Exhaust vent hoods remove smoke, steam, and odors by venting air outside, providing superior air quality and reducing moisture buildup in the kitchen. Recirculating vent hoods draw air through filters to trap grease and odors before releasing cleaned air back into the room, making them suitable for kitchens without external venting options. Choosing between the two depends on kitchen layout, ventilation availability, and the need for effective removal of airborne contaminants.
Table of Comparison
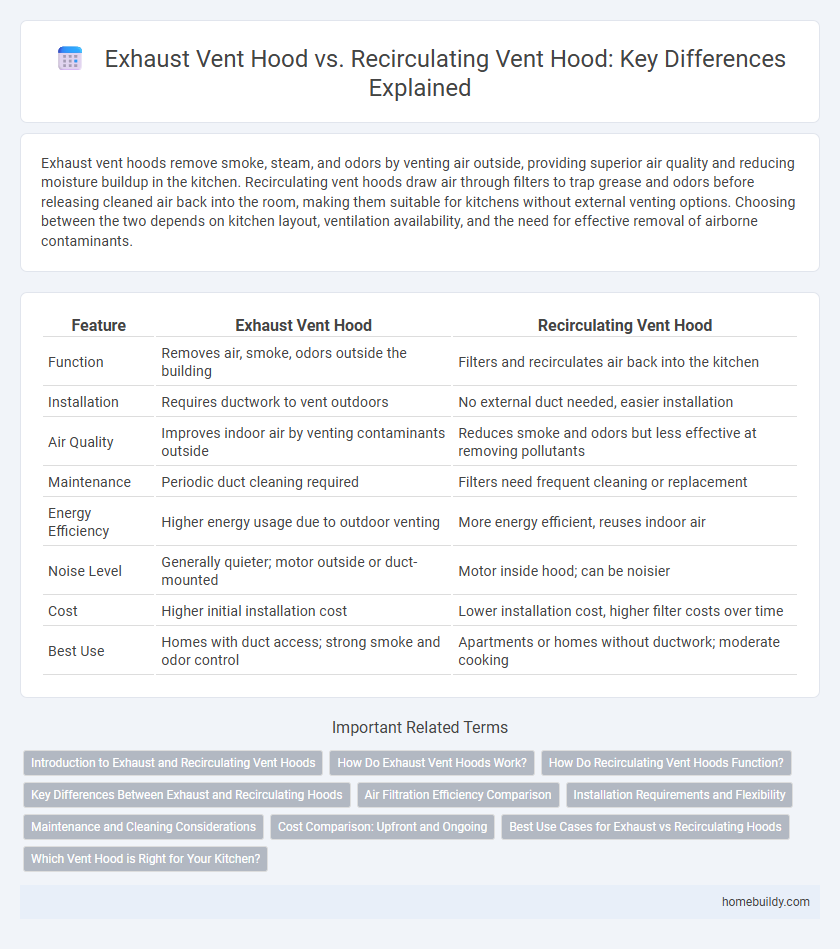
| Feature | Exhaust Vent Hood | Recirculating Vent Hood |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Removes air, smoke, odors outside the building | Filters and recirculates air back into the kitchen |
| Installation | Requires ductwork to vent outdoors | No external duct needed, easier installation |
| Air Quality | Improves indoor air by venting contaminants outside | Reduces smoke and odors but less effective at removing pollutants |
| Maintenance | Periodic duct cleaning required | Filters need frequent cleaning or replacement |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher energy usage due to outdoor venting | More energy efficient, reuses indoor air |
| Noise Level | Generally quieter; motor outside or duct-mounted | Motor inside hood; can be noisier |
| Cost | Higher initial installation cost | Lower installation cost, higher filter costs over time |
| Best Use | Homes with duct access; strong smoke and odor control | Apartments or homes without ductwork; moderate cooking |
Introduction to Exhaust and Recirculating Vent Hoods
Exhaust vent hoods remove cooking fumes and airborne grease by venting them outdoors, improving indoor air quality and preventing moisture buildup. Recirculating vent hoods filter air through charcoal or carbon filters before releasing it back into the kitchen, making them ideal for spaces without ductwork. Choosing between exhaust and recirculating vent hoods depends on kitchen layout, ventilation needs, and installation feasibility.
How Do Exhaust Vent Hoods Work?
Exhaust vent hoods operate by drawing kitchen air through a filtration system and expelling it outside the building via ductwork, effectively removing smoke, odors, heat, and airborne grease. This ventilation process relies on powerful fans that create negative pressure, ensuring contaminants are pulled away from the cooking area to improve indoor air quality. Proper installation and duct routing are essential for maximizing the efficiency and performance of exhaust vent hoods in maintaining a healthier kitchen environment.
How Do Recirculating Vent Hoods Function?
Recirculating vent hoods function by drawing in kitchen air through a grease filter and then passing it through a charcoal filter to remove odors before releasing the cleaned air back into the room. Unlike exhaust vent hoods that vent air outside, recirculating hoods do not require ductwork and are ideal for kitchens without external ventilation options. Their effectiveness depends on regular maintenance and replacement of filters to ensure efficient removal of grease and odors.
Key Differences Between Exhaust and Recirculating Hoods
Exhaust vent hoods remove smoke, heat, and odors by venting air outside, ensuring better air quality and moisture control, while recirculating vent hoods filter air through charcoal or carbon filters and release it back into the kitchen. Exhaust hoods typically require ductwork and professional installation, making them more effective but less flexible compared to the easier-to-install recirculating models. The choice between the two depends on kitchen layout, ventilation needs, and installation feasibility.
Air Filtration Efficiency Comparison
Exhaust vent hoods expel air and contaminants outside, ensuring superior air filtration by removing smoke, odors, and grease effectively from the kitchen environment. Recirculating vent hoods use charcoal filters to trap odors and grease but recycle air back into the room, resulting in lower air filtration efficiency compared to exhaust systems. The efficiency difference is critical for air quality, with exhaust vent hoods providing a more comprehensive removal of airborne pollutants.
Installation Requirements and Flexibility
Exhaust vent hoods require direct ductwork to the exterior, demanding precise installation to ensure proper airflow and avoid indoor air contamination. Recirculating vent hoods offer greater flexibility by filtering and returning air back into the kitchen, eliminating the need for exterior venting and simplifying installation in spaces without external walls. Choosing between these hoods depends largely on kitchen layout constraints and the ability to accommodate ductwork.
Maintenance and Cleaning Considerations
Exhaust vent hoods require regular cleaning of the ductwork and filters to prevent grease buildup and ensure efficient airflow, often demanding professional maintenance for duct inspections and cleaning. Recirculating vent hoods primarily need frequent filter replacement or washing, typically using charcoal or carbon filters that trap odors but do not require duct cleaning since air is recirculated back into the kitchen. Proper maintenance of either type includes timely filter care to maintain performance and indoor air quality while minimizing fire hazards.
Cost Comparison: Upfront and Ongoing
Exhaust vent hoods typically have higher upfront costs due to installation of ductwork and external venting, often ranging from $300 to $1,000 or more, depending on kitchen layout. Recirculating vent hoods generally cost less initially, between $150 and $500, as they do not require external ducting, making installation simpler and cheaper. However, ongoing costs for exhaust hoods are lower because they do not require frequent filter replacements, unlike recirculating models that need regular carbon filter changes, increasing maintenance expenses over time.
Best Use Cases for Exhaust vs Recirculating Hoods
Exhaust vent hoods are ideal for kitchens with external wall access, effectively removing smoke, odors, and moisture by venting air outside, making them best for heavy cooking and frequent high-heat use. Recirculating vent hoods suit apartments or spaces without ductwork, using filters to clean and recycle air, which is optimal for low to moderate cooking in confined areas. Choosing between these depends on kitchen layout, ventilation availability, and cooking intensity to ensure optimal air quality and energy efficiency.
Which Vent Hood is Right for Your Kitchen?
Exhaust vent hoods effectively remove smoke, heat, and odors by venting air outside, making them ideal for kitchens with existing ductwork and heavy cooking. Recirculating vent hoods filter and recirculate air through charcoal filters, suitable for kitchens without external venting options. Choosing the right vent hood depends on your kitchen layout, cooking habits, and installation feasibility.
Exhaust vent hood vs Recirculating vent hood Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com