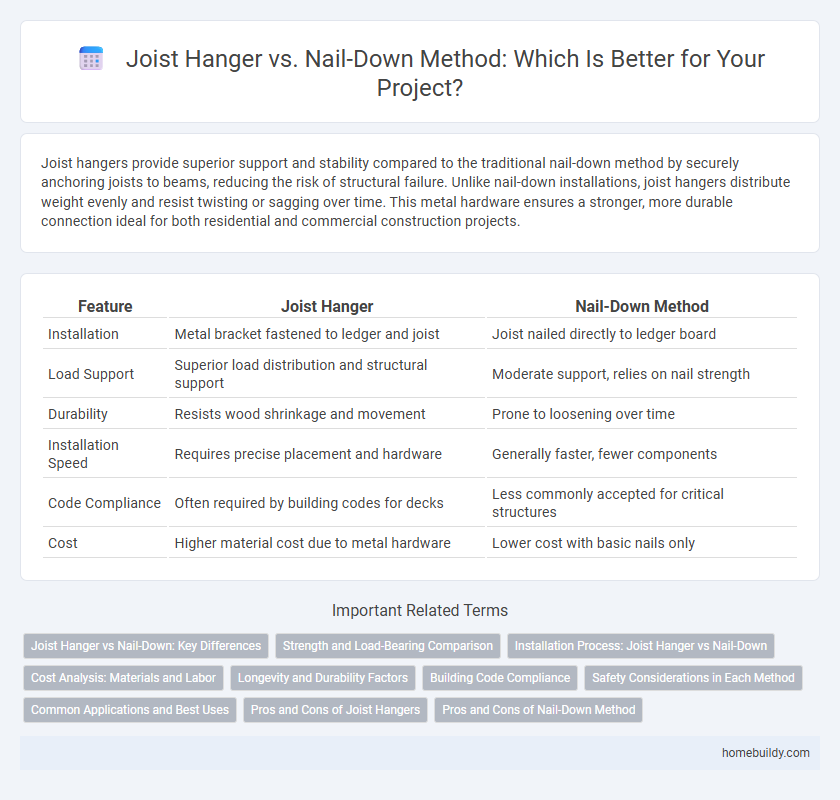
Joist hangers provide superior support and stability compared to the traditional nail-down method by securely anchoring joists to beams, reducing the risk of structural failure. Unlike nail-down installations, joist hangers distribute weight evenly and resist twisting or sagging over time. This metal hardware ensures a stronger, more durable connection ideal for both residential and commercial construction projects.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Joist Hanger | Nail-Down Method |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Metal bracket fastened to ledger and joist | Joist nailed directly to ledger board |
| Load Support | Superior load distribution and structural support | Moderate support, relies on nail strength |
| Durability | Resists wood shrinkage and movement | Prone to loosening over time |
| Installation Speed | Requires precise placement and hardware | Generally faster, fewer components |
| Code Compliance | Often required by building codes for decks | Less commonly accepted for critical structures |
| Cost | Higher material cost due to metal hardware | Lower cost with basic nails only |
Joist Hanger vs Nail-Down: Key Differences
Joist hangers provide a stronger, more secure connection by fully supporting the joist on the ledger, distributing loads evenly and reducing potential movement or sagging compared to the nail-down method. The nail-down approach relies solely on nails driven into the joist and ledger, which may result in weaker connections and increased risk of structural failure over time due to less load distribution. Building codes and structural engineering standards often recommend joist hangers for their enhanced stability, load capacity, and ease of inspection versus the traditional nail-down technique.
Strength and Load-Bearing Comparison
Joist hangers provide superior strength and load-bearing capacity compared to the nail-down method by distributing weight more evenly and securely around the joist. Engineered metal hangers resist twisting and shifting under heavy loads, ensuring greater structural stability. In contrast, the nail-down method relies heavily on fastener shear strength and may weaken over time due to wood movement and stress concentration.
Installation Process: Joist Hanger vs Nail-Down
Joist hanger installation involves securing metal brackets to support joists, offering precise alignment and increased load distribution compared to the nail-down method. The nail-down technique requires driving nails directly through joists into beams, which can compromise structural integrity and alignment over time. Using joist hangers streamlines the installation process by reducing manual adjustments and enhancing overall stability.
Cost Analysis: Materials and Labor
Joist hangers typically incur higher upfront material costs due to steel components but reduce labor expenses with faster installation times compared to the nail-down method, which uses cheaper nails but demands more time and skilled labor. The nail-down method may result in increased long-term maintenance costs due to potential structural weaknesses, whereas joist hangers provide consistent durability and stability. Overall, joist hangers offer a cost-effective balance between material investment and labor efficiency, especially in large-scale or commercial projects.
Longevity and Durability Factors
Joist hangers provide superior longevity and durability compared to the nail-down method by securely distributing loads and minimizing wood splitting. Made from galvanized steel, joist hangers resist corrosion and maintain structural integrity over time, unlike nails that can loosen or rust. This metal connector system reduces the risk of joist movement, enhancing the overall lifespan of deck and floor framing systems.
Building Code Compliance
Joist hangers provide superior Building Code Compliance compared to the nail-down method by ensuring stronger load-bearing connections and consistent alignment, which meet or exceed requirements outlined in the International Residential Code (IRC) and International Building Code (IBC). Building codes specify the use of metal connectors like joist hangers to enhance structural safety, particularly in seismic or high-wind regions, reducing the risk of joist failure. Inspections often mandate joist hangers for compliance verification, as they guarantee minimum fastening standards and improved resistance to uplift and shear forces.
Safety Considerations in Each Method
Joist hangers provide superior structural support by securely fastening joists to beams, reducing the risk of shifting or collapse compared to the nail-down method. The nail-down technique relies heavily on the quality and placement of nails, which can lead to loosening over time and increased safety hazards in dynamic loads or seismic activity. Building codes and engineering standards often favor joist hangers for critical load-bearing connections to enhance overall safety and durability.
Common Applications and Best Uses
Joist hangers are commonly used in framing decks and floors where strong, precise support is critical for load-bearing joists, offering superior stability and ease of alignment compared to the nail-down method. The nail-down technique is often favored for simpler or temporary constructions where speed and cost-efficiency are priorities, but it lacks the enhanced shear strength and code compliance provided by joist hangers. For long-lasting structural integrity in residential and commercial building projects, joist hangers deliver optimal performance in load distribution and connection durability.
Pros and Cons of Joist Hangers
Joist hangers provide superior structural support by securely fastening joists to beams, reducing the risk of joist movement and improving load distribution compared to the nail-down method. They offer enhanced durability and resistance to twisting and settling, which can prolong the lifespan of decking and flooring structures. However, joist hangers require precise installation and additional hardware, potentially increasing labor costs and project complexity.
Pros and Cons of Nail-Down Method
The nail-down method for joist installation offers simplicity and speed, requiring minimal hardware and reducing upfront costs. However, it often compromises long-term structural stability and is more prone to wood movement and joint loosening compared to joist hangers. Nail-down connections lack the enhanced load distribution and resistance to shear forces provided by metal joist hangers, increasing the risk of joist failure under heavy or dynamic loads.
joist hanger vs nail-down method Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com