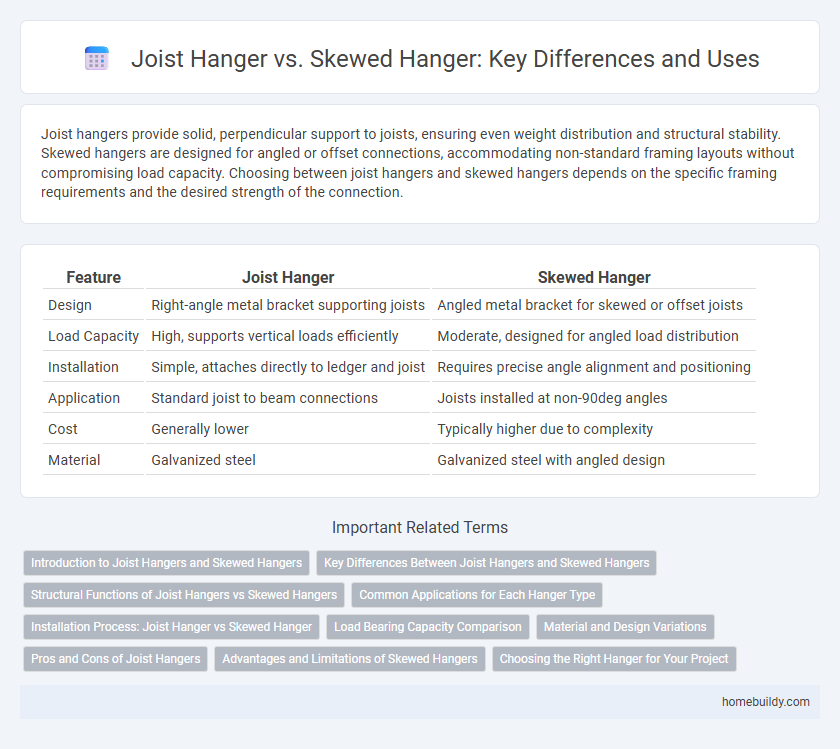
Joist hangers provide solid, perpendicular support to joists, ensuring even weight distribution and structural stability. Skewed hangers are designed for angled or offset connections, accommodating non-standard framing layouts without compromising load capacity. Choosing between joist hangers and skewed hangers depends on the specific framing requirements and the desired strength of the connection.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Joist Hanger | Skewed Hanger |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Right-angle metal bracket supporting joists | Angled metal bracket for skewed or offset joists |
| Load Capacity | High, supports vertical loads efficiently | Moderate, designed for angled load distribution |
| Installation | Simple, attaches directly to ledger and joist | Requires precise angle alignment and positioning |
| Application | Standard joist to beam connections | Joists installed at non-90deg angles |
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher due to complexity |
| Material | Galvanized steel | Galvanized steel with angled design |
Introduction to Joist Hangers and Skewed Hangers
Joist hangers are metal connectors designed to provide strong vertical load support for wood joists, ensuring uniform weight distribution and structural stability in flooring or decking systems. Skewed hangers, a specialized type of joist hanger, are engineered to accommodate joists that meet beams or ledgers at an angle other than 90 degrees, maintaining secure attachment despite angular placement. Both types are essential in framing construction, offering tailored solutions for different joist alignment requirements while enhancing overall framework integrity.
Key Differences Between Joist Hangers and Skewed Hangers
Joist hangers are designed to support perpendicular connections between joists and beams, providing maximum load-bearing capacity and structural stability. Skewed hangers accommodate angled or skewed joist connections, allowing for flexibility in framing where joists meet beams at non-right angles. The key difference lies in their application: joist hangers suit standard right-angle framing, while skewed hangers are engineered for accommodating customized, angled framing requirements.
Structural Functions of Joist Hangers vs Skewed Hangers
Joist hangers provide vertical support by securely connecting joists to beams or ledgers with perpendicular alignment, ensuring load is evenly distributed and structural rigidity is maintained. Skewed hangers, designed for angled or non-perpendicular connections, accommodate oblique framing but can introduce complex load paths requiring precise installation for optimal strength. Proper selection between joist hangers and skewed hangers depends on framing geometry and load direction to guarantee structural integrity and prevent joint failure.
Common Applications for Each Hanger Type
Joist hangers are primarily used for connecting perpendicular joists to beams or ledger boards, ensuring strong, square support in deck construction and floor framing. Skewed hangers accommodate angled connections where joists meet beams at non-right angles, often utilized in complex roof framing and custom architectural designs. Both hangers enhance structural integrity but cater to different alignment needs, optimizing load distribution in specific construction scenarios.
Installation Process: Joist Hanger vs Skewed Hanger
Joist hangers require precise perpendicular placement to support joists securely, involving straightforward nailing or screwing into structural beams. Skewed hangers demand more complex installation with angled alignment, often requiring customized adjustments and careful measurement to accommodate oblique joist connections. The installation time for skewed hangers generally exceeds that of joist hangers due to their specialized positioning and fastening requirements.
Load Bearing Capacity Comparison
Joist hangers provide superior load-bearing capacity compared to skewed hangers due to their perpendicular alignment and full seat support, which distributes weight evenly along the joist and ledger. Skewed hangers, angled to accommodate offset joists, often experience reduced load capacity because the load is concentrated on fewer fasteners and less surface area. Engineers typically recommend using joist hangers for maximum structural integrity in standard framing applications where load capacity is critical.
Material and Design Variations
Joist hangers are typically made from galvanized steel and feature a straightforward, symmetrical design for direct beam support, ensuring maximum load distribution and corrosion resistance. Skewed hangers, often constructed from similar steel materials, incorporate angled or offset shapes to accommodate beams set at non-perpendicular angles, enhancing flexibility in framing and structural alignment. Differences in design and material thickness between joist and skewed hangers influence their load capacity and installation methods, making selection crucial for structural integrity in varied construction scenarios.
Pros and Cons of Joist Hangers
Joist hangers provide strong, secure connections for framing joists, offering excellent load distribution and ease of installation with standard angles, ensuring structural stability in building projects. Unlike skewed hangers, which accommodate angled or irregular joist placements but can be more complex to install and less standardized, joist hangers are widely available and typically cost-effective. However, joist hangers require precise positioning and nailing to avoid structural weaknesses, and they may not be suitable for non-standard angled connections without additional modifications.
Advantages and Limitations of Skewed Hangers
Skewed joist hangers offer the advantage of accommodating angled or non-perpendicular connections, making them ideal for complex framing situations where standard joist hangers cannot fit. They provide reliable structural support for skewed joists, maintaining load distribution and preventing warping or sagging. However, skewed hangers have limitations including higher installation complexity, increased cost compared to standard hangers, and potential challenges ensuring optimal nail placement for maximum strength.
Choosing the Right Hanger for Your Project
Joist hangers provide strong, perpendicular support for beams, ensuring optimal load distribution and structural integrity. Skewed hangers are designed for angled connections, accommodating framing that departs from right angles, which makes them ideal for complex architectural designs. Selecting the right hanger depends on the specific angle and load requirements of your project, as well as compatibility with your framing materials.
joist hanger vs skewed hanger Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com