Window frame insulation involves adding materials such as foam or weatherstripping to reduce heat transfer and improve energy efficiency by maintaining indoor temperatures. Window frame sealing focuses on closing gaps and cracks around the frame using caulking or sealant to prevent drafts, moisture, and air leaks. Both insulation and sealing are essential for maximizing thermal performance and enhancing overall comfort in a building.
Table of Comparison
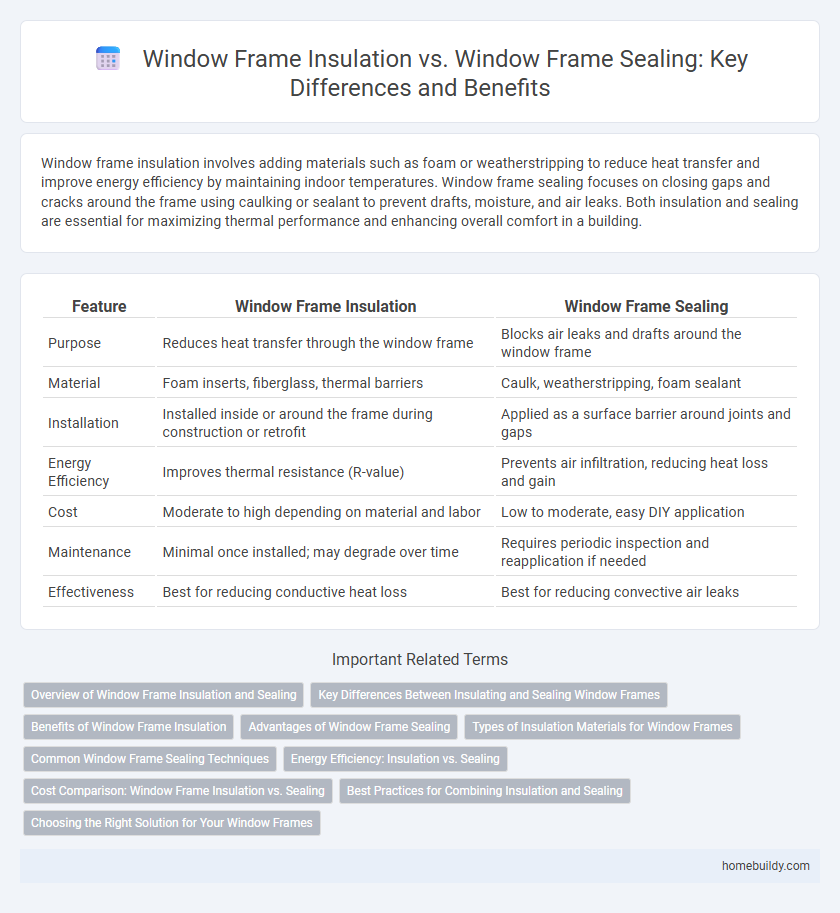
| Feature | Window Frame Insulation | Window Frame Sealing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reduces heat transfer through the window frame | Blocks air leaks and drafts around the window frame |
| Material | Foam inserts, fiberglass, thermal barriers | Caulk, weatherstripping, foam sealant |
| Installation | Installed inside or around the frame during construction or retrofit | Applied as a surface barrier around joints and gaps |
| Energy Efficiency | Improves thermal resistance (R-value) | Prevents air infiltration, reducing heat loss and gain |
| Cost | Moderate to high depending on material and labor | Low to moderate, easy DIY application |
| Maintenance | Minimal once installed; may degrade over time | Requires periodic inspection and reapplication if needed |
| Effectiveness | Best for reducing conductive heat loss | Best for reducing convective air leaks |
Overview of Window Frame Insulation and Sealing
Window frame insulation involves adding materials such as foam, fiberglass, or thermal barriers to reduce heat transfer through the frame, significantly improving energy efficiency. Window frame sealing focuses on eliminating drafts and air leaks by using caulk, weatherstripping, or sealants around the edges and joints of the frame to maintain indoor temperature stability. Both methods play critical roles in enhancing thermal performance, reducing utility costs, and preventing moisture intrusion in residential and commercial buildings.
Key Differences Between Insulating and Sealing Window Frames
Insulating window frames involves adding materials like foam or fiberglass to reduce heat transfer, improving energy efficiency and thermal comfort. Sealing window frames focuses on eliminating air leaks by applying caulking or weatherstripping to prevent drafts and moisture infiltration. While insulation enhances thermal resistance, sealing primarily blocks air exchange, making both essential for optimal window frame performance.
Benefits of Window Frame Insulation
Window frame insulation enhances energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer through the frame, leading to lower heating and cooling costs. It also improves indoor comfort by maintaining consistent temperatures and minimizing drafts. Proper insulation helps prevent condensation and moisture buildup, protecting the frame from rot and extending its lifespan.
Advantages of Window Frame Sealing
Window frame sealing significantly enhances energy efficiency by preventing air leaks and reducing drafts, which lowers heating and cooling costs. It also improves indoor comfort by maintaining consistent indoor temperatures and minimizing moisture infiltration that can cause mold and rot. Compared to insulation, sealing provides a more immediate and effective barrier against air and water infiltration, boosting the durability and lifespan of window frames.
Types of Insulation Materials for Window Frames
Window frame insulation primarily involves materials like foam inserts, fiberglass, and mineral wool, which enhance thermal resistance and reduce heat transfer. Sealing window frames typically uses weatherstripping and caulks to prevent air infiltration and moisture intrusion. Combining effective insulation materials with proper sealing ensures optimal energy efficiency and indoor comfort.
Common Window Frame Sealing Techniques
Common window frame sealing techniques include applying weatherstripping materials such as foam tape, V-strip, and rubber gaskets to block air leaks efficiently. Caulking with silicone or latex-based sealants provides a durable barrier against moisture and drafts around gaps between the frame and the wall. These methods complement insulation efforts by preventing thermal bridging and improving overall energy efficiency in residential or commercial buildings.
Energy Efficiency: Insulation vs. Sealing
Window frame insulation reduces heat transfer through the frame material, enhancing energy efficiency by maintaining indoor temperatures and reducing HVAC load. Window frame sealing prevents air leaks around the frame, minimizing drafts and improving airtightness, which also lowers energy consumption. Combining proper insulation with effective sealing maximizes thermal performance and significantly decreases energy costs.
Cost Comparison: Window Frame Insulation vs. Sealing
Window frame insulation typically incurs higher upfront costs due to materials like foam or fiberglass, averaging $5 to $10 per square foot, but offers long-term energy savings by reducing heat transfer. In contrast, window frame sealing, using caulking or weatherstripping, is more affordable, often costing under $1 per linear foot, and provides a quick fix for air leaks. Choosing between insulation and sealing depends on budget constraints and the desired balance between immediate cost and long-term energy efficiency.
Best Practices for Combining Insulation and Sealing
Effective window frame insulation paired with thorough sealing enhances energy efficiency by minimizing heat transfer and air leakage. Using materials such as spray foam insulation alongside high-quality weatherstripping or caulking ensures both thermal resistance and airtightness around the frame. Regular inspection and maintenance of seals combined with adequate insulation thickness optimize comfort and reduce heating and cooling costs.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Window Frames
Window frame insulation enhances energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer through materials such as foam or fiberglass, while window frame sealing blocks air leaks using caulking or weatherstripping. Selecting the right solution depends on the window frame material, climate conditions, and existing gaps; insulation suits poor thermal barriers, whereas sealing targets drafts and moisture intrusion. Combining both methods often provides optimal performance, minimizing energy loss and improving indoor comfort.
window frame insulation vs window frame sealing Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com