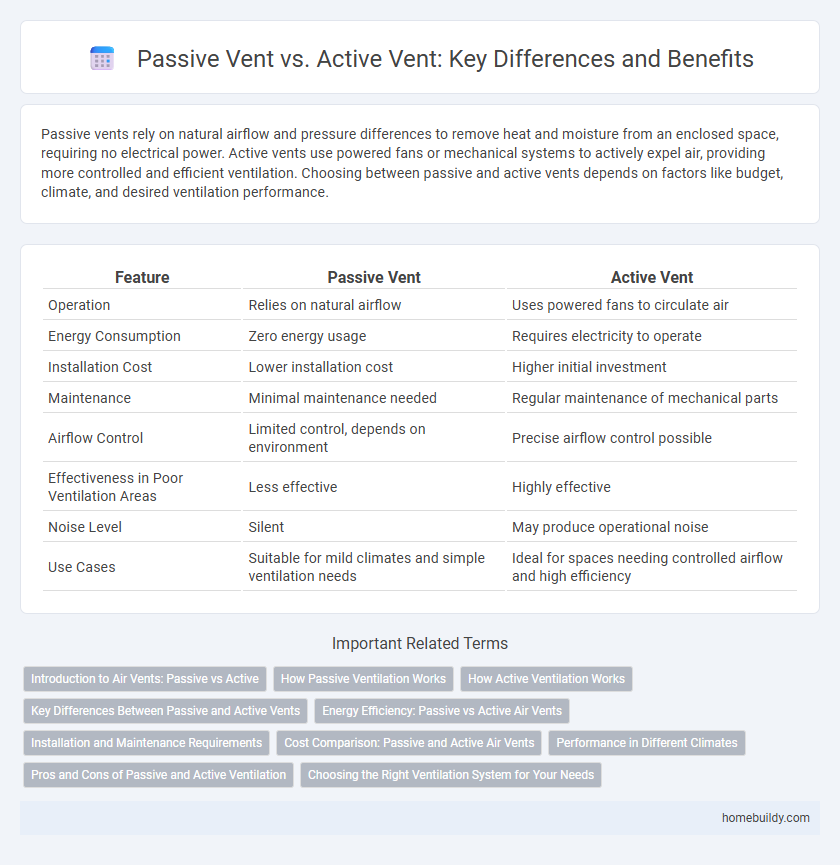
Passive vents rely on natural airflow and pressure differences to remove heat and moisture from an enclosed space, requiring no electrical power. Active vents use powered fans or mechanical systems to actively expel air, providing more controlled and efficient ventilation. Choosing between passive and active vents depends on factors like budget, climate, and desired ventilation performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Passive Vent | Active Vent |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Relies on natural airflow | Uses powered fans to circulate air |
| Energy Consumption | Zero energy usage | Requires electricity to operate |
| Installation Cost | Lower installation cost | Higher initial investment |
| Maintenance | Minimal maintenance needed | Regular maintenance of mechanical parts |
| Airflow Control | Limited control, depends on environment | Precise airflow control possible |
| Effectiveness in Poor Ventilation Areas | Less effective | Highly effective |
| Noise Level | Silent | May produce operational noise |
| Use Cases | Suitable for mild climates and simple ventilation needs | Ideal for spaces needing controlled airflow and high efficiency |
Introduction to Air Vents: Passive vs Active
Passive air vents rely on natural airflow and pressure differences to facilitate ventilation without the use of mechanical systems, making them energy-efficient and low-maintenance options. Active air vents incorporate fans or mechanical devices to actively control airflow, providing greater ventilation control and efficiency in environments with limited natural ventilation. Understanding the differences between passive and active air vents is crucial for optimizing indoor air quality and energy consumption in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
How Passive Ventilation Works
Passive ventilation operates by utilizing natural forces such as wind and thermal buoyancy to facilitate airflow without mechanical assistance. Air enters through intake vents and exits via exhaust vents, creating a continuous exchange that removes stale air and regulates indoor temperature. This method is energy-efficient and relies on strategically placed vents to optimize air circulation based on pressure differences and temperature gradients.
How Active Ventilation Works
Active ventilation uses powered fans or mechanical systems to circulate air efficiently, enhancing indoor air quality by actively removing stale air and introducing fresh air. This method relies on electrical energy to drive airflow, allowing precise control over ventilation rates and improving moisture and pollutant reduction. Compared to passive vents that depend on natural air pressure and temperature differences, active ventilation ensures consistent and targeted air exchange regardless of external conditions.
Key Differences Between Passive and Active Vents
Passive vents rely on natural airflow and pressure differences to facilitate ventilation without mechanical assistance, making them energy-efficient but less controllable. Active vents use powered fans or mechanical systems to control airflow precisely, offering improved ventilation performance and adaptability in various environments. Key differences include energy consumption, airflow control, installation complexity, and maintenance requirements.
Energy Efficiency: Passive vs Active Air Vents
Passive air vents leverage natural airflow through convection and pressure differences, providing energy-efficient ventilation without electricity consumption. Active air vents require powered fans or motors, increasing energy use but offering precise control and higher airflow rates. For sustainable building designs, passive vents significantly reduce energy costs while maintaining adequate ventilation compared to the energy demands of active vent systems.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Passive vents require minimal installation, often involving simple placement or mounting with no electrical connections, making them cost-effective and easy to set up. Maintenance involves occasional cleaning to prevent blockage from dust or debris, ensuring consistent airflow without mechanical parts that can fail. Active vents demand more complex installation, including wiring for power and integration with control systems, and require regular maintenance to check and service fans or motors to maintain optimal performance.
Cost Comparison: Passive and Active Air Vents
Passive air vents typically have lower installation and maintenance costs due to their simple design and lack of mechanical components. Active air vents, equipped with fans and electrical systems, involve higher upfront expenses and ongoing energy consumption, increasing overall operational costs. Choosing between passive and active vents depends on budget constraints and the required ventilation efficiency for the space.
Performance in Different Climates
Passive vents rely on natural airflow and temperature differences to regulate indoor air quality, performing efficiently in moderate climates with stable breezes and temperature gradients. Active vents utilize powered fans to control ventilation rates, offering superior performance in extreme climates by maintaining consistent air exchange regardless of external weather conditions. In hot and humid regions, active vents prevent moisture buildup more effectively, while passive vents excel in energy savings under mild environmental conditions.
Pros and Cons of Passive and Active Ventilation
Passive vents provide natural airflow with low energy consumption and minimal maintenance, making them cost-effective and eco-friendly; however, they rely on external environmental factors like wind and temperature differences, which can limit their efficiency in stagnant or extreme conditions. Active vents use fans or mechanical systems to ensure consistent ventilation, improving air quality and moisture control regardless of weather, but they incur higher energy costs and require regular upkeep to prevent system failures. Choosing between passive and active ventilation depends on balancing energy efficiency, reliability, and specific ventilation needs in residential or commercial buildings.
Choosing the Right Ventilation System for Your Needs
Passive vents rely on natural airflow to exchange indoor and outdoor air, making them energy-efficient and low-maintenance but less effective in areas with poor air movement. Active vents use fans or mechanical systems to control ventilation rates, providing consistent air exchange and better humidity control, ideal for spaces requiring precise air quality management. Selecting the right system depends on factors such as climate, building design, and specific ventilation requirements to balance energy consumption and indoor air quality effectively.
passive vent vs active vent Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com