An air vent is the visible grille or opening that allows air to flow into or out of a room, while an air duct is the enclosed conduit system that transports air throughout the building. Air ducts are typically made from metal or flexible materials and are hidden within walls or ceilings, distributing heated or cooled air from HVAC units to various spaces. Efficient air circulation depends on properly designed air ducts paired with strategically placed air vents.
Table of Comparison
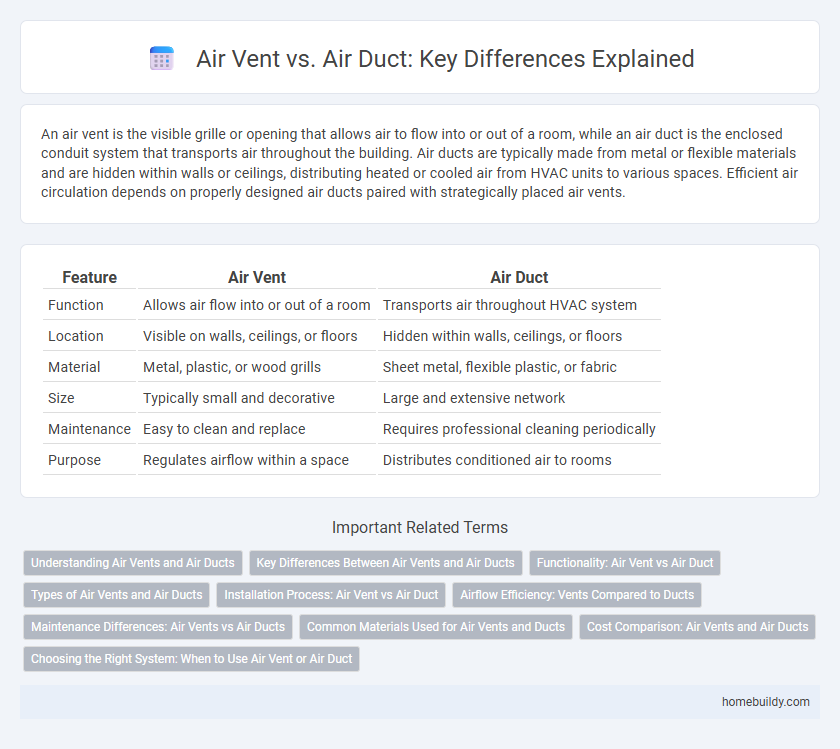
| Feature | Air Vent | Air Duct |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Allows air flow into or out of a room | Transports air throughout HVAC system |
| Location | Visible on walls, ceilings, or floors | Hidden within walls, ceilings, or floors |
| Material | Metal, plastic, or wood grills | Sheet metal, flexible plastic, or fabric |
| Size | Typically small and decorative | Large and extensive network |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean and replace | Requires professional cleaning periodically |
| Purpose | Regulates airflow within a space | Distributes conditioned air to rooms |
Understanding Air Vents and Air Ducts
Air vents are openings that allow air to enter or exit a room, designed for airflow regulation and indoor air quality improvement, while air ducts are enclosed passages that transport heated or cooled air throughout a building. Understanding the distinction between air vents and air ducts is essential for HVAC system efficiency, as vents control air distribution, and ducts serve as the channels for air movement. Proper maintenance of both air vents and air ducts ensures optimal ventilation, prevents energy loss, and contributes to a healthier indoor environment.
Key Differences Between Air Vents and Air Ducts
Air vents serve as the visible outlets or inlets that allow air to flow into or out of a room, while air ducts are the hidden channels that transport air throughout the HVAC system. Unlike air vents, which regulate air distribution at the room level, air ducts are responsible for the overall air circulation across the building. The key differences lie in their function and placement: air ducts facilitate air movement behind walls and ceilings, whereas air vents provide controlled airflow at the surface level.
Functionality: Air Vent vs Air Duct
Air vents regulate airflow by allowing conditioned air to enter or exit rooms, providing control over temperature and air quality. Air ducts serve as the main channels that transport air from heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems throughout a building. Together, vents and ducts work to ensure efficient distribution and circulation of air in indoor environments.
Types of Air Vents and Air Ducts
Air vents typically include types such as supply vents, return vents, and exhaust vents, each designed to regulate airflow in specific areas of a building. Air ducts, on the other hand, come in various forms like flexible ducts, spiral ducts, and rectangular ducts, serving as the primary channels for distributing air throughout HVAC systems. Understanding the differences between vent types and duct designs is essential for optimizing ventilation efficiency and indoor air quality.
Installation Process: Air Vent vs Air Duct
The installation process of an air vent involves securing it to existing ductwork or wall openings, typically requiring minimal tools and time, focusing on precise placement for airflow efficiency. In contrast, air duct installation demands extensive planning, cutting, sealing, and often custom fabrication to integrate into building frameworks, ensuring optimal ventilation performance. Proper sealing and insulation during duct installation are critical to prevent energy loss and maintain system effectiveness.
Airflow Efficiency: Vents Compared to Ducts
Air vents are designed to regulate the flow of air into specific rooms, improving localized airflow efficiency, whereas air ducts serve as the primary channels that transport air throughout the building's HVAC system. Properly sized and strategically placed air vents optimize air distribution and can reduce pressure loss compared to larger, less flexible air ducts. The combination of well-designed air ducts and efficient air vents ensures balanced airflow, enhancing overall HVAC performance and energy efficiency.
Maintenance Differences: Air Vents vs Air Ducts
Air vents require frequent cleaning to remove dust and prevent blockages, ensuring optimal airflow and indoor air quality, while air ducts need professional inspection and cleaning to address accumulated debris and mold deep within the system. Air vents are easier to access for routine maintenance, whereas air duct maintenance often involves specialized tools and equipment due to their hidden placement within walls or ceilings. Proper maintenance of both components is essential to maintain HVAC system efficiency and extend equipment lifespan.
Common Materials Used for Air Vents and Ducts
Air vents are commonly made from materials like aluminum, plastic, and steel, which provide durability and resistance to corrosion. In contrast, air ducts often utilize galvanized steel or flexible aluminum foil for enhanced strength and flexibility in extensive HVAC systems. Both air vents and ducts may incorporate insulation materials such as fiberglass to improve energy efficiency and reduce noise transmission.
Cost Comparison: Air Vents and Air Ducts
Air vents generally cost less than air ducts due to their smaller size and simpler installation requirements, with typical air vent prices ranging from $20 to $100 each compared to air duct materials and installation which can exceed $1,000 for a whole system. Air ducts require extensive labor and materials such as sheet metal or flexible tubing, driving up overall costs in HVAC projects. Choosing between air vents and air ducts depends on budget constraints, with vents offering a more affordable option for directing airflow in localized areas.
Choosing the Right System: When to Use Air Vent or Air Duct
Air vents serve as the endpoints for airflow distribution, controlling the release of heated or cooled air into living spaces, while air ducts function as the conduits that channel air from HVAC units throughout a building. Selecting between an air vent and an air duct depends on system design needs: air ducts are essential for air transportation, whereas air vents are crucial for regulating airflow and ensuring proper ventilation. Effective HVAC performance relies on integrating both components strategically to maintain air quality, temperature control, and energy efficiency.
air vent vs air duct Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com