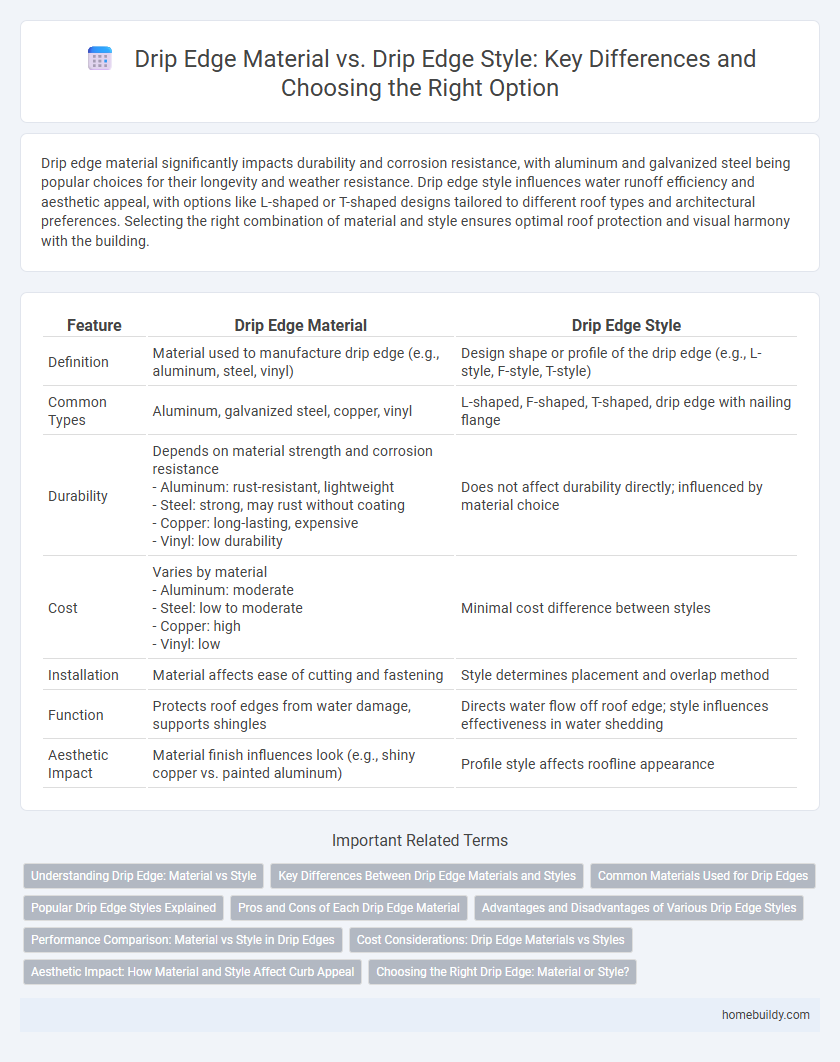
Drip edge material significantly impacts durability and corrosion resistance, with aluminum and galvanized steel being popular choices for their longevity and weather resistance. Drip edge style influences water runoff efficiency and aesthetic appeal, with options like L-shaped or T-shaped designs tailored to different roof types and architectural preferences. Selecting the right combination of material and style ensures optimal roof protection and visual harmony with the building.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Drip Edge Material | Drip Edge Style |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Material used to manufacture drip edge (e.g., aluminum, steel, vinyl) | Design shape or profile of the drip edge (e.g., L-style, F-style, T-style) |
| Common Types | Aluminum, galvanized steel, copper, vinyl | L-shaped, F-shaped, T-shaped, drip edge with nailing flange |
| Durability | Depends on material strength and corrosion resistance - Aluminum: rust-resistant, lightweight - Steel: strong, may rust without coating - Copper: long-lasting, expensive - Vinyl: low durability |
Does not affect durability directly; influenced by material choice |
| Cost | Varies by material - Aluminum: moderate - Steel: low to moderate - Copper: high - Vinyl: low |
Minimal cost difference between styles |
| Installation | Material affects ease of cutting and fastening | Style determines placement and overlap method |
| Function | Protects roof edges from water damage, supports shingles | Directs water flow off roof edge; style influences effectiveness in water shedding |
| Aesthetic Impact | Material finish influences look (e.g., shiny copper vs. painted aluminum) | Profile style affects roofline appearance |
Understanding Drip Edge: Material vs Style
Drip edge material, commonly aluminum, galvanized steel, or copper, determines durability, corrosion resistance, and suitability for various climates in roofing applications. Drip edge style, including L-shaped, T-shaped, or wide flange designs, affects water diversion efficiency and ease of installation along roof edges. Selecting the right combination of material and style ensures optimal protection against water damage and extends the lifespan of roofing systems.
Key Differences Between Drip Edge Materials and Styles
Drip edge materials commonly include aluminum, galvanized steel, and copper, each offering distinct durability, corrosion resistance, and cost benefits suited to varying climates and roofing systems. Drip edge styles, such as Type L, Type F, and Type D, differ in flange dimensions and design to accommodate specific roof edges and water drainage needs. Selecting the appropriate material and style ensures optimal protection against water damage and enhances the lifespan of roof edges.
Common Materials Used for Drip Edges
Common materials used for drip edges include aluminum, galvanized steel, copper, and vinyl, each offering specific benefits related to durability, weather resistance, and cost. Aluminum drip edges provide lightweight corrosion resistance, while galvanized steel offers enhanced strength and longevity for harsh climates. Copper drip edges are prized for their aesthetic appeal and natural patina over time, whereas vinyl options serve as budget-friendly, low-maintenance alternatives.
Popular Drip Edge Styles Explained
Popular drip edge styles include L-shaped, T-shaped, and inverted-L profiles, each designed to direct water away from roofing and fascia effectively. Material choices like aluminum, galvanized steel, and copper influence durability, corrosion resistance, and cost, impacting the drip edge's performance and lifespan. Selecting the appropriate style and material combination ensures optimal protection against water damage and enhances roof longevity.
Pros and Cons of Each Drip Edge Material
Aluminum drip edges offer excellent rust resistance and lightweight durability, making them ideal for long-lasting roof protection, though they can be prone to denting in harsh weather. Galvanized steel drip edges provide superior strength and impact resistance but may corrode over time without proper coating or maintenance. Copper drip edges combine unmatched aesthetic appeal and longevity with high cost, requiring professional installation and periodic upkeep to prevent patina development.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Various Drip Edge Styles
Drip edge styles vary primarily between L-shaped, T-shaped, and fascia drip edges, each offering distinct advantages and disadvantages in roofing applications. L-shaped drip edges provide superior water diversion and are easy to install but may be less visually appealing compared to T-shaped designs, which offer enhanced aesthetics and better wind resistance but can be more complex to fit properly. Fascia drip edges combine seamless edge protection with improved gutter integration, yet their installation requires precise measurements to avoid gaps that could lead to water intrusion.
Performance Comparison: Material vs Style in Drip Edges
Metal drip edges, typically made from aluminum, galvanized steel, or copper, offer superior durability and resistance to weather conditions compared to vinyl or plastic styles, enhancing roof longevity. Style influences water management efficiency, as L-shaped drip edges provide optimal water diversion, while inverted "T" styles may offer added protection against wind-driven rain. Overall, material choice dictates lifespan and robustness, whereas style impacts functional performance in specific environmental scenarios.
Cost Considerations: Drip Edge Materials vs Styles
Drip edge materials such as aluminum, galvanized steel, and copper differ significantly in cost, with aluminum being the most affordable and copper the most expensive, impacting overall budget decisions. Styles like L-shaped or T-shaped drip edges influence pricing moderately but primarily affect installation complexity rather than direct material cost. Choosing the right combination of drip edge material and style balances durability, aesthetic appeal, and expense to fit specific roofing project requirements.
Aesthetic Impact: How Material and Style Affect Curb Appeal
Drip edge materials such as aluminum, galvanized steel, and copper offer distinct textures and colors that significantly influence a roof's aesthetic appeal. Styles like L-shaped, T-shaped, or custom-formed drip edges create varied shadow lines and edge profiles that enhance the home's visual character. Selecting the right combination of material and style maximizes curb appeal by complementing architectural design while protecting roof edges.
Choosing the Right Drip Edge: Material or Style?
Selecting the right drip edge involves balancing material durability with style compatibility; metal options like aluminum and galvanized steel offer superior weather resistance, while copper provides long-lasting aesthetic appeal. The drip edge style, including L-shaped, T-shaped, and wide-flange designs, impacts water diversion efficiency and roof edge protection. Prioritize material performance for longevity and style that complements roofing architecture to optimize both functionality and curb appeal.
Drip edge material vs Drip edge style Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com