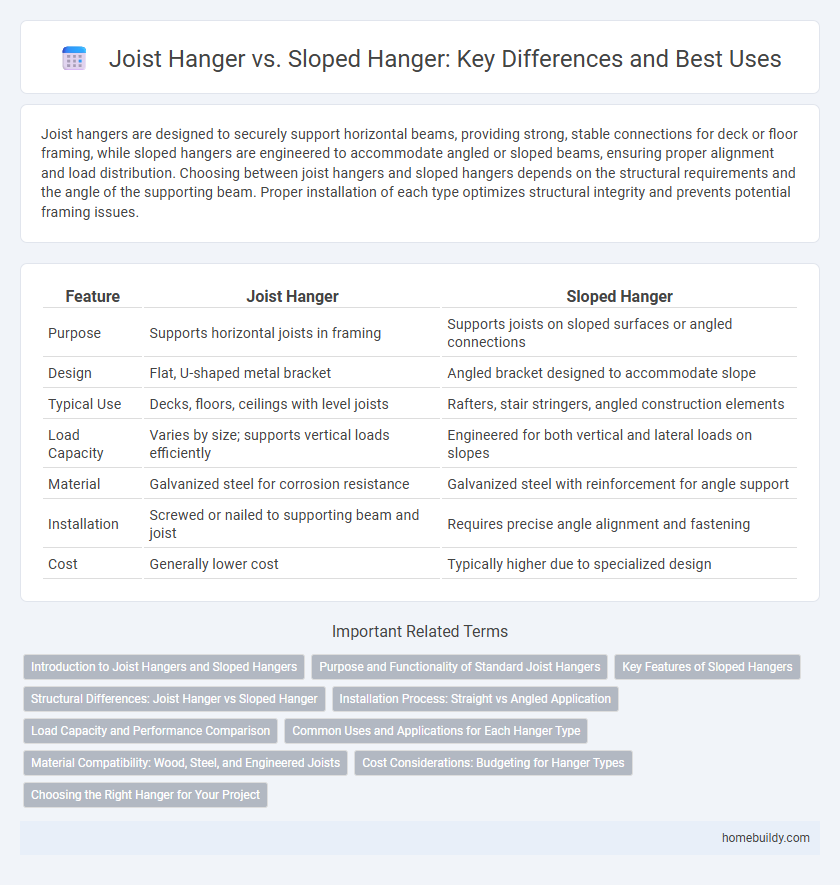
Joist hangers are designed to securely support horizontal beams, providing strong, stable connections for deck or floor framing, while sloped hangers are engineered to accommodate angled or sloped beams, ensuring proper alignment and load distribution. Choosing between joist hangers and sloped hangers depends on the structural requirements and the angle of the supporting beam. Proper installation of each type optimizes structural integrity and prevents potential framing issues.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Joist Hanger | Sloped Hanger |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Supports horizontal joists in framing | Supports joists on sloped surfaces or angled connections |
| Design | Flat, U-shaped metal bracket | Angled bracket designed to accommodate slope |
| Typical Use | Decks, floors, ceilings with level joists | Rafters, stair stringers, angled construction elements |
| Load Capacity | Varies by size; supports vertical loads efficiently | Engineered for both vertical and lateral loads on slopes |
| Material | Galvanized steel for corrosion resistance | Galvanized steel with reinforcement for angle support |
| Installation | Screwed or nailed to supporting beam and joist | Requires precise angle alignment and fastening |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Typically higher due to specialized design |
Introduction to Joist Hangers and Sloped Hangers
Joist hangers provide essential support by securing horizontal beams to vertical structures, ensuring stability and load distribution in framing projects. Sloped hangers are specifically designed to accommodate angled or sloped joists, maintaining strong connections despite non-horizontal orientations. Both types are crucial in construction, with joist hangers offering versatile, standard use and sloped hangers addressing angled framing challenges.
Purpose and Functionality of Standard Joist Hangers
Standard joist hangers serve as crucial structural connectors designed to support and secure horizontal lumber beams in construction, ensuring load distribution and stability without accommodating angled or sloped connections. Unlike sloped hangers, which are specifically engineered to hold beams at various angles, standard joist hangers maintain a 90-degree alignment between joists and ledger boards. Their purpose centers on providing a reliable, efficient method to transfer weight and resist lateral forces in floor framing and deck building applications.
Key Features of Sloped Hangers
Sloped hangers are specifically designed to support joists at an angle, ensuring structural stability on sloped surfaces such as rafters or stair stringers. Their key features include angled seats that conform to various slopes, enhanced load-bearing capacity for uneven forces, and corrosion-resistant coatings suitable for outdoor or exposed environments. These attributes make sloped hangers essential for secure joist attachment in non-horizontal framing applications.
Structural Differences: Joist Hanger vs Sloped Hanger
Joist hangers are designed with a flat base and perpendicular sides to support horizontal joists, providing strong connections for level framing. In contrast, sloped hangers feature angled sides that accommodate joists installed at an incline, ensuring structural stability on pitched surfaces. The critical difference lies in their geometry: joist hangers maintain joist alignment parallel to the ledger board, while sloped hangers adjust for the vertical angle, distributing loads according to the roof or floor slope.
Installation Process: Straight vs Angled Application
Joist hangers are designed for straight, perpendicular installation onto beams, making the attachment process straightforward with nails or screws aligned at 90 degrees. Sloped hangers require a more precise angled placement to accommodate roof pitches or stair stringers, often involving specialized fasteners and careful positioning to ensure proper load distribution. The installation of sloped hangers typically demands advanced skills and additional hardware compared to the simpler, quicker setup of standard joist hangers.
Load Capacity and Performance Comparison
Joist hangers generally provide higher load capacity than sloped hangers, making them ideal for supporting heavy, horizontal loads in traditional framing. Sloped hangers are specifically designed to accommodate angled or sloped joists but typically have reduced load capacity due to their geometry and connection points. Load performance varies with material thickness, nail size, and installation precision, but joist hangers consistently offer superior structural stability in standard residential and commercial applications.
Common Uses and Applications for Each Hanger Type
Joist hangers are primarily used for securing horizontal wood beams in floor and ceiling framing, providing strong support in flat constructions such as decks and subfloors. Sloped hangers are specifically designed for connecting joists at an angle, commonly applied in roof framing where rafters meet beams or ledger boards on pitched structures. Both hanger types ensure structural integrity but are optimized for their particular load orientations and building requirements.
Material Compatibility: Wood, Steel, and Engineered Joists
Joist hangers are typically designed to provide strong support for wood and engineered wood joists, ensuring secure load transfer and resistance to deformation. Sloped hangers accommodate angled connections but may require specific material ratings to maintain compatibility with steel or engineered joists that have unique structural properties. Selecting the appropriate hanger ensures proper corrosion resistance and mechanical performance for wood, steel, or engineered joists in both horizontal and sloped applications.
Cost Considerations: Budgeting for Hanger Types
Joist hangers typically offer a cost-effective solution for standard framing projects, with prices generally lower than specialized sloped hangers. Sloped hangers require custom fabrication to accommodate angled connections, which increases materials and labor expenses, impacting overall budget allocation. Evaluating project requirements against budget constraints is essential to ensure the selected hanger type delivers structural integrity without excessive cost overruns.
Choosing the Right Hanger for Your Project
Joist hangers provide strong horizontal support for beams and joists, ensuring stable, level connections in construction projects. Sloped hangers are designed to accommodate angled joists, making them essential for roofs or stairs where the framing is not perpendicular. Selecting the right hanger depends on the project's structural requirements and load specifications to maintain safety and durability.
Joist hanger vs sloped hanger Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com