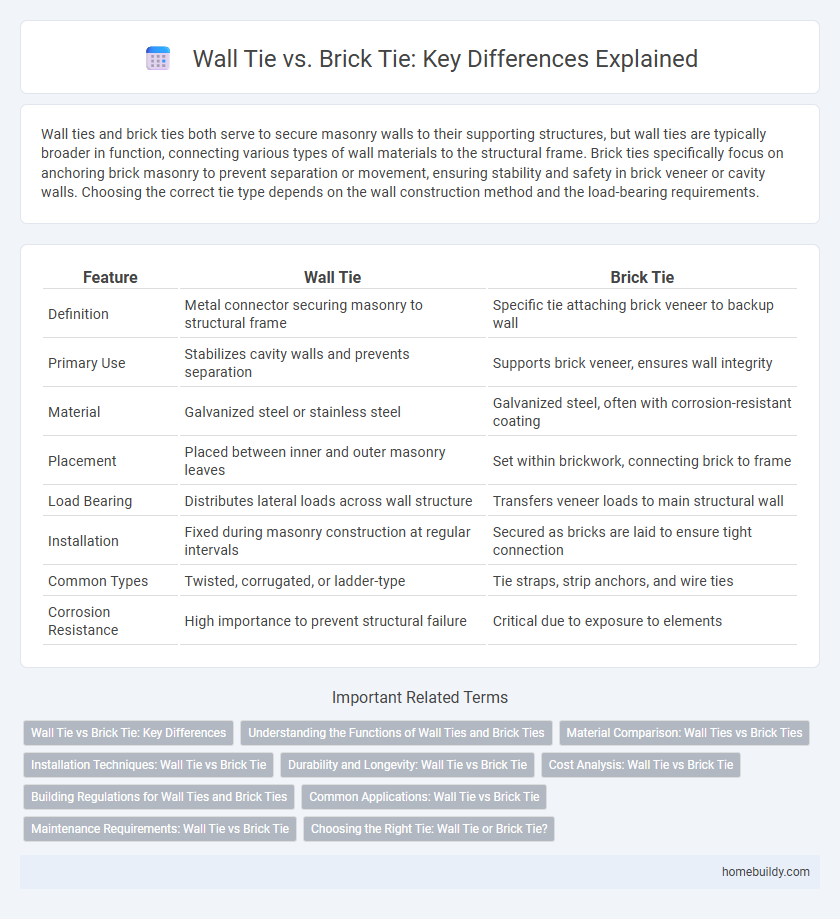
Wall ties and brick ties both serve to secure masonry walls to their supporting structures, but wall ties are typically broader in function, connecting various types of wall materials to the structural frame. Brick ties specifically focus on anchoring brick masonry to prevent separation or movement, ensuring stability and safety in brick veneer or cavity walls. Choosing the correct tie type depends on the wall construction method and the load-bearing requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wall Tie | Brick Tie |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Metal connector securing masonry to structural frame | Specific tie attaching brick veneer to backup wall |
| Primary Use | Stabilizes cavity walls and prevents separation | Supports brick veneer, ensures wall integrity |
| Material | Galvanized steel or stainless steel | Galvanized steel, often with corrosion-resistant coating |
| Placement | Placed between inner and outer masonry leaves | Set within brickwork, connecting brick to frame |
| Load Bearing | Distributes lateral loads across wall structure | Transfers veneer loads to main structural wall |
| Installation | Fixed during masonry construction at regular intervals | Secured as bricks are laid to ensure tight connection |
| Common Types | Twisted, corrugated, or ladder-type | Tie straps, strip anchors, and wire ties |
| Corrosion Resistance | High importance to prevent structural failure | Critical due to exposure to elements |
Wall Tie vs Brick Tie: Key Differences
Wall ties and brick ties both serve to connect masonry veneer to the structural frame, but wall ties are typically used in cavity wall construction, creating a mechanical link between the outer brick and inner wall. Brick ties are a subset of wall ties specifically designed to anchor brick veneers to structural backing, often featuring corrugated metal for enhanced grip and corrosion resistance. The key differences lie in their application scope and design, with wall ties accommodating various wall assemblies while brick ties focus exclusively on brick veneer stabilization.
Understanding the Functions of Wall Ties and Brick Ties
Wall ties and brick ties serve crucial roles in masonry construction by providing structural stability and preventing wall separation. Wall ties primarily connect the inner and outer walls in cavity wall systems, ensuring load distribution and resistance to lateral forces. Brick ties specifically secure brick veneers to supporting structural walls, enhancing the wall's durability and reducing the risk of brick detachment.
Material Comparison: Wall Ties vs Brick Ties
Wall ties are typically made from stainless steel or galvanized steel to ensure corrosion resistance and structural stability in masonry cavity walls. Brick ties, often constructed from galvanized steel or stainless steel as well, specifically connect brick veneers to supporting structures, maintaining the wall's integrity while accommodating movement. The choice of material for both wall ties and brick ties is crucial for durability, with stainless steel offering superior resistance to rust and environmental degradation compared to standard galvanized options.
Installation Techniques: Wall Tie vs Brick Tie
Wall ties are installed by embedding them into mortar joints between backing walls and outer bricks, ensuring structural stability through direct connection. Brick ties typically attach to the inner frame of a cavity wall and extend into the brickwork, using metal ties with corrosion-resistant coatings to secure the brick veneer. Proper installation techniques for both involve precise alignment and avoiding mortar contamination to maintain load transfer and prevent wall movement.
Durability and Longevity: Wall Tie vs Brick Tie
Wall ties and brick ties both serve to secure masonry to the structural frame, but wall ties typically offer enhanced durability due to their robust stainless steel construction, which resists corrosion and extends lifespan. Brick ties, often made from galvanized steel, provide adequate strength but may face corrosion issues in harsh environments, potentially reducing longevity. Choosing wall ties can result in longer-lasting structural integrity, particularly in moisture-prone or coastal areas where corrosion resistance is critical.
Cost Analysis: Wall Tie vs Brick Tie
Wall ties generally cost less than brick ties due to simpler design and easier installation processes. Brick ties, designed specifically for attaching brick veneers to structural walls, may increase labor expenses and material costs because of their specialized shapes and corrosion resistance features. Evaluating long-term durability and maintenance expenses is crucial for an accurate cost analysis between wall ties and brick ties.
Building Regulations for Wall Ties and Brick Ties
Building Regulations specify strict requirements for wall ties and brick ties to ensure structural stability and weather resistance in cavity walls. Wall ties must comply with BS EN 845-1 standards, ensuring corrosion resistance and appropriate tensile strength, while brick ties are typically used for veneer walls and must meet similar durability criteria. Proper installation according to Building Regulations prevents moisture ingress and maintains the integrity of load-bearing masonry.
Common Applications: Wall Tie vs Brick Tie
Wall ties are commonly used to connect cavity walls by linking the inner and outer masonry layers for structural stability, while brick ties specifically secure brick veneers to wood or metal framing. Wall ties are prevalent in load-bearing walls and cavity construction to prevent wall separation, whereas brick ties are favored in veneer applications to ensure proper attachment of brick facades. Both ties play critical roles in maintaining wall integrity but differ in application based on the construction type and material compatibility.
Maintenance Requirements: Wall Tie vs Brick Tie
Wall ties generally require less frequent maintenance due to their robust stainless steel construction, which resists corrosion and structural degradation. Brick ties, often made from galvanized steel, may demand more regular inspections and upkeep to prevent rust and ensure wall stability. Proper maintenance of both types is essential to preserve the integrity of cavity walls and prevent moisture ingress.
Choosing the Right Tie: Wall Tie or Brick Tie?
Selecting the right tie depends on the specific wall construction and load requirements; wall ties are primarily designed to connect cavity walls by anchoring the outer brick veneer to the inner structural wall, providing lateral stability. Brick ties, a subset of wall ties, focus on fastening individual bricks or brickwork to framed structures, ensuring proper alignment and strength in masonry veneer applications. Understanding material compatibility, corrosion resistance, and building codes is essential to ensure the longevity and structural integrity of the wall system.
Wall tie vs Brick tie Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com