Gusset plates are flat steel components used to connect beams and columns, providing strength and stability at joints in frameworks. Truss connectors, on the other hand, are specialized fasteners or fittings designed to join truss members, ensuring proper load distribution and alignment. Both are essential in structural engineering, but gusset plates focus on reinforcing connections while truss connectors facilitate precise assembly of truss systems.
Table of Comparison
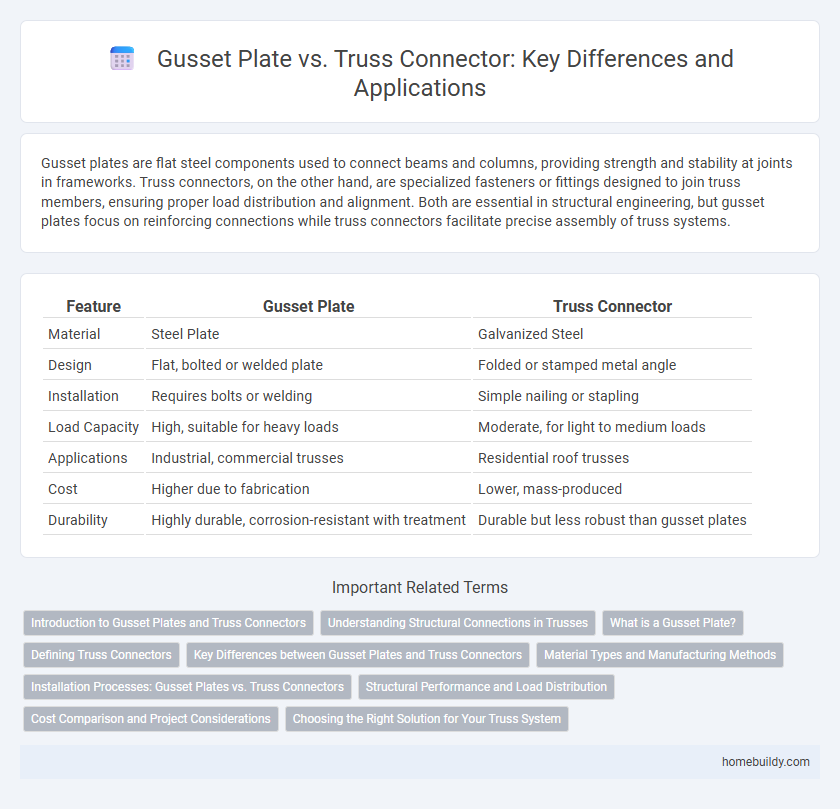
| Feature | Gusset Plate | Truss Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Steel Plate | Galvanized Steel |
| Design | Flat, bolted or welded plate | Folded or stamped metal angle |
| Installation | Requires bolts or welding | Simple nailing or stapling |
| Load Capacity | High, suitable for heavy loads | Moderate, for light to medium loads |
| Applications | Industrial, commercial trusses | Residential roof trusses |
| Cost | Higher due to fabrication | Lower, mass-produced |
| Durability | Highly durable, corrosion-resistant with treatment | Durable but less robust than gusset plates |
Introduction to Gusset Plates and Truss Connectors
Gusset plates and truss connectors serve as critical structural components in frame and truss systems, providing essential support at joint intersections. Gusset plates are flat, thick steel plates used to join multiple members and resist shear forces, enhancing the overall stability of the structure. Truss connectors, which include gusset plates, are specialized fasteners designed to secure truss members efficiently, ensuring load transfer and structural integrity.
Understanding Structural Connections in Trusses
Gusset plates serve as critical components that reinforce truss connections by distributing loads across multiple members, enhancing overall stability and strength. Truss connectors, often specialized metal fasteners or plates, provide precise alignment and secure joint assembly, ensuring efficient load transfer within truss systems. Understanding the distinct roles and installation methods of gusset plates versus truss connectors is essential for optimizing structural performance and safety in roof and bridge trusses.
What is a Gusset Plate?
A gusset plate is a thick, flat piece of steel used to connect beams and trusses at joints, providing structural stability and load distribution. Unlike typical truss connectors, gusset plates offer a broad surface area to distribute forces evenly across multiple members, enhancing the joint's strength. Commonly found in bridges and steel frameworks, gusset plates are essential for maintaining structural integrity in complex load-bearing connections.
Defining Truss Connectors
Truss connectors are metal fasteners designed to join multiple wood members in a truss system, providing structural stability and load distribution. Unlike gusset plates, which are typically flat and used to reinforce joints by being bolted or nailed onto wood surfaces, truss connectors often feature stamped, welded, or formed designs enabling quick installation and enhanced strength. These connectors are engineered to resist shear, tension, and compression forces within roof and floor trusses, ensuring long-term performance in construction.
Key Differences between Gusset Plates and Truss Connectors
Gusset plates are flat steel plates used to connect multiple structural members at a joint, providing stability and load distribution, while truss connectors often refer to specialized hardware like gusset plates, connector plates, or brackets designed specifically for truss assembly. Gusset plates are typically welded or bolted to members to resist shear forces, whereas truss connectors may include metal plates with embedded teeth for wooden truss connections or engineered steel fittings for various materials. The key differences lie in their application scope, material compatibility, and load transfer mechanisms within the overall truss system.
Material Types and Manufacturing Methods
Gusset plates are typically made from carbon steel or stainless steel, offering high strength and corrosion resistance, and are manufactured through processes like cutting, punching, and welding. Truss connectors often utilize galvanized steel or aluminum, which provides lightweight durability and enhanced resistance to environmental factors, produced via stamping or forging methods. Material selection and manufacturing techniques directly impact the load-bearing capacity and longevity of both gusset plates and truss connectors in structural applications.
Installation Processes: Gusset Plates vs. Truss Connectors
Gusset plates require precise alignment and multiple fasteners such as bolts or welds, often demanding skilled labor and extended installation time. Truss connectors, designed for rapid assembly, utilize stamped or pressed metal components that can be quickly nailed or screwed, streamlining the connection process. The simpler installation workflow of truss connectors reduces labor costs and accelerates project timelines compared to traditional gusset plate methods.
Structural Performance and Load Distribution
Gusset plates enhance structural performance by providing rigid connections between truss members, ensuring efficient load transfer and minimizing deformation under heavy loads. Truss connectors, such as toothed plates or metal connectors, facilitate quicker assembly while distributing loads evenly across the joint, reducing stress concentrations. The choice between gusset plates and truss connectors impacts overall load distribution, with gusset plates better suited for high-load applications requiring increased stiffness.
Cost Comparison and Project Considerations
Gusset plates generally offer a lower material cost compared to specialized truss connectors, making them a cost-effective choice for standard truss assemblies. However, truss connectors provide enhanced installation speed and structural precision, which can reduce labor costs and project timelines significantly. Project considerations such as load requirements, design complexity, and construction speed heavily influence the overall cost-effectiveness between gusset plates and truss connectors.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Truss System
Selecting between a gusset plate and a truss connector depends on the specific structural demands and load distribution of your truss system. Gusset plates offer enhanced strength and stability for heavy-load applications by providing a rigid, flat surface to join multiple members, while truss connectors are typically easier to install and suited for lighter, prefabricated truss systems. Evaluating factors such as material type, load capacity, connection complexity, and installation environment ensures optimal performance and longevity of the truss structure.
gusset plate vs truss connector Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com