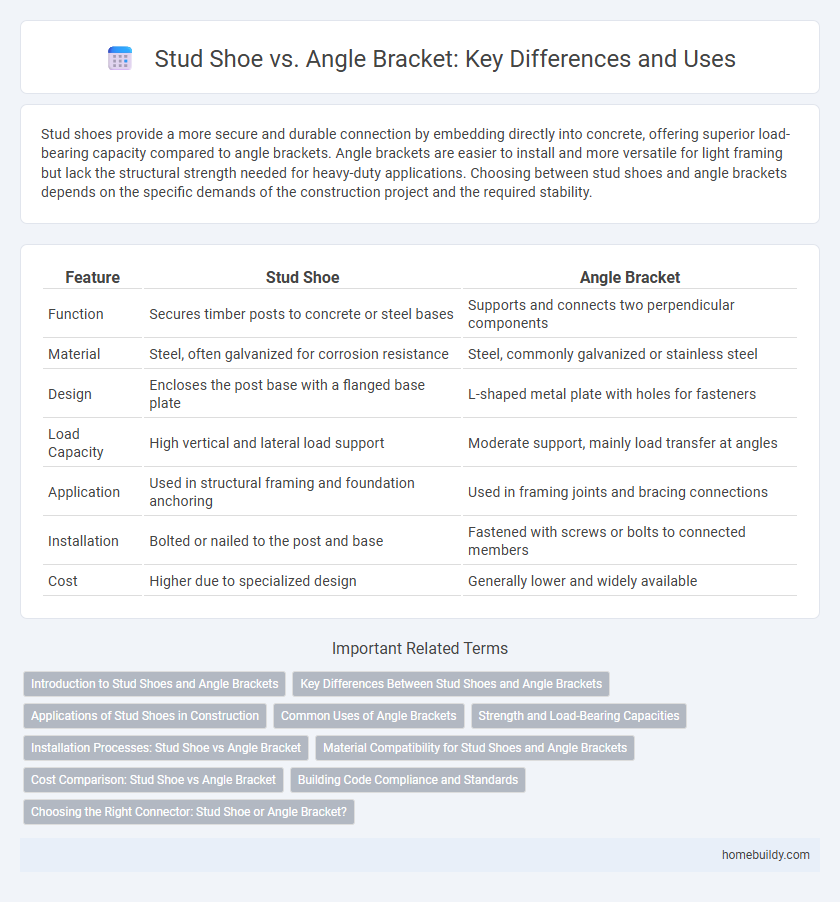
Stud shoes provide a more secure and durable connection by embedding directly into concrete, offering superior load-bearing capacity compared to angle brackets. Angle brackets are easier to install and more versatile for light framing but lack the structural strength needed for heavy-duty applications. Choosing between stud shoes and angle brackets depends on the specific demands of the construction project and the required stability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Stud Shoe | Angle Bracket |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Secures timber posts to concrete or steel bases | Supports and connects two perpendicular components |
| Material | Steel, often galvanized for corrosion resistance | Steel, commonly galvanized or stainless steel |
| Design | Encloses the post base with a flanged base plate | L-shaped metal plate with holes for fasteners |
| Load Capacity | High vertical and lateral load support | Moderate support, mainly load transfer at angles |
| Application | Used in structural framing and foundation anchoring | Used in framing joints and bracing connections |
| Installation | Bolted or nailed to the post and base | Fastened with screws or bolts to connected members |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized design | Generally lower and widely available |
Introduction to Stud Shoes and Angle Brackets
Stud shoes provide enhanced lateral support and secure anchoring for wood framing, improving structural stability compared to traditional angle brackets. Angle brackets offer basic connection functions but lack the load distribution efficiency of stud shoes, which are engineered to handle vertical and shear forces more effectively. Using stud shoes in framing projects optimizes joint strength and longevity, making them a preferred choice in modern construction for durable wood-to-foundation attachments.
Key Differences Between Stud Shoes and Angle Brackets
Stud shoes provide superior load-bearing capacity and enhanced lateral stability compared to angle brackets, making them ideal for high-stress structural connections. Unlike angle brackets, stud shoes are designed to distribute loads more evenly along the stud, reducing stress concentrations and potential material fatigue. Their robust construction and ease of installation make stud shoes a preferred choice in heavy-duty framing applications over traditional angle brackets.
Applications of Stud Shoes in Construction
Stud shoes are specifically designed for securing steel beams to concrete or steel columns, providing a strong connection point that transfers loads efficiently in structural frameworks. Unlike angle brackets, which are often used for lighter framing or secondary supports, stud shoes accommodate heavy-duty applications such as high-rise buildings, bridges, and industrial structures where precise alignment and load-bearing capacity are critical. These components enhance construction durability by resisting shear and moment forces, ensuring the stability and safety of complex structural systems.
Common Uses of Angle Brackets
Angle brackets are commonly used in construction to reinforce connections between wood beams, providing strong support at corners and joints. Unlike stud shoes, which are designed to secure studs to concrete or steel, angle brackets offer versatile applications including framing, cabinetry, and shelving installations. Their L-shaped design allows for easy fastening to various surfaces, enhancing structural stability in both residential and commercial projects.
Strength and Load-Bearing Capacities
Stud shoes provide superior strength and load-bearing capacities compared to angle brackets, as they are specifically designed to connect wood studs to concrete or masonry foundations securely. Engineered with heavy-gauge steel and often including welded reinforcement, stud shoes distribute loads more evenly and reduce the risk of deformation under heavy pressure. This enhanced structural integrity makes stud shoes ideal for high-stress applications in framing and foundation anchoring where reliable support is critical.
Installation Processes: Stud Shoe vs Angle Bracket
Stud shoe installation involves securing the base of a steel stud to the floor or ceiling track using screws, ensuring precise alignment and enhanced load transfer, while angle brackets require fastening both vertical and horizontal members at their junction with multiple fasteners. Stud shoes offer quicker installation by reducing drilling and alignment steps compared to angle brackets, which demand careful positioning for accurate corner reinforcement. The simplified process of stud shoe attachment minimizes labor time and potential installation errors, making it a preferred choice for efficient framing connections.
Material Compatibility for Stud Shoes and Angle Brackets
Stud shoes are typically made from galvanised steel or stainless steel, offering superior corrosion resistance and strength for securing timber in structural applications, while angle brackets often use similar materials but vary in thickness and finish to suit different load requirements. The compatibility of stud shoes with treated lumber is enhanced by their coated or stainless steel construction, reducing the risk of metal corrosion and ensuring long-term durability. Angle brackets, though versatile, may require specific coatings or materials to match the chemical properties of certain wood treatments, impacting their performance and lifespan.
Cost Comparison: Stud Shoe vs Angle Bracket
Stud shoes generally offer a higher upfront cost compared to angle brackets due to their specialized design and materials, but they provide enhanced structural stability that can reduce long-term maintenance expenses. Angle brackets are more cost-effective initially and widely available, making them suitable for budget-sensitive projects, but may require additional reinforcements to match the support level of stud shoes. When evaluating total project costs, stud shoes can provide better value by minimizing labor and repair costs, while angle brackets appeal to smaller-scale or non-critical applications with lower initial investment.
Building Code Compliance and Standards
Stud shoes and angle brackets serve as crucial connectors in framing construction, but stud shoes offer enhanced load distribution and better compliance with building codes such as the International Residential Code (IRC) and the International Building Code (IBC). Stud shoes are designed to accommodate dimensional lumber sizes and allow for precise alignment, reducing the risk of structural failure and ensuring adherence to ASTM standards for fastener strength and corrosion resistance. Angle brackets, while versatile, may not provide the same level of engineered support or meet specific code requirements for seismic or wind loads in certain jurisdictions.
Choosing the Right Connector: Stud Shoe or Angle Bracket?
Stud shoes provide a secure and durable connection between wood framing members and concrete, offering superior load transfer and resistance to shear forces compared to angle brackets. Angle brackets are versatile, easy to install, and suitable for lighter loads or applications requiring quick fastening, but they may lack the structural strength needed in high-stress areas. Selecting the right connector depends on the specific construction requirements, load conditions, and environmental factors to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Stud shoe vs angle bracket Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com