Air vents facilitate passive airflow, allowing fresh air to enter or stale air to exit a space naturally, enhancing ventilation without mechanical assistance. Exhaust fans actively expel air from an area, effectively removing moisture, odors, and pollutants to improve indoor air quality and prevent issues like mold and mildew. Choosing between an air vent and an exhaust fan depends on ventilation needs, space size, and the level of air circulation required.
Table of Comparison
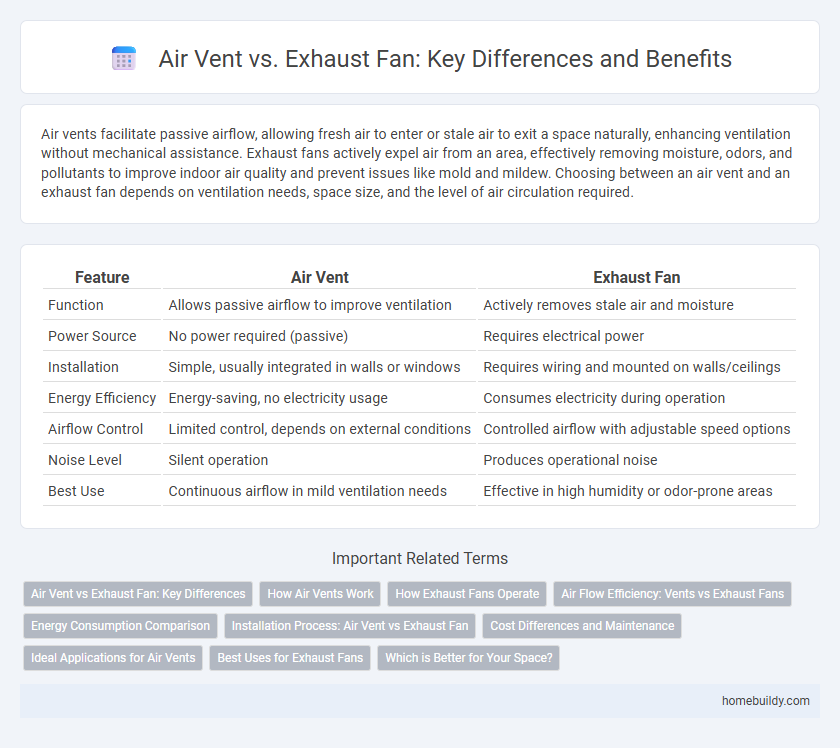
| Feature | Air Vent | Exhaust Fan |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Allows passive airflow to improve ventilation | Actively removes stale air and moisture |
| Power Source | No power required (passive) | Requires electrical power |
| Installation | Simple, usually integrated in walls or windows | Requires wiring and mounted on walls/ceilings |
| Energy Efficiency | Energy-saving, no electricity usage | Consumes electricity during operation |
| Airflow Control | Limited control, depends on external conditions | Controlled airflow with adjustable speed options |
| Noise Level | Silent operation | Produces operational noise |
| Best Use | Continuous airflow in mild ventilation needs | Effective in high humidity or odor-prone areas |
Air Vent vs Exhaust Fan: Key Differences
An air vent primarily facilitates passive airflow, allowing fresh air to enter or stale air to exit a space, while an exhaust fan actively removes air using mechanical power. Air vents are typically static openings integrated into walls or ceilings, whereas exhaust fans consist of motorized blades designed to enhance ventilation efficiency. Understanding these distinctions helps optimize indoor air quality management based on the specific ventilation requirements of a building.
How Air Vents Work
Air vents function by facilitating the passive flow of air between indoor and outdoor environments, allowing fresh air to enter and stale air to exit naturally. Unlike exhaust fans that use mechanical power to actively withdraw air from a space, air vents rely on pressure differences and natural convection to maintain airflow. Properly designed air vents enhance indoor air quality and temperature regulation without consuming electricity.
How Exhaust Fans Operate
Exhaust fans operate by drawing stale indoor air out through a ventilated space, creating negative pressure that allows fresh air to enter and circulate. They use an electric motor to spin blades that push air outside, effectively removing moisture, odors, and pollutants. Unlike passive air vents, exhaust fans actively control airflow, improving indoor air quality and ventilation efficiency.
Air Flow Efficiency: Vents vs Exhaust Fans
Air vents provide passive airflow, allowing natural ventilation by facilitating the exchange of indoor and outdoor air without mechanical assistance. Exhaust fans actively remove stale air and moisture, offering higher air flow efficiency in targeted areas such as kitchens and bathrooms. While vents rely on pressure differences and temperature gradients for air movement, exhaust fans deliver consistent and controlled ventilation, improving indoor air quality more effectively.
Energy Consumption Comparison
Air vents consume significantly less energy than exhaust fans as they rely on passive airflow without mechanical components, resulting in zero electricity use. Exhaust fans require electric power to operate motors that actively expel air, leading to higher energy consumption and utility costs. Efficient air vent placement can reduce the need for exhaust fans, maximizing energy savings in ventilation systems.
Installation Process: Air Vent vs Exhaust Fan
Air vent installation involves embedding grilles or ducts into walls or ceilings to facilitate passive airflow, requiring minimal electrical work and simpler mounting. Exhaust fan installation demands wiring to a power source and sealing of ducting to the exterior, ensuring active ventilation and efficient expulsion of air pollutants. The complexity and time for installing exhaust fans are generally higher, involving electrical safety protocols and more structural modifications compared to air vents.
Cost Differences and Maintenance
Air vents typically have lower upfront costs compared to exhaust fans due to their simpler design and installation requirements, making them a budget-friendly option for basic ventilation. Maintenance for air vents involves occasional cleaning to prevent dust buildup, whereas exhaust fans require more frequent upkeep, including motor lubrication and fan blade cleaning, leading to higher long-term maintenance expenses. The energy consumption of exhaust fans can also contribute to increased operational costs relative to the passive nature of air vents.
Ideal Applications for Air Vents
Air vents are ideal for continuous air circulation in residential and commercial spaces, promoting natural ventilation without mechanical assistance. They effectively regulate indoor air quality and humidity by allowing fresh air to enter and stale air to exit passively. In contrast to exhaust fans, air vents are best suited for applications where energy efficiency and noise reduction are priorities.
Best Uses for Exhaust Fans
Exhaust fans are ideal for removing moisture, odors, and airborne contaminants from specific areas such as bathrooms, kitchens, and laundry rooms, preventing mold growth and improving indoor air quality. Unlike passive air vents, exhaust fans actively expel stale air and humidity, making them essential in high-moisture environments. Their best use is in spaces requiring rapid air exchange to maintain a healthy and comfortable atmosphere.
Which is Better for Your Space?
An air vent provides passive airflow by allowing fresh air to circulate naturally, while an exhaust fan actively removes stale air and moisture, making it more efficient for areas prone to humidity or odors. For spaces like bathrooms or kitchens, exhaust fans offer better ventilation by preventing mold and maintaining air quality. Air vents work well in rooms needing subtle air exchange without noise or energy consumption, but exhaust fans deliver more powerful and immediate ventilation.
Air vent vs Exhaust fan Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com