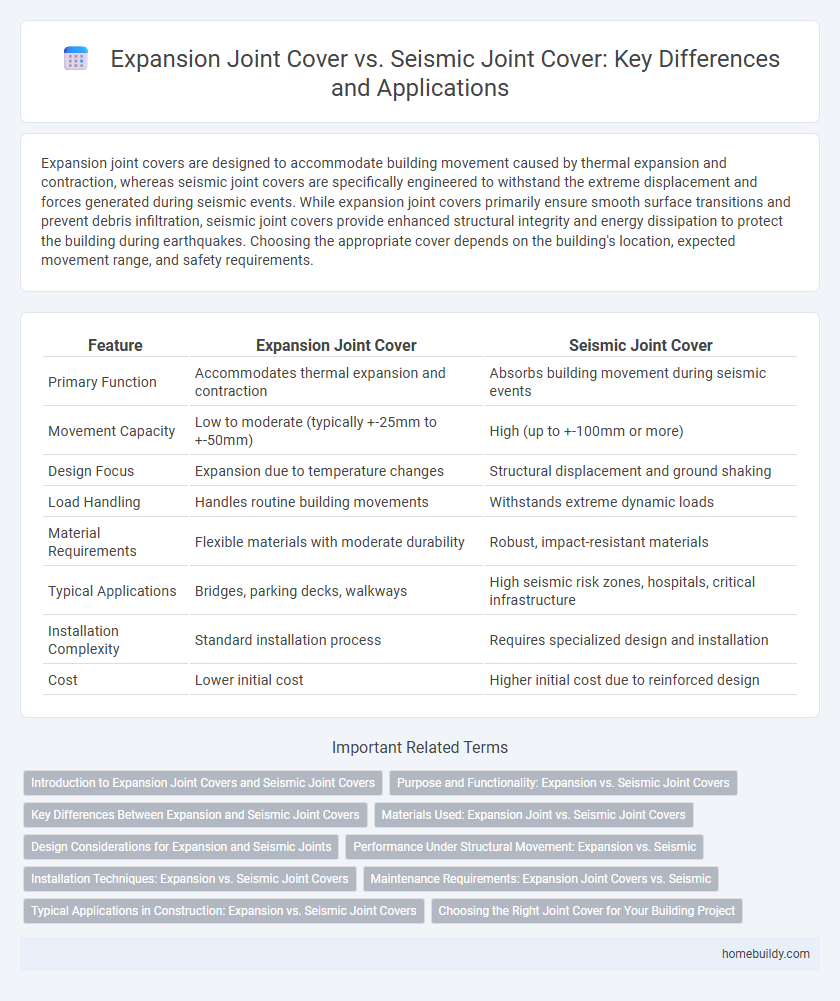
Expansion joint covers are designed to accommodate building movement caused by thermal expansion and contraction, whereas seismic joint covers are specifically engineered to withstand the extreme displacement and forces generated during seismic events. While expansion joint covers primarily ensure smooth surface transitions and prevent debris infiltration, seismic joint covers provide enhanced structural integrity and energy dissipation to protect the building during earthquakes. Choosing the appropriate cover depends on the building's location, expected movement range, and safety requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Expansion Joint Cover | Seismic Joint Cover |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Accommodates thermal expansion and contraction | Absorbs building movement during seismic events |
| Movement Capacity | Low to moderate (typically +-25mm to +-50mm) | High (up to +-100mm or more) |
| Design Focus | Expansion due to temperature changes | Structural displacement and ground shaking |
| Load Handling | Handles routine building movements | Withstands extreme dynamic loads |
| Material Requirements | Flexible materials with moderate durability | Robust, impact-resistant materials |
| Typical Applications | Bridges, parking decks, walkways | High seismic risk zones, hospitals, critical infrastructure |
| Installation Complexity | Standard installation process | Requires specialized design and installation |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost due to reinforced design |
Introduction to Expansion Joint Covers and Seismic Joint Covers
Expansion joint covers accommodate building movement by bridging gaps created by thermal expansion, contraction, or structural shifts, ensuring continuity and protection of surfaces. Seismic joint covers are specifically designed to absorb and withstand intense, rapid movements during earthquakes, providing enhanced safety and structural integrity in seismic zones. Both covers play crucial roles in preventing damage but differ primarily in their response capabilities to dynamic versus static structural movements.
Purpose and Functionality: Expansion vs. Seismic Joint Covers
Expansion joint covers are designed primarily to accommodate thermal movement and structural shifts caused by temperature variations, preventing damage and maintaining building integrity. Seismic joint covers focus on enabling building components to withstand lateral displacements and vibrations during earthquakes, ensuring safety and minimizing structural failure. While expansion joint covers manage gradual, predictable movements, seismic joint covers must absorb sudden, dynamic forces.
Key Differences Between Expansion and Seismic Joint Covers
Expansion joint covers accommodate thermal movement and structural expansion in buildings, allowing for controlled flexibility to prevent damage from temperature-induced material changes. Seismic joint covers are specifically designed to withstand dynamic forces and large displacements caused by earthquakes, providing enhanced durability and energy absorption to maintain structural integrity during seismic events. The key differences lie in their functional focus: expansion joint covers handle gradual, predictable movements while seismic joint covers are engineered for sudden, intense seismic activity.
Materials Used: Expansion Joint vs. Seismic Joint Covers
Expansion joint covers are typically made from flexible materials like neoprene, rubber, or metal alloys that accommodate thermal expansion and contraction in building structures. Seismic joint covers, however, utilize more robust and ductile materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, and reinforced elastomers designed to withstand intense lateral and vertical movements during earthquakes. The material choice for seismic joint covers prioritizes durability and energy absorption, while expansion joint covers focus on elasticity and weather resistance.
Design Considerations for Expansion and Seismic Joints
Expansion joint covers are engineered to accommodate thermal expansion and contraction in structures, focusing on materials and designs that absorb movement without compromising structural integrity. Seismic joint covers must withstand abrupt, multidirectional forces during earthquakes, requiring enhanced flexibility, impact resistance, and secure anchoring systems. Design considerations for both include ensuring durability, water resistance, and alignment with building codes, but seismic joint covers demand more rigorous testing for performance under dynamic seismic loads.
Performance Under Structural Movement: Expansion vs. Seismic
Expansion joint covers accommodate building movements from thermal expansion and contraction, ensuring structural integrity by absorbing dimensional changes without damage. Seismic joint covers provide superior flexibility and strength, designed to withstand intense lateral and vertical displacements during earthquakes, preventing structural failure. Performance under structural movement prioritizes thermal adaptability in expansion covers, while seismic covers emphasize dynamic resilience and energy dissipation during seismic events.
Installation Techniques: Expansion vs. Seismic Joint Covers
Installation techniques for expansion joint covers prioritize accommodating thermal movement and building settling through flexible materials and sliding mechanisms, often using modular sections for easy replacement. Seismic joint covers require robust anchoring and energy-absorbing components to withstand and dissipate seismic forces, incorporating wider movement capabilities and reinforced substrates for structural integrity. Both systems demand precise alignment and integration with adjacent surfaces to ensure functional durability under their respective stress conditions.
Maintenance Requirements: Expansion Joint Covers vs. Seismic
Expansion joint covers typically require routine inspection and lubrication to accommodate thermal movement, preventing wear and debris buildup, whereas seismic joint covers demand more frequent maintenance due to their critical role in absorbing dynamic seismic forces. Seismic joint covers often involve specialized components like energy dissipaters, which necessitate detailed examinations after seismic events to ensure structural integrity. Maintenance protocols for seismic covers are more stringent, prioritizing safety and compliance with seismic standards compared to the generally lower upkeep intensity of expansion joint covers.
Typical Applications in Construction: Expansion vs. Seismic Joint Covers
Expansion joint covers are typically used in buildings, bridges, and parking structures to accommodate thermal movement and prevent structural damage, ensuring durability and safety during regular temperature fluctuations. Seismic joint covers, by contrast, are specifically designed for high seismic zones to absorb and dissipate energy from earthquakes, protecting structures from sudden, violent movements. While expansion joint covers focus on gradual movement due to thermal expansion and contraction, seismic joint covers prioritize flexibility and resilience during rapid seismic activity.
Choosing the Right Joint Cover for Your Building Project
Expansion joint covers accommodate structural movement caused by thermal expansion and contraction, while seismic joint covers are specifically designed to withstand dynamic forces during earthquakes. Selecting the right joint cover depends on evaluating building location, expected structural movement, and seismic risk factors to ensure durability and safety. Prioritizing performance criteria such as flexibility, load capacity, and fire resistance enables optimal joint cover selection for long-term structural integrity.
Expansion joint cover vs Seismic joint cover Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com