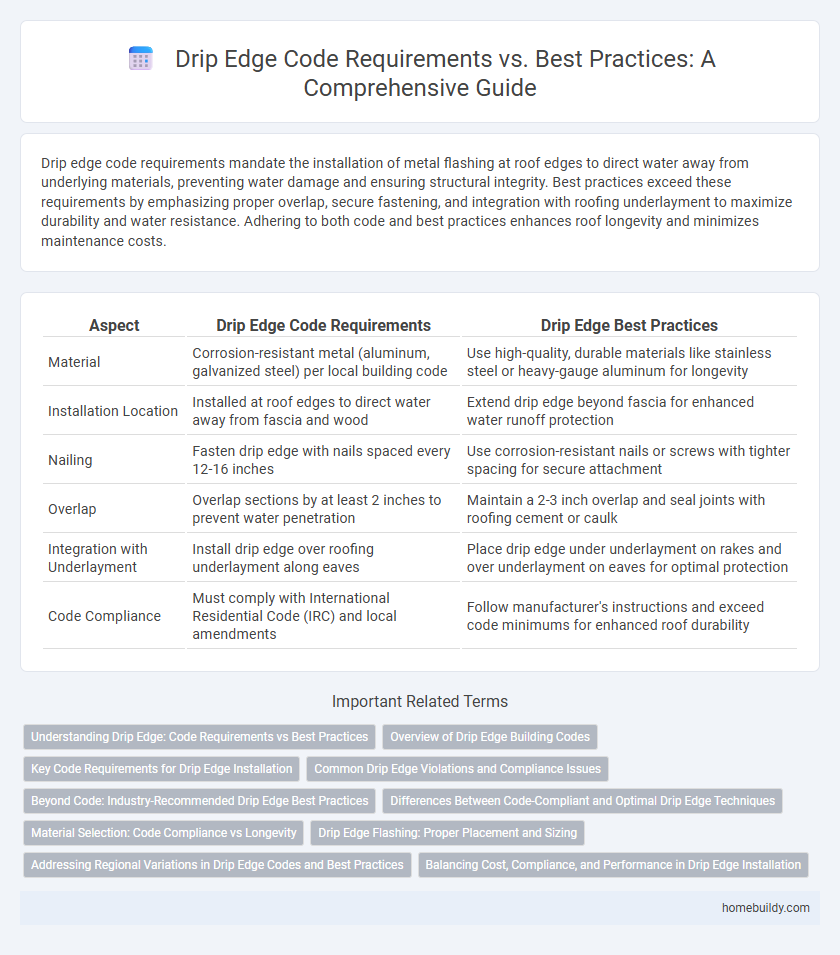
Drip edge code requirements mandate the installation of metal flashing at roof edges to direct water away from underlying materials, preventing water damage and ensuring structural integrity. Best practices exceed these requirements by emphasizing proper overlap, secure fastening, and integration with roofing underlayment to maximize durability and water resistance. Adhering to both code and best practices enhances roof longevity and minimizes maintenance costs.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Drip Edge Code Requirements | Drip Edge Best Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Corrosion-resistant metal (aluminum, galvanized steel) per local building code | Use high-quality, durable materials like stainless steel or heavy-gauge aluminum for longevity |
| Installation Location | Installed at roof edges to direct water away from fascia and wood | Extend drip edge beyond fascia for enhanced water runoff protection |
| Nailing | Fasten drip edge with nails spaced every 12-16 inches | Use corrosion-resistant nails or screws with tighter spacing for secure attachment |
| Overlap | Overlap sections by at least 2 inches to prevent water penetration | Maintain a 2-3 inch overlap and seal joints with roofing cement or caulk |
| Integration with Underlayment | Install drip edge over roofing underlayment along eaves | Place drip edge under underlayment on rakes and over underlayment on eaves for optimal protection |
| Code Compliance | Must comply with International Residential Code (IRC) and local amendments | Follow manufacturer's instructions and exceed code minimums for enhanced roof durability |
Understanding Drip Edge: Code Requirements vs Best Practices
Drip edge code requirements typically mandate metal flashing installation at roof edges to prevent water infiltration and wood rot, ensuring compliance with local building codes like the International Residential Code (IRC). Best practices extend beyond code by recommending wider drip edges for enhanced water diversion, integration with underlayment for improved roof deck protection, and corrosion-resistant materials to prolong lifespan. Understanding these distinctions helps balance regulatory compliance and optimal roof performance by combining mandated standards with proactive measures.
Overview of Drip Edge Building Codes
Drip edge building codes mandate metal flashing installation along roof edges to direct water away from the fascia and protect underlying wood from moisture damage, with the International Residential Code (IRC) specifying minimum dimensions and placement. Best practices exceed code by ensuring continuous drip edge installation overlapping shingles correctly to optimize water shedding and prevent ice dam formation. Compliance with code and best practice guidelines enhances roof durability and minimizes maintenance costs by effectively managing roof-edge water runoff.
Key Code Requirements for Drip Edge Installation
Key code requirements for drip edge installation typically mandate metal flashing along roof edges to prevent water infiltration and protect roof decking. Codes such as the International Residential Code (IRC) specify that drip edges must be installed at eaves and rakes to direct water away from the fascia and into the gutters. Proper attachment using corrosion-resistant fasteners, ensuring continuous coverage, and compatibility with roofing materials are essential for meeting these standards while enhancing roof longevity.
Common Drip Edge Violations and Compliance Issues
Drip edge code requirements mandate proper installation to ensure water is diverted away from roofing and fascia, preventing water damage and wood rot, yet common drip edge violations include improper placement, inadequate fastening, and use of non-corrosion resistant materials. Compliance issues often arise from failure to overlap sections correctly, omission of drip edge at eaves or rakes, and neglecting manufacturer specifications, which can compromise roof longevity and warranty coverage. Adhering to best practices involves selecting appropriate metal gauges, ensuring seamless laps, and following local building codes to maintain structural integrity and effective water management.
Beyond Code: Industry-Recommended Drip Edge Best Practices
Drip edge code requirements specify minimum standards for installation to ensure water management and roof protection, typically mandating fastening along roof edges and sufficient metal extension over the fascia. Beyond code, industry-recommended best practices emphasize precise alignment with roof shingles, use of corrosion-resistant materials, and overlapping sections to prevent water infiltration and extend roof life. Implementing these advanced methods minimizes potential damage and optimizes the performance and durability of the roofing system.
Differences Between Code-Compliant and Optimal Drip Edge Techniques
Drip edge code requirements typically mandate minimum dimensions and material specifications to prevent water intrusion and roof deck damage, ensuring basic compliance with local building codes. Optimal drip edge techniques go beyond code by emphasizing enhanced water runoff control, corrosion resistance through premium materials like galvanized steel or copper, and precise installation angles to maximize durability and roof performance. Differences between code-compliant and best practice methods lie in the level of detail and quality applied, affecting the longevity and effectiveness of the roof's protection against moisture.
Material Selection: Code Compliance vs Longevity
Drip edge code requirements typically mandate corrosion-resistant materials such as aluminum or galvanized steel to ensure basic weather protection and compliance with building standards. Best practices for material selection prioritize durability and longevity, often recommending higher-grade metals like copper or stainless steel to extend the lifespan and improve resistance to environmental damage. Choosing premium materials enhances the overall performance of the drip edge beyond minimum code compliance while preventing costly repairs.
Drip Edge Flashing: Proper Placement and Sizing
Drip edge flashing must comply with local building codes, which typically require a minimum width of 2 inches to prevent water infiltration and protect roof decking. Best practices recommend installing the drip edge under the roofing underlayment along eaves and over the underlayment at rakes to ensure effective water shedding and roof longevity. Proper sizing and placement minimize the risk of ice dams and water damage, exceeding basic code requirements for enhanced roof protection.
Addressing Regional Variations in Drip Edge Codes and Best Practices
Drip edge code requirements vary significantly across regions due to differing climate conditions and local building regulations, impacting material selection and installation methods. Best practices emphasize adapting drip edge design to address these regional variations, such as increased corrosion resistance in coastal areas and enhanced water diversion in heavy rainfall zones. Proper adherence to both code requirements and regional best practices ensures optimal roof protection and longevity.
Balancing Cost, Compliance, and Performance in Drip Edge Installation
Drip edge code requirements primarily focus on minimum standards for protecting roof edges from water damage and ensuring proper water runoff management, typically mandating metal flashing extending at least 2 inches over the roof edge. Best practices, however, recommend using corrosion-resistant materials like aluminum or galvanized steel, ensuring precise overlap and secure fastening to enhance durability and prevent uplift from wind, which may increase initial costs but improve long-term performance and reduce maintenance. Balancing cost, compliance, and performance requires selecting drip edge materials and installation methods that meet local building codes while providing optimal protection and lifespan to minimize costly repairs and maintain structural integrity.
Drip edge code requirements vs Drip edge best practices Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com