacity into the downspouts. Evaluating the specific roofing material, local climate conditions, and existing drainage infrastructure helps determine the most suitable profile to maintain roof integrity and prevent costly water-related repairs.
Drip edge profiles vs Gutter profiles Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com