An air vent is a general term for openings that allow air to flow in and out of a space, promoting ventilation and regulating temperature. A soffit vent is a specific type of air vent installed under the eaves of a roof to facilitate intake ventilation in attics, preventing moisture buildup and improving energy efficiency. Proper use of soffit vents ensures balanced airflow when combined with ridge or exhaust vents to maintain optimal attic ventilation.
Table of Comparison
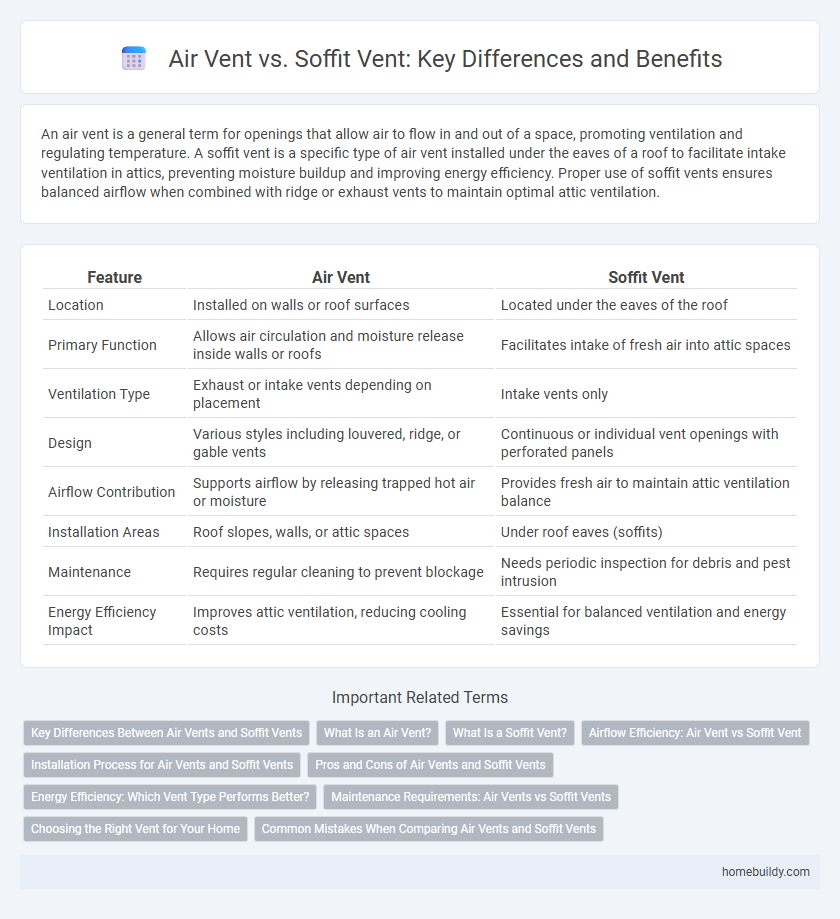
| Feature | Air Vent | Soffit Vent |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Installed on walls or roof surfaces | Located under the eaves of the roof |
| Primary Function | Allows air circulation and moisture release inside walls or roofs | Facilitates intake of fresh air into attic spaces |
| Ventilation Type | Exhaust or intake vents depending on placement | Intake vents only |
| Design | Various styles including louvered, ridge, or gable vents | Continuous or individual vent openings with perforated panels |
| Airflow Contribution | Supports airflow by releasing trapped hot air or moisture | Provides fresh air to maintain attic ventilation balance |
| Installation Areas | Roof slopes, walls, or attic spaces | Under roof eaves (soffits) |
| Maintenance | Requires regular cleaning to prevent blockage | Needs periodic inspection for debris and pest intrusion |
| Energy Efficiency Impact | Improves attic ventilation, reducing cooling costs | Essential for balanced ventilation and energy savings |
Key Differences Between Air Vents and Soffit Vents
Air vents and soffit vents serve different roles in home ventilation systems, with air vents facilitating general airflow in various areas, while soffit vents specifically regulate attic ventilation by allowing fresh air to enter through the eaves. Air vents can include a variety of types such as wall vents, floor vents, and ceiling vents, designed to control temperature and air quality inside living spaces. Soffit vents, usually installed under roof eaves, help prevent moisture buildup and maintain attic temperature, thereby protecting the roof structure and improving energy efficiency.
What Is an Air Vent?
An air vent is a crucial component in residential and commercial ventilation systems, designed to facilitate airflow and maintain indoor air quality by allowing fresh air to enter and stale air to exit spaces. Unlike soffit vents, which are specifically installed under the eaves of a roof to provide attic ventilation, air vents can be positioned in various locations such as walls, ceilings, or floors, serving broader ventilation needs. Proper placement and sizing of air vents are essential for efficient air circulation, moisture control, and temperature regulation within buildings.
What Is a Soffit Vent?
A soffit vent is an intake vent installed under the eaves of a roof, designed to allow fresh air to enter the attic space and promote proper ventilation. Unlike standard air vents that may be located on walls or roof surfaces, soffit vents work in conjunction with ridge vents or other exhaust vents to create a continuous airflow that prevents moisture buildup and reduces heat accumulation. Properly installed soffit vents improve attic ventilation, enhancing energy efficiency and prolonging the lifespan of roofing materials.
Airflow Efficiency: Air Vent vs Soffit Vent
Air vents and soffit vents both facilitate attic ventilation, but air vents often provide more direct and targeted airflow by allowing air to enter or exit specific points in a structure. Soffit vents are installed under the eaves and promote continuous airflow along the underside of the roof deck, enhancing overall attic ventilation. Comparing airflow efficiency, soffit vents create a consistent intake path that works best when paired with ridge or exhaust vents, while air vents can be strategically placed to optimize localized ventilation and prevent moisture buildup.
Installation Process for Air Vents and Soffit Vents
The installation process for air vents involves cutting appropriately sized openings in walls or ceilings, securing the vent covers with screws or adhesive, and connecting ductwork to ensure proper airflow. Soffit vent installation requires drilling evenly spaced holes or slots in the soffit boards, then attaching vent screens or panels to facilitate attic ventilation. Proper placement and sealing during both installations optimize airflow and prevent moisture buildup for long-term durability.
Pros and Cons of Air Vents and Soffit Vents
Air vents provide targeted airflow control and are easy to install, offering improved ventilation for specific areas, but they can be less effective in ensuring whole-roof ventilation compared to soffit vents. Soffit vents promote continuous intake of fresh air along the eaves, enhancing attic ventilation and reducing moisture buildup, though they may require more extensive installation and maintenance. Choosing between air vents and soffit vents depends on factors like roof design, ventilation needs, and budget constraints.
Energy Efficiency: Which Vent Type Performs Better?
Air vents and soffit vents both play crucial roles in attic ventilation, but soffit vents generally offer superior energy efficiency by facilitating continuous airflow at the eaves, which helps maintain consistent attic temperatures and reduces cooling costs. Air vents, often installed higher on walls or ceilings, may not provide the same level of passive intake ventilation, potentially causing uneven air circulation and increased energy consumption. Properly balanced soffit vents combined with ridge vents create optimal airflow, enhancing overall home energy performance more effectively than standalone air vents.
Maintenance Requirements: Air Vents vs Soffit Vents
Air vents require less frequent cleaning compared to soffit vents, which can accumulate dust and debris quickly due to their location under the eaves. Regular inspection of soffit vents is necessary to prevent blockages that could impair attic ventilation and increase moisture buildup. Proper maintenance of both vent types ensures optimal airflow and energy efficiency in home ventilation systems.
Choosing the Right Vent for Your Home
Choosing the right vent for your home depends on proper airflow management; air vents provide direct ventilation and air exchange within rooms, while soffit vents facilitate continuous intake ventilation under eaves to prevent moisture buildup in attic spaces. Air vents are ideal for improving indoor air quality in living areas, whereas soffit vents work best for attic ventilation by promoting proper air circulation and reducing heat accumulation. Consider your home's ventilation needs, climate, and attic design to select between air vents and soffit vents for optimal performance.
Common Mistakes When Comparing Air Vents and Soffit Vents
Common mistakes when comparing air vents and soffit vents include confusing their functions, as air vents primarily regulate airflow throughout a building, while soffit vents specifically provide intake ventilation in the roof eaves. Another error is overlooking the importance of proper placement, since soffit vents must be strategically installed to optimize attic ventilation and prevent moisture buildup but air vents can vary in location based on overall HVAC design. Failing to consider airflow balance between soffit vents and other attic vents leads to inadequate ventilation, which can cause issues such as mold growth, ice dams, and reduced energy efficiency.
air vent vs soffit vent Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com