Cable tray material directly impacts its strength, durability, and suitability for specific environments, with common options including steel, aluminum, and fiberglass. The cable tray finish, such as galvanization or powder coating, provides an extra layer of protection against corrosion and wear, extending the lifespan of the tray. Selecting the right combination of material and finish ensures optimal performance and longevity in cable management systems.
Table of Comparison
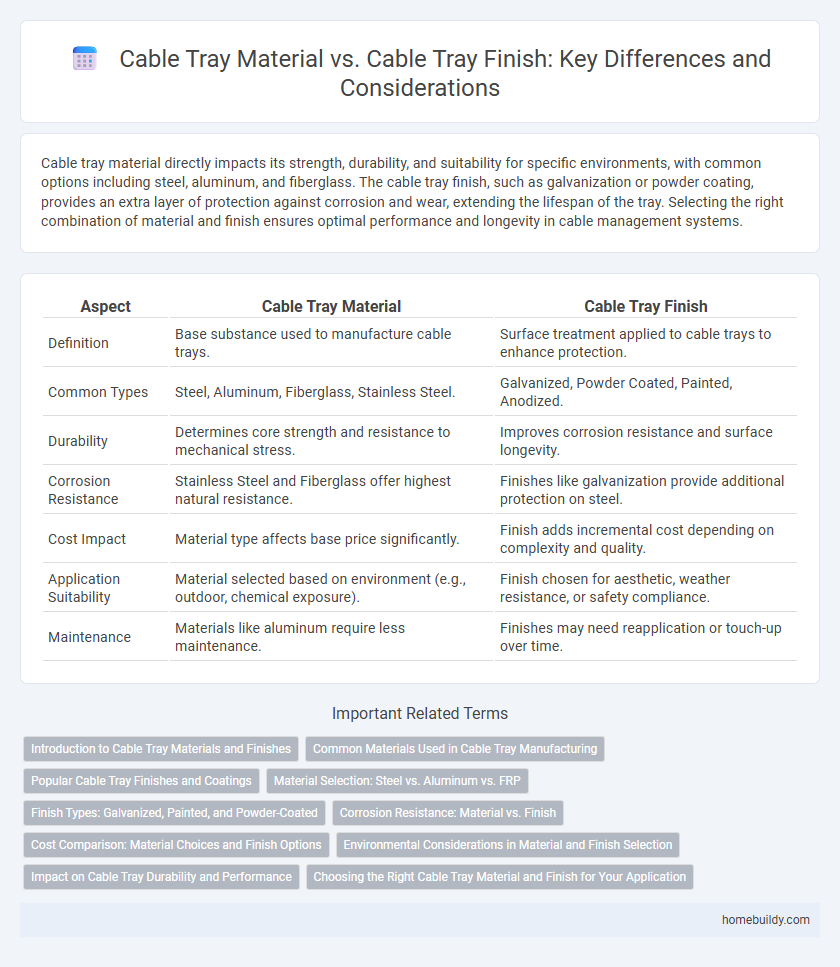
| Aspect | Cable Tray Material | Cable Tray Finish |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Base substance used to manufacture cable trays. | Surface treatment applied to cable trays to enhance protection. |
| Common Types | Steel, Aluminum, Fiberglass, Stainless Steel. | Galvanized, Powder Coated, Painted, Anodized. |
| Durability | Determines core strength and resistance to mechanical stress. | Improves corrosion resistance and surface longevity. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Stainless Steel and Fiberglass offer highest natural resistance. | Finishes like galvanization provide additional protection on steel. |
| Cost Impact | Material type affects base price significantly. | Finish adds incremental cost depending on complexity and quality. |
| Application Suitability | Material selected based on environment (e.g., outdoor, chemical exposure). | Finish chosen for aesthetic, weather resistance, or safety compliance. |
| Maintenance | Materials like aluminum require less maintenance. | Finishes may need reapplication or touch-up over time. |
Introduction to Cable Tray Materials and Finishes
Cable tray materials primarily include steel, aluminum, and fiberglass, each offering distinct strength, corrosion resistance, and weight advantages. Finishes such as galvanized, powder-coated, or stainless steel provide enhanced durability and protection against environmental factors. Selecting the appropriate material and finish combination ensures optimal performance and longevity in specific installation conditions.
Common Materials Used in Cable Tray Manufacturing
Common materials used in cable tray manufacturing include steel, aluminum, fiberglass, and stainless steel, each selected for specific environmental and load-bearing requirements. Steel cable trays often feature finishes like galvanized, powder-coated, or painted surfaces to enhance corrosion resistance and durability. Aluminum offers a lightweight alternative with natural corrosion resistance, typically requiring minimal finishing, while fiberglass trays provide excellent insulation and chemical resistance without the need for additional surface treatments.
Popular Cable Tray Finishes and Coatings
Popular cable tray finishes and coatings enhance durability and corrosion resistance, with galvanized steel providing a zinc layer that protects against rust and UV exposure. Powder coating is a preferred finish for aesthetic appeal and additional protection, offering a smooth, scratch-resistant surface that extends tray lifespan in harsh environments. Stainless steel cable trays, often finished with a brushed or polished look, combine inherent corrosion resistance with low maintenance, making them ideal for chemical or coastal installations.
Material Selection: Steel vs. Aluminum vs. FRP
Steel cable trays offer superior strength and durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications and environments requiring high mechanical protection. Aluminum trays provide excellent corrosion resistance and lightweight characteristics, suitable for outdoor installations or corrosive environments without adding excessive weight. FRP (Fiber Reinforced Plastic) trays combine corrosion resistance with non-conductivity, offering a lightweight, non-metallic solution ideal for chemical plants and explosive atmospheres.
Finish Types: Galvanized, Painted, and Powder-Coated
Cable tray finish types such as galvanized, painted, and powder-coated significantly influence durability and corrosion resistance in various environments. Galvanized finishes offer superior protection against rust by applying a zinc coating, ideal for outdoor or industrial settings. Painted finishes provide a cost-effective aesthetic option with moderate protection, while powder-coated trays ensure a durable, impact-resistant surface suitable for harsh conditions and extended lifespan.
Corrosion Resistance: Material vs. Finish
Cable tray corrosion resistance depends heavily on the base material and the applied finish, with materials like stainless steel offering inherent corrosion immunity while galvanized steel relies on protective coatings. Steel cable trays commonly use hot-dip galvanizing or powder coating to enhance corrosion resistance, but these finishes may degrade over time compared to corrosion-resistant alloys. Selecting the appropriate cable tray involves balancing the durability of the material against the protective qualities of finishes to ensure long-term performance in corrosive environments.
Cost Comparison: Material Choices and Finish Options
Cable tray material choices such as steel, aluminum, and fiberglass significantly affect initial costs, with steel generally offering the lowest price but requiring corrosion-resistant finishes like galvanized or powder coating to ensure durability in harsh environments. Aluminum trays provide a balance of lightweight design and moderate cost but often include anodized finishes to prevent oxidation, increasing overall expense compared to unfinished steel. Fiberglass cable trays feature high corrosion resistance inherently, reducing the need for additional finishes and resulting in higher upfront costs but lower maintenance expenses over time.
Environmental Considerations in Material and Finish Selection
Steel and aluminum are common cable tray materials chosen for their durability and corrosion resistance, but environmental factors like humidity and exposure to chemicals influence the optimal finish. Hot-dip galvanizing offers robust protection against rust in outdoor or industrial settings, while powder coating provides a UV-resistant and aesthetically pleasing layer for exposed installations. Selecting a material and finish combination tailored to specific environmental conditions ensures longevity and reduces maintenance costs in cable tray systems.
Impact on Cable Tray Durability and Performance
Cable tray material significantly determines its durability and corrosion resistance, with common options including stainless steel, aluminum, and galvanized steel, each offering varying strengths and environmental resilience. The cable tray finish, such as powder coating or hot-dip galvanizing, enhances protection against moisture, UV exposure, and chemical exposure, directly impacting the tray's lifespan and performance in harsh conditions. Selecting the right combination of material and finish is crucial for maintaining structural integrity and ensuring reliable cable support in industrial and outdoor installations.
Choosing the Right Cable Tray Material and Finish for Your Application
Selecting the appropriate cable tray material such as stainless steel, aluminum, or galvanized steel depends on environmental exposure, mechanical strength, and corrosion resistance requirements. The cable tray finish, including powder coating, hot-dip galvanizing, or anodizing, enhances durability and protects against rust and chemical damage in specific conditions like outdoor, industrial, or marine settings. Matching the cable tray material with the optimal finish ensures longevity, cost-effectiveness, and compliance with industry standards such as NEMA or IEC for your particular application.
Cable tray material vs cable tray finish Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com