Skylight frames often provide better energy efficiency than traditional roof window frames due to tighter seals and advanced insulating materials that reduce heat loss and minimize drafts. Roof windows, while offering increased ventilation and natural light, may have more exposed edges that can contribute to thermal bridging and energy loss. Choosing high-performance glazing and quality framing materials is essential to maximize energy efficiency for both skylights and roof windows.
Table of Comparison
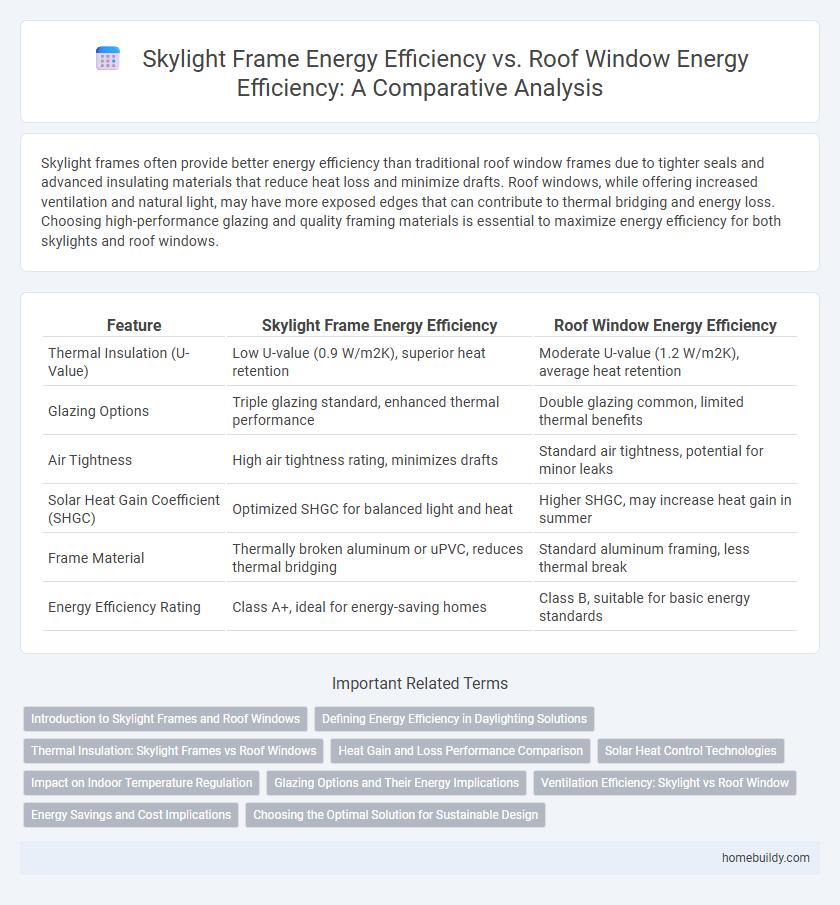
| Feature | Skylight Frame Energy Efficiency | Roof Window Energy Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation (U-Value) | Low U-value (0.9 W/m2K), superior heat retention | Moderate U-value (1.2 W/m2K), average heat retention |
| Glazing Options | Triple glazing standard, enhanced thermal performance | Double glazing common, limited thermal benefits |
| Air Tightness | High air tightness rating, minimizes drafts | Standard air tightness, potential for minor leaks |
| Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) | Optimized SHGC for balanced light and heat | Higher SHGC, may increase heat gain in summer |
| Frame Material | Thermally broken aluminum or uPVC, reduces thermal bridging | Standard aluminum framing, less thermal break |
| Energy Efficiency Rating | Class A+, ideal for energy-saving homes | Class B, suitable for basic energy standards |
Introduction to Skylight Frames and Roof Windows
Skylight frames and roof windows both enhance natural light in buildings but differ significantly in energy efficiency due to their construction and installation methods. Skylight frames often feature advanced insulation materials and multiple glazing layers, reducing heat loss and improving U-value performance compared to traditional roof windows. Roof windows typically have a larger surface area exposed to external temperatures, resulting in higher thermal transmittance and less energy efficiency than well-designed skylight frames.
Defining Energy Efficiency in Daylighting Solutions
Energy efficiency in skylight frames is primarily determined by their thermal insulation properties, often quantified by U-values, with lower U-values indicating better insulation and reduced heat loss compared to roof windows. Skylight frames typically incorporate advanced glazing technologies and airtight seals that enhance daylight penetration while minimizing energy consumption for heating and cooling. Roof windows, designed for operability and ventilation, may have higher U-values, making skylights generally more effective for maximizing natural light without compromising thermal performance.
Thermal Insulation: Skylight Frames vs Roof Windows
Skylight frames generally offer superior thermal insulation compared to traditional roof windows due to advanced multi-chamber designs and high-performance glazing options that reduce heat transfer. The integration of insulated spacers and low-emissivity coatings in skylight frames further enhances energy efficiency by minimizing heat loss during winter and heat gain in summer. Roof windows, while effective, typically have lower insulation values, resulting in increased energy consumption for heating and cooling.
Heat Gain and Loss Performance Comparison
Skylight frames typically offer superior energy efficiency compared to traditional roof windows due to their advanced insulation materials and tighter sealing, reducing unwanted heat loss in winter and minimizing heat gain in summer. High-performance skylight frames often incorporate multi-chambered profiles and low-emissivity (Low-E) glass, which significantly enhances thermal resistance and reduces U-values, leading to better overall heat retention. This results in optimized energy conservation, decreased reliance on HVAC systems, and improved indoor comfort throughout the year.
Solar Heat Control Technologies
Skylight frames equipped with advanced solar heat control technologies significantly reduce heat gain compared to traditional roof windows, enhancing overall energy efficiency. Low-emissivity (Low-E) coatings and spectrally selective glazing in skylight frames minimize infrared and ultraviolet radiation penetration while maximizing natural light. These features not only decrease cooling loads but also improve thermal comfort, making skylight frames a superior choice for sustainable building design.
Impact on Indoor Temperature Regulation
Skylight frames with advanced thermal breaks and insulated glazing significantly enhance indoor temperature regulation by minimizing heat loss during winter and reducing heat gain in summer compared to traditional roof window frames. High-performance skylight frames maintain stable indoor temperatures, lowering HVAC energy consumption by up to 25%. Optimized skylight designs contribute to improved occupant comfort and consistent thermal performance throughout the year.
Glazing Options and Their Energy Implications
Skylight frames with advanced glazing options, such as triple-pane glass and low-emissivity coatings, significantly enhance energy efficiency by reducing heat loss and minimizing solar heat gain compared to traditional roof windows. Roof windows often utilize double-pane glazing, which provides moderate insulation but may allow greater thermal transfer and energy inefficiency in extreme climates. Selecting skylight frames with high-performance glazing optimizes natural light ingress while maintaining superior thermal performance, leading to reduced heating and cooling costs.
Ventilation Efficiency: Skylight vs Roof Window
Skylight frames often provide superior ventilation efficiency compared to traditional roof windows due to their strategic positioning on roof planes, allowing for optimized airflow and natural cooling. Enhanced air circulation through skylights reduces reliance on mechanical ventilation systems, contributing to overall energy savings and improved indoor air quality. Roof windows, while effective, typically have limited ventilation capacity as their operation is constrained by size and placement, making skylights a preferred choice for maximizing ventilation benefits in energy-efficient building designs.
Energy Savings and Cost Implications
Skylight frames with advanced thermal breaks and double or triple glazing offer superior energy savings by reducing heat loss and improving insulation compared to traditional roof windows. Enhanced energy efficiency in skylight frames can lower heating and cooling costs, resulting in significant long-term cost savings on utility bills. Choosing energy-efficient skylight frames not only contributes to a reduced carbon footprint but also increases property value through improved sustainability features.
Choosing the Optimal Solution for Sustainable Design
Skylight frames often provide superior energy efficiency compared to traditional roof windows due to enhanced insulation materials and airtight sealing technology, reducing heat loss and improving thermal performance. Selecting skylight frames with multi-layer glazing and thermal breaks can significantly lower energy consumption in sustainable building projects. Prioritizing these advanced skylight solutions supports optimal energy conservation and long-term cost savings in environmentally conscious architectural design.
Skylight frame energy efficiency vs roof window energy efficiency Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com