Expansion joint covers accommodate building movement by spanning gaps between structural elements, prioritizing flexibility and durability without consistently supporting heavy loads. Load-bearing joint covers, designed to withstand significant weight and pressure, provide structural support while accommodating movement in areas subject to vehicular or heavy pedestrian traffic. Selecting the appropriate joint cover depends on balancing movement accommodation with the required load capacity for the specific application.
Table of Comparison
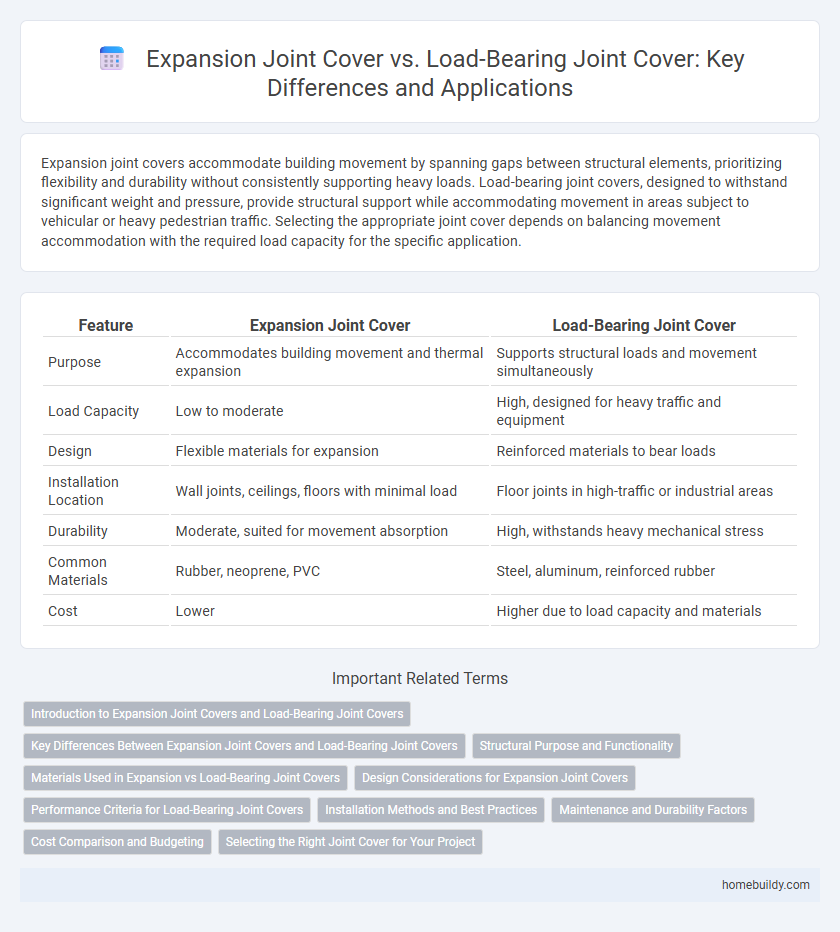
| Feature | Expansion Joint Cover | Load-Bearing Joint Cover |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Accommodates building movement and thermal expansion | Supports structural loads and movement simultaneously |
| Load Capacity | Low to moderate | High, designed for heavy traffic and equipment |
| Design | Flexible materials for expansion | Reinforced materials to bear loads |
| Installation Location | Wall joints, ceilings, floors with minimal load | Floor joints in high-traffic or industrial areas |
| Durability | Moderate, suited for movement absorption | High, withstands heavy mechanical stress |
| Common Materials | Rubber, neoprene, PVC | Steel, aluminum, reinforced rubber |
| Cost | Lower | Higher due to load capacity and materials |
Introduction to Expansion Joint Covers and Load-Bearing Joint Covers
Expansion joint covers accommodate building movements caused by thermal expansion, seismic activity, and structural shifts, preventing damage to surfaces and maintaining aesthetic continuity. Load-bearing joint covers are engineered to withstand heavy traffic loads, supporting weight from vehicles and machinery while protecting joints from wear and structural stress. Selecting the appropriate expansion joint cover depends on the specific load requirements and environmental conditions of the building project.
Key Differences Between Expansion Joint Covers and Load-Bearing Joint Covers
Expansion joint covers accommodate building movement and thermal expansion, providing flexibility while protecting underlying structures from debris and moisture. Load-bearing joint covers not only allow for movement but also support heavy loads such as vehicular traffic, ensuring structural integrity under pressure. The key difference lies in load capacity, with expansion joint covers being non-structural and load-bearing joint covers engineered to sustain significant weight and impact.
Structural Purpose and Functionality
Expansion joint covers accommodate building movement and thermal expansion, preventing structural damage by absorbing stress and allowing flexibility between concrete slabs or structural elements. Load-bearing joint covers are specifically designed to support heavy loads and vehicular traffic while maintaining structural integrity, ensuring durability under compressive forces. The primary difference lies in expansion joint covers focusing on flexibility and movement accommodation, whereas load-bearing joint covers prioritize load distribution and strength.
Materials Used in Expansion vs Load-Bearing Joint Covers
Expansion joint covers are typically made from flexible materials such as rubber, neoprene, or silicone to accommodate building movement and thermal expansion. Load-bearing joint covers incorporate more robust materials like steel, aluminum, or reinforced composites designed to support heavy traffic loads and structural stress. The choice of materials directly influences the joint cover's durability, flexibility, and load capacity, aligning with the specific functional requirements of expansion versus load-bearing applications.
Design Considerations for Expansion Joint Covers
Design considerations for expansion joint covers prioritize flexibility and movement accommodation to withstand building shifts caused by thermal expansion, seismic activity, and structural settling. Materials such as aluminum or stainless steel are selected for their durability and corrosion resistance, while the cover's profile must allow for variable joint widths and multi-directional movement without compromising the building envelope. Load-bearing joint covers differ by requiring enhanced strength and load distribution features to support pedestrian or vehicular traffic, influencing profile thickness and reinforcement design.
Performance Criteria for Load-Bearing Joint Covers
Load-bearing joint covers must meet stringent performance criteria including high compressive strength, durability under repeated dynamic loads, and resistance to environmental factors such as corrosion and temperature fluctuations. These covers are designed to accommodate structural movements while supporting heavy pedestrian or vehicular traffic without compromising the integrity of the joint or adjoining surfaces. Performance metrics often include load capacity ratings in accordance with standards like AASHTO or ASTM and rigorous testing for long-term deformation and wear resistance.
Installation Methods and Best Practices
Expansion joint covers typically utilize flexible installation methods such as adhesive bonding or mechanical anchoring to accommodate building movement and thermal expansion, while load-bearing joint covers require robust installation techniques including embedding in concrete or bolting to structural supports to ensure they can withstand heavy loads. Best practices for expansion joint cover installation emphasize precise joint size measurement, surface preparation, and allowing for movement tolerance, whereas load-bearing joint cover installation prioritizes load capacity verification, alignment with structural elements, and compliance with building codes. Proper sealing and regular maintenance are critical for both types to ensure durability, prevent debris intrusion, and maintain structural integrity.
Maintenance and Durability Factors
Expansion joint covers typically require more frequent maintenance due to their flexible materials designed to accommodate building movement, which may wear or tear over time. Load-bearing joint covers are constructed with robust materials like steel or aluminum, enhancing durability and reducing maintenance needs in high-traffic areas. The choice between these covers depends on balancing flexibility requirements with expected load conditions and maintenance capabilities.
Cost Comparison and Budgeting
Expansion joint covers typically incur lower initial costs compared to load-bearing joint covers due to simpler design and materials, making them a cost-effective solution for non-structural applications. Load-bearing joint covers demand higher investment because of reinforced materials and engineering complexity to withstand heavy loads, impacting the overall project budget significantly. Accurate budgeting requires evaluating long-term maintenance and durability, as load-bearing options may reduce repair expenses despite higher upfront costs.
Selecting the Right Joint Cover for Your Project
Selecting the right joint cover requires understanding the differences between expansion joint covers and load-bearing joint covers. Expansion joint covers accommodate building movement caused by thermal expansion, seismic activity, and structural shifts, ensuring flexibility and protection without damage. Load-bearing joint covers, designed to support heavy traffic and structural loads, provide durability and safety in high-traffic areas such as parking garages and industrial facilities.
expansion joint cover vs load-bearing joint cover Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com