Heavy-duty truss connectors are designed to support larger loads and provide enhanced strength for structural applications, making them ideal for commercial and industrial buildings. Light-duty truss connectors are suitable for smaller, residential projects where lower load capacities are required, offering ease of installation and cost efficiency. Choosing between heavy-duty and light-duty connectors depends on the span length, load requirements, and safety factors of the truss design.
Table of Comparison
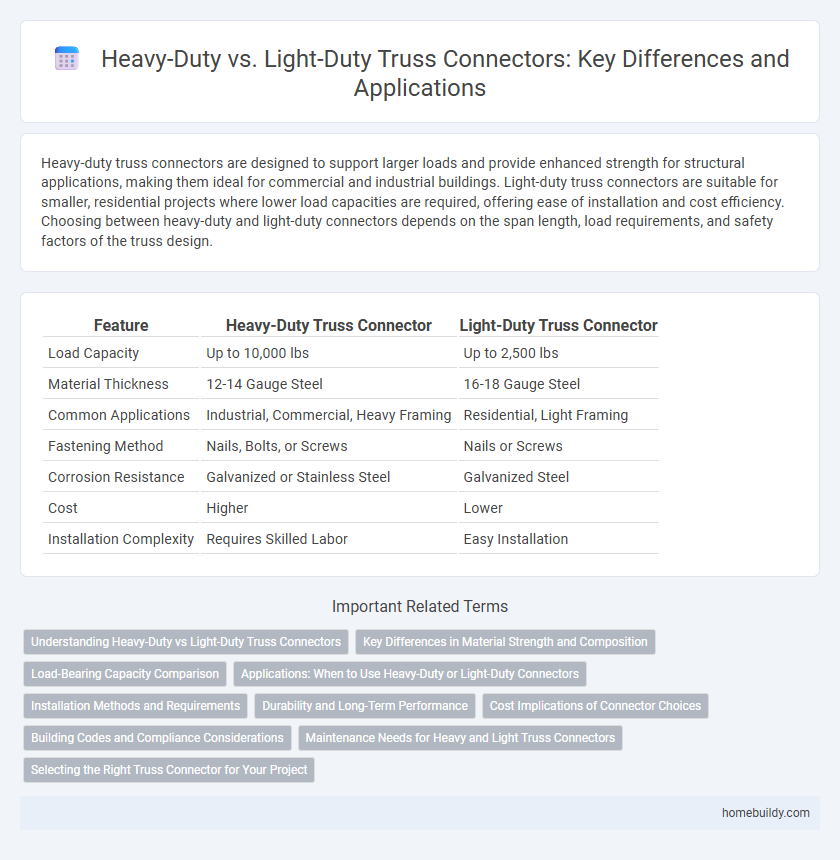
| Feature | Heavy-Duty Truss Connector | Light-Duty Truss Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Load Capacity | Up to 10,000 lbs | Up to 2,500 lbs |
| Material Thickness | 12-14 Gauge Steel | 16-18 Gauge Steel |
| Common Applications | Industrial, Commercial, Heavy Framing | Residential, Light Framing |
| Fastening Method | Nails, Bolts, or Screws | Nails or Screws |
| Corrosion Resistance | Galvanized or Stainless Steel | Galvanized Steel |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Installation Complexity | Requires Skilled Labor | Easy Installation |
Understanding Heavy-Duty vs Light-Duty Truss Connectors
Heavy-duty truss connectors are engineered to support significantly higher loads and provide enhanced structural stability for complex or large-scale construction projects. Light-duty truss connectors are designed for lighter applications, offering sufficient strength for residential or small commercial structures while maintaining ease of installation. Selecting the appropriate connector depends on load requirements, environmental conditions, and specific engineering criteria to ensure safety and durability.
Key Differences in Material Strength and Composition
Heavy-duty truss connectors are typically made from high-grade steel alloys with enhanced tensile strength, enabling them to support greater loads and resist deformation under stress. In contrast, light-duty truss connectors use thinner gauge metals or lower-grade steel with reduced strength, suitable for lighter structural applications. The material composition of heavy-duty connectors often includes zinc galvanization or corrosion-resistant coatings, which improve durability and longevity in demanding environments compared to the basic coating on light-duty options.
Load-Bearing Capacity Comparison
Heavy-duty truss connectors offer significantly higher load-bearing capacity compared to light-duty truss connectors, making them suitable for structural applications requiring robust support and durability. Typically designed with thicker gauge metal and reinforced fasteners, heavy-duty connectors can handle larger shear and tensile forces, essential in commercial and industrial framing. Light-duty truss connectors, constructed from thinner materials, are ideal for residential or non-critical load scenarios where weight and cost reduction are prioritized over maximum strength.
Applications: When to Use Heavy-Duty or Light-Duty Connectors
Heavy-duty truss connectors are ideal for applications involving large load-bearing structures such as commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and long-span bridges, where high strength and durability are critical. Light-duty truss connectors suit residential projects, small-scale roof framing, and non-structural elements where loads are moderate and ease of installation is prioritized. Selecting the appropriate connector type ensures structural integrity, safety, and compliance with engineering specifications for the specific construction demands.
Installation Methods and Requirements
Heavy-duty truss connectors require precise installation techniques including the use of high-strength fasteners such as bolts or specialized nails to ensure structural integrity under significant loads. Light-duty truss connectors are typically installed with standard nails or screws and simpler alignment processes suitable for less demanding applications. Proper fastening patterns and manufacturer guidelines are critical for both types to guarantee safety and performance in truss assembly.
Durability and Long-Term Performance
Heavy-duty truss connectors are engineered with thicker gauge steel and reinforced welds, providing superior durability and enhanced resistance to heavy loads and environmental stress compared to light-duty truss connectors. Their robust design ensures long-term performance in critical structural applications, minimizing maintenance and prolonging service life under demanding conditions. Light-duty truss connectors, made from thinner materials, are suitable for less strenuous applications but may experience faster wear and reduced lifespan in high-stress scenarios.
Cost Implications of Connector Choices
Heavy-duty truss connectors typically involve higher initial costs due to thicker gauge steel and increased fastening requirements, but they offer enhanced structural stability that can reduce long-term maintenance expenses. Light-duty truss connectors are less expensive upfront, making them suitable for smaller projects or non-critical load-bearing applications, yet they may lead to higher repair costs and potential safety issues over time. Selecting the appropriate connector type requires balancing immediate budget constraints against durability and lifecycle cost considerations to optimize overall investment.
Building Codes and Compliance Considerations
Heavy-duty truss connectors must meet stringent building codes such as the International Building Code (IBC) and require testing for higher load capacities, ensuring structural integrity in commercial and industrial applications. Light-duty truss connectors are generally used in residential settings and comply with less rigorous standards, often aligned with local or regional building codes emphasizing lower stress requirements. Choosing the appropriate connector type is crucial for code compliance, safety, and durability, as failure to adhere to these standards can result in structural deficiencies and legal liabilities.
Maintenance Needs for Heavy and Light Truss Connectors
Heavy-duty truss connectors require less frequent maintenance due to their robust materials and enhanced corrosion resistance compared to light-duty truss connectors, which demand more regular inspections and protective treatments to prevent wear and damage. Steel grade, coating type, and load capacity significantly impact the maintenance intervals, with heavy-duty connectors often featuring galvanized or stainless steel finishes that reduce rust and extend service life. Light-duty connectors, typically made from thinner gauge steel, are more susceptible to environmental factors, necessitating routine cleaning and timely replacement to maintain structural integrity.
Selecting the Right Truss Connector for Your Project
Heavy-duty truss connectors provide superior load-bearing capacity and enhanced structural support, making them ideal for large-scale or high-stress construction projects. Light-duty truss connectors are best suited for smaller, residential applications where weight and force demands are minimal. Selecting the right truss connector involves assessing project load requirements, environmental conditions, and compliance with building codes to ensure safety and longevity.
heavy-duty truss connector vs light-duty truss connector Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com