Bolted beam connectors offer easier installation and faster assembly, making them ideal for projects requiring flexibility and on-site adjustments. Welded beam connectors provide higher strength and stiffness due to the continuous metal bond, which is essential for heavy-load structures and permanent connections. Choosing between bolted and welded connectors depends on factors such as load requirements, construction speed, and long-term maintenance considerations.
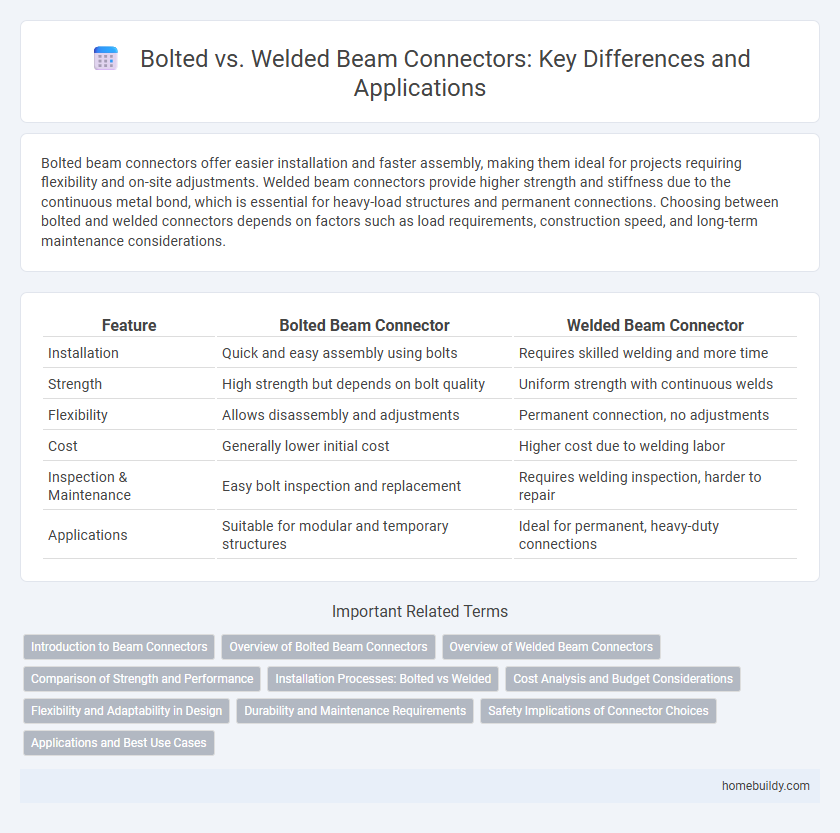
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bolted Beam Connector | Welded Beam Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Quick and easy assembly using bolts | Requires skilled welding and more time |
| Strength | High strength but depends on bolt quality | Uniform strength with continuous welds |
| Flexibility | Allows disassembly and adjustments | Permanent connection, no adjustments |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher cost due to welding labor |
| Inspection & Maintenance | Easy bolt inspection and replacement | Requires welding inspection, harder to repair |
| Applications | Suitable for modular and temporary structures | Ideal for permanent, heavy-duty connections |
Introduction to Beam Connectors
Bolted beam connectors offer ease of installation and flexibility in structural assembly by allowing components to be fastened without specialized welding equipment. Welded beam connectors provide superior strength and seamless integration, making them ideal for high-load applications requiring permanent joints. Selecting between bolted and welded connectors depends on project requirements such as load capacity, installation speed, and maintenance considerations.
Overview of Bolted Beam Connectors
Bolted beam connectors provide a reliable and adjustable method for joining structural beams, offering ease of installation and future disassembly compared to welded connectors. These connectors utilize high-strength bolts to create secure connections that accommodate slight movements and minimize stress concentrations, enhancing structural flexibility. Bolted connections reduce on-site labor time and eliminate the need for specialized welding equipment, making them cost-effective for both new constructions and retrofits.
Overview of Welded Beam Connectors
Welded beam connectors provide a rigid and permanent connection between steel components, ensuring high structural integrity in construction projects. These connectors eliminate the need for mechanical fasteners, resulting in a seamless joint that offers superior load transfer and resistance to shear forces. Their application is ideal in scenarios requiring enhanced durability and minimal maintenance over time.
Comparison of Strength and Performance
Bolted beam connectors provide strong mechanical fastening with ease of on-site assembly, allowing for controlled tension and shear load transfer, but may exhibit slight slip under high loads compared to welded connectors. Welded beam connectors offer robust, continuous joint strength with superior resistance to dynamic and cyclic stresses, resulting in higher overall structural rigidity and reduced deflection. Performance differences largely depend on the precision of installation and quality of materials, with welded connections generally excelling in fatigue resistance and bolted connections favored for flexibility and inspection.
Installation Processes: Bolted vs Welded
Bolted beam connectors offer a faster installation process with minimal specialized equipment, as bolts can be tightened on-site without extensive preparation. Welded beam connectors require skilled welders and controlled conditions to ensure strong and safe joints, often leading to longer installation times. The choice between bolted and welded connectors depends on project timelines, labor availability, and site conditions.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Bolted beam connectors generally offer lower upfront labor costs due to simpler installation and reduced need for specialized welding equipment, making them more budget-friendly for projects with tight time constraints. Welded beam connectors provide greater long-term cost benefits through enhanced structural integrity and reduced maintenance, potentially lowering lifecycle expenses despite higher initial investment. Budget considerations should weigh labor rates, project complexity, and maintenance forecasts to determine the most cost-efficient beam connector option.
Flexibility and Adaptability in Design
Bolted beam connectors offer greater flexibility and adaptability in design by enabling easier adjustments and disassembly during construction or future modifications. Welded beam connectors provide strong, permanent joints but limit on-site design changes due to their fixed nature. The choice between bolted and welded connectors impacts project timelines and potential design revisions, with bolted connections favoring adaptability in complex or evolving structures.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Bolted beam connectors offer enhanced durability through resistance to fatigue and corrosion, making them suitable for structures exposed to dynamic loads and harsh environments. Maintenance requirements are lower for bolted connections since they can be easily inspected and tightened without specialized equipment or extensive downtime. Welded beam connectors provide a rigid, continuous joint but often require more frequent inspections and skilled labor for maintenance due to potential weld cracking and corrosion at the weld interface.
Safety Implications of Connector Choices
Bolted beam connectors offer enhanced safety by allowing for better inspection and easier replacement or adjustment in structural applications, reducing the risk of undetected damage or fatigue. Welded beam connectors provide strong, continuous joints but pose higher safety risks due to potential weld defects like cracks or incomplete fusion that are difficult to detect without advanced testing. Engineering standards recommend rigorous inspection protocols for welded connections, while bolted connections often benefit from visual checks and simpler maintenance, influencing the overall safety management strategy in construction projects.
Applications and Best Use Cases
Bolted beam connectors are ideal for applications requiring ease of installation, adjustability, and future disassembly, commonly used in steel structures with limited access or where field adjustments are necessary. Welded beam connectors offer superior strength and rigidity, making them best suited for permanent, high-load applications such as bridges, industrial buildings, and heavy-frame construction. Choosing between bolted and welded connectors depends on project requirements like load capacity, environmental conditions, and maintenance considerations.
bolted beam connector vs welded beam connector Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com