Expansion joint covers are designed to accommodate building movements caused by thermal expansion, seismic activity, or structural shifts, ensuring the integrity of the building envelope. Floor joint covers specifically address joints in flooring systems, providing a smooth transition between floor sections while allowing for movement and load distribution. Compared to floor joint covers, expansion joint covers offer broader flexibility and resilience, catering to larger structural gaps and dynamic stresses in various construction environments.
Table of Comparison
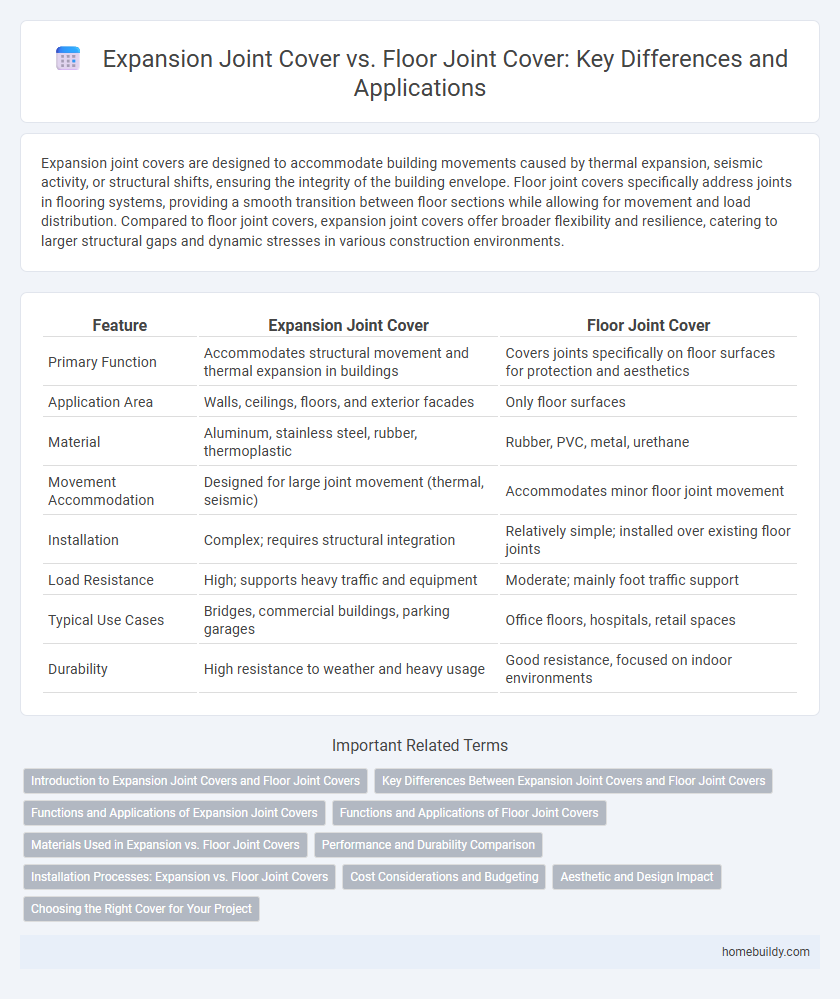
| Feature | Expansion Joint Cover | Floor Joint Cover |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Accommodates structural movement and thermal expansion in buildings | Covers joints specifically on floor surfaces for protection and aesthetics |
| Application Area | Walls, ceilings, floors, and exterior facades | Only floor surfaces |
| Material | Aluminum, stainless steel, rubber, thermoplastic | Rubber, PVC, metal, urethane |
| Movement Accommodation | Designed for large joint movement (thermal, seismic) | Accommodates minor floor joint movement |
| Installation | Complex; requires structural integration | Relatively simple; installed over existing floor joints |
| Load Resistance | High; supports heavy traffic and equipment | Moderate; mainly foot traffic support |
| Typical Use Cases | Bridges, commercial buildings, parking garages | Office floors, hospitals, retail spaces |
| Durability | High resistance to weather and heavy usage | Good resistance, focused on indoor environments |
Introduction to Expansion Joint Covers and Floor Joint Covers
Expansion joint covers are specifically designed to accommodate building movement caused by thermal expansion, seismic activity, and structural shifts, ensuring seamless protection across joints while maintaining structural integrity. Floor joint covers, a subset of expansion joint covers, focus on covering gaps in flooring systems, providing a smooth, safe walking surface that prevents tripping hazards and protects the joint from debris and wear. Both types are essential in construction but differ in application, with expansion joint covers addressing overall structural flexibility and floor joint covers emphasizing pedestrian safety and floor surface continuity.
Key Differences Between Expansion Joint Covers and Floor Joint Covers
Expansion joint covers accommodate building movement by bridging gaps in structural elements, providing flexibility and preventing damage from thermal expansion, seismic activity, or settling. Floor joint covers, designed specifically for floor surfaces, protect and conceal joints while supporting foot and vehicle traffic, focusing on aesthetic integration and durability under load. The key differences lie in their structural application and movement accommodation, with expansion joint covers handling larger, multi-directional movements compared to the more static, load-bearing role of floor joint covers.
Functions and Applications of Expansion Joint Covers
Expansion joint covers are designed to accommodate building movement caused by thermal expansion, contraction, seismic activity, or structural shifts, ensuring structural integrity and preventing damage. Unlike floor joint covers, which primarily protect and conceal floor joint gaps, expansion joint covers provide flexibility and water resistance across walls, ceilings, and floors in commercial, industrial, and infrastructure projects. Their applications include airports, hospitals, parking garages, and bridges, where continuous protection and movement absorption are critical for safety and longevity.
Functions and Applications of Floor Joint Covers
Floor joint covers serve to protect and conceal gaps in flooring that accommodate structural movement, providing a safe, smooth surface for pedestrian and vehicular traffic. Unlike expansion joint covers, which primarily compensate for thermal expansion and contraction, floor joint covers focus on absorbing vibration, minimizing wear, and maintaining aesthetic continuity in high-traffic environments such as commercial buildings and industrial facilities. These covers are designed to handle heavy loads and prevent debris accumulation, ensuring durability and ease of maintenance.
Materials Used in Expansion vs. Floor Joint Covers
Expansion joint covers typically utilize flexible materials such as neoprene, silicone, and aluminum to accommodate building movement and thermal expansion, whereas floor joint covers often incorporate more rigid materials like steel or brass to withstand heavy foot traffic and mechanical loads. The choice of materials in expansion joint covers prioritizes elasticity and durability to maintain a watertight seal and absorb vibrations. In contrast, floor joint covers focus on abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity while still allowing for structural movement.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Expansion joint covers are engineered to accommodate building movement and thermal expansion, offering superior flexibility and resistance to mechanical stress compared to floor joint covers, which primarily address surface-level joint protection. Performance metrics indicate that expansion joint covers maintain structural integrity under dynamic loads and environmental fluctuations, whereas floor joint covers tend to exhibit accelerated wear due to limited flexibility. Durability studies confirm that high-quality expansion joint covers provide extended service life in demanding architectural and infrastructure applications.
Installation Processes: Expansion vs. Floor Joint Covers
Expansion joint covers require precise alignment with structural movement allowances, involving anchoring systems that accommodate thermal expansion and contraction within building components. Floor joint covers focus on durability and slip resistance, necessitating embedded installation methods flush with the floor surface to maintain even walking paths and prevent tripping hazards. The installation of expansion joint covers often involves integration with walls or ceilings, while floor joint covers demand specialized sealing and fastening techniques to withstand foot traffic and heavy loads.
Cost Considerations and Budgeting
Expansion joint covers generally incur higher initial costs than floor joint covers due to their complex design and materials needed to handle building movement. Budgeting must account for long-term durability and maintenance expenses, as expansion joint covers reduce structural damage and potential repair costs over time. Selecting the appropriate cover depends on balancing upfront investment with lifecycle cost efficiency in construction projects.
Aesthetic and Design Impact
Expansion joint covers offer seamless integration with architectural elements, enhancing aesthetic appeal by concealing structural gaps more effectively than typical floor joint covers. Designed with various materials and finishes, expansion joint covers provide customizable options that align with modern interior design trends, maintaining visual continuity across surfaces. Their low-profile design minimizes disruption to the floor plane, contributing to a cleaner and more polished overall appearance.
Choosing the Right Cover for Your Project
Selecting the appropriate expansion joint cover versus a floor joint cover depends on the specific structural movement and load requirements of your project. Expansion joint covers are designed to accommodate thermal expansion and contraction in large structural elements, while floor joint covers focus on bridging gaps in walking surfaces and supporting pedestrian or vehicular traffic. Evaluating factors such as joint width, expected movement, load capacity, and environmental exposure ensures optimal performance and longevity.
expansion joint cover vs floor joint cover Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com