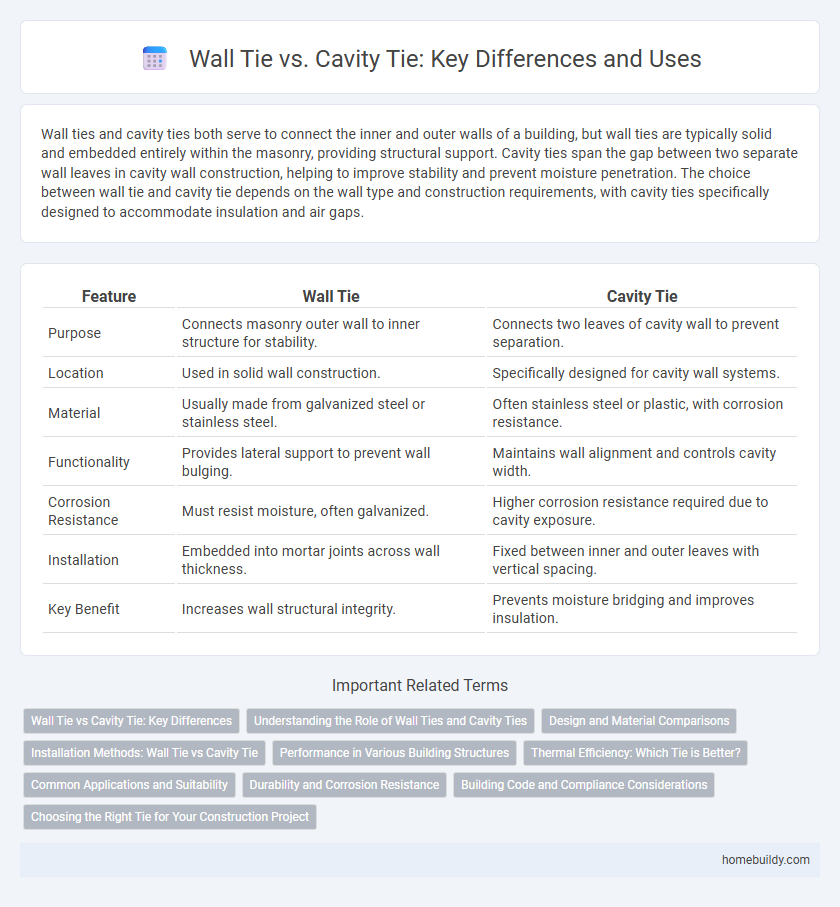
Wall ties and cavity ties both serve to connect the inner and outer walls of a building, but wall ties are typically solid and embedded entirely within the masonry, providing structural support. Cavity ties span the gap between two separate wall leaves in cavity wall construction, helping to improve stability and prevent moisture penetration. The choice between wall tie and cavity tie depends on the wall type and construction requirements, with cavity ties specifically designed to accommodate insulation and air gaps.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wall Tie | Cavity Tie |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Connects masonry outer wall to inner structure for stability. | Connects two leaves of cavity wall to prevent separation. |
| Location | Used in solid wall construction. | Specifically designed for cavity wall systems. |
| Material | Usually made from galvanized steel or stainless steel. | Often stainless steel or plastic, with corrosion resistance. |
| Functionality | Provides lateral support to prevent wall bulging. | Maintains wall alignment and controls cavity width. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Must resist moisture, often galvanized. | Higher corrosion resistance required due to cavity exposure. |
| Installation | Embedded into mortar joints across wall thickness. | Fixed between inner and outer leaves with vertical spacing. |
| Key Benefit | Increases wall structural integrity. | Prevents moisture bridging and improves insulation. |
Wall Tie vs Cavity Tie: Key Differences
Wall ties connect the inner and outer leaves of a masonry cavity wall, providing structural stability and load distribution, while cavity ties primarily serve to maintain the gap between the leaves and prevent relative movement. Wall ties are typically made of stainless steel or galvanized steel for corrosion resistance, designed to support lateral loads, whereas cavity ties focus on positioning and spacing without significant load-bearing capacity. Understanding the material composition, function, and load transfer capabilities distinguishes wall ties from cavity ties in construction applications.
Understanding the Role of Wall Ties and Cavity Ties
Wall ties serve as essential connectors that secure the outer wall to the inner wall in masonry construction, ensuring structural stability by preventing lateral displacement. Cavity ties specifically address moisture control by bridging the cavity between two wall leaves while allowing drainage and ventilation. Understanding the distinct functions of wall ties and cavity ties helps optimize building durability and moisture management in cavity wall systems.
Design and Material Comparisons
Wall ties are primarily designed to connect the outer masonry to the inner frame, providing structural stability; they are typically made from stainless steel or galvanized metal to resist corrosion. Cavity ties serve a similar purpose but are specifically engineered to maintain a controlled cavity between walls, often featuring a twist or perforation for enhanced mechanical locking and moisture drainage. Material selection for both wall ties and cavity ties prioritizes durability and corrosion resistance, with cavity ties generally incorporating additional design features to prevent thermal bridging and water ingress.
Installation Methods: Wall Tie vs Cavity Tie
Wall ties are typically installed by embedding them directly into mortar joints between inner and outer masonry walls to ensure structural stability, while cavity ties are fixed across the cavity to connect two separate wall leaves, providing lateral support and maintaining wall integrity. Installation of wall ties requires precise placement at regular intervals to distribute loads evenly, whereas cavity ties often incorporate flexible or adjustable features allowing accommodation of thermal expansion and movement. The choice of installation method directly impacts moisture control, with cavity ties designed to reduce bridging that can lead to damp issues, unlike traditional wall ties.
Performance in Various Building Structures
Wall ties and cavity ties differ in materials and design, influencing their performance in various building structures. Wall ties, typically made of galvanized steel or stainless steel, ensure structural stability by anchoring masonry walls to the inner structure, offering strong resistance to lateral forces in solid wall constructions. Cavity ties, designed with built-in insulation and moisture barriers, excel in cavity wall systems by preventing thermal bridging and managing moisture, enhancing energy efficiency and durability in modern insulated buildings.
Thermal Efficiency: Which Tie is Better?
Wall ties and cavity ties differ significantly in thermal efficiency, with cavity ties typically offering better insulation performance by maintaining the separation between inner and outer wall leaves, reducing thermal bridging. Materials used in cavity ties, such as stainless steel or plastic with thermal breaks, are designed to minimize heat transfer, enhancing the overall energy efficiency of a building. In contrast, traditional wall ties can create thermal bridges that compromise insulation, leading to higher heat loss and reduced thermal performance.
Common Applications and Suitability
Wall ties are primarily used in traditional masonry construction to connect solid walls and provide structural stability, making them suitable for single-leaf walls or solid masonry structures. Cavity ties are designed to bridge cavities in double-wall construction, effectively tying the inner and outer leaves while preventing moisture transfer, which makes them ideal for cavity walls in modern insulation-focused buildings. Both wall and cavity ties enhance structural integrity, but cavity ties are preferred in applications requiring improved thermal performance and moisture control.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Wall ties, typically made from stainless steel or galvanized steel, offer superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to cavity ties, which are often manufactured from lower-grade metals prone to rust. The enhanced protective coatings on wall ties prevent moisture penetration and structural weakening, ensuring long-term stability in masonry walls. Choosing wall ties over cavity ties minimizes maintenance costs and extends the lifespan of building envelopes exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Building Code and Compliance Considerations
Wall ties and cavity ties must comply with building codes such as the International Building Code (IBC) and British Standards BS EN 845-1, which specify material strength, corrosion resistance, and spacing requirements to ensure structural stability. Building codes often mandate stainless steel or galvanized steel ties to prevent corrosion and maintain the integrity of the wall assembly in cavity and solid wall construction. Compliance with these regulations ensures proper load transfer and moisture resistance, critical for both cavity tie and traditional wall tie installations.
Choosing the Right Tie for Your Construction Project
Wall ties and cavity ties are essential components in masonry construction, serving different structural purposes based on wall design. Wall ties connect solid walls or veneer to the structural frame, while cavity ties stabilize two separate masonry leaves separated by a cavity for insulation and moisture control. Selecting the right tie depends on factors such as wall type, environmental conditions, load requirements, and thermal performance goals to ensure structural integrity and durability.
Wall tie vs Cavity tie Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com