Threshold and baseboard serve different functions in home design, with thresholds positioned on floors at doorways to provide a smooth transition between rooms, while baseboards run along the bottom of walls to protect against damage and cover gaps. Thresholds often help in sealing gaps under doors to prevent drafts and moisture, whereas baseboards enhance wall aesthetics and offer protection from scuffs and furniture. Choosing the appropriate material and style for both elements ensures durability and complements the overall interior design.
Table of Comparison
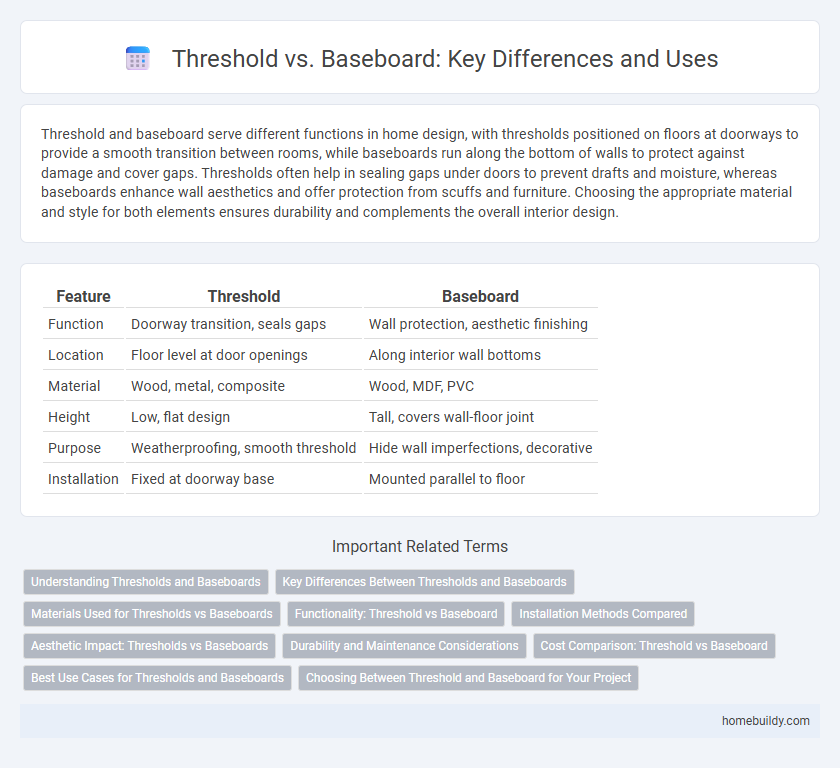
| Feature | Threshold | Baseboard |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Doorway transition, seals gaps | Wall protection, aesthetic finishing |
| Location | Floor level at door openings | Along interior wall bottoms |
| Material | Wood, metal, composite | Wood, MDF, PVC |
| Height | Low, flat design | Tall, covers wall-floor joint |
| Purpose | Weatherproofing, smooth threshold | Hide wall imperfections, decorative |
| Installation | Fixed at doorway base | Mounted parallel to floor |
Understanding Thresholds and Baseboards
Thresholds serve as transitional elements between different flooring materials or rooms, providing a smooth and safe passage while helping to seal gaps against drafts, dust, and moisture. Baseboards are installed along the bottom perimeter of walls to cover expansion gaps between flooring and walls, protect walls from impacts, and add a finished aesthetic to rooms. Understanding the distinct functions and installation requirements of thresholds and baseboards ensures proper flooring transitions and wall protection in interior spaces.
Key Differences Between Thresholds and Baseboards
Thresholds serve as horizontal transition strips placed at doorways to bridge flooring surfaces, while baseboards run vertically along walls to cover the joint between wall and floor. Thresholds are designed to provide a smooth passage and protect floor edges from wear, whereas baseboards primarily protect walls from damage and offer a finished aesthetic. Material composition differs, with thresholds often made from hardwood, metal, or vinyl for durability, compared to baseboards commonly crafted from wood, MDF, or PVC for decorative and protective purposes.
Materials Used for Thresholds vs Baseboards
Thresholds are commonly made from durable materials like hardwood, aluminum, and vinyl to withstand heavy foot traffic and environmental exposure, whereas baseboards typically use MDF, pine, or oak wood designed for interior aesthetic appeal. The resilience of threshold materials is crucial for preventing wear and moisture damage at doorway transitions, contrasting with the decorative and protective role of baseboard materials along interior walls. Choosing appropriate materials ensures functionality for thresholds and visual consistency and protection for baseboards in building interiors.
Functionality: Threshold vs Baseboard
Thresholds provide a transition between different flooring surfaces, enhancing safety by reducing tripping hazards and accommodating door clearance, whereas baseboards primarily protect walls from damage and cover gaps between the wall and floor. Thresholds often incorporate weatherstripping features for insulation and moisture control, while baseboards focus on aesthetic finishing and wall protection. Both serve complementary roles in interior design but address distinct functional needs within a space.
Installation Methods Compared
Threshold installation involves securing the strip between two flooring types, often using adhesive or screws, providing a smooth transition and preventing tripping hazards. Baseboard installation requires nailing or gluing the board directly onto the wall at floor level to cover gaps and protect walls from damage. Thresholds demand precise measurements for height alignment, while baseboards focus on seamless wall-floor junctions with caulk or paint finishing.
Aesthetic Impact: Thresholds vs Baseboards
Thresholds create a defined transition between rooms, offering a subtle yet functional aesthetic that complements flooring changes. Baseboards enhance wall-floor junctions by providing a polished, finished look that can be tailored with various styles and heights to suit interior design themes. Both elements contribute to overall room aesthetics, but thresholds emphasize spatial division while baseboards focus on wall protection and decorative appeal.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Thresholds generally offer superior durability compared to baseboards, as they are designed to withstand foot traffic and resist wear from door movement. Maintenance for thresholds involves periodic cleaning and occasional sealing to protect from moisture and damage, making them relatively low upkeep. Baseboards, while easier to clean, are more susceptible to dents and scratches, requiring frequent touch-ups or repainting to maintain appearance.
Cost Comparison: Threshold vs Baseboard
Thresholds typically cost between $10 and $50 per piece, depending on material and design, while baseboards range from $1 to $5 per linear foot, with higher-end options reaching $10 or more. Installation costs for thresholds usually remain lower due to simpler fitting requirements, whereas baseboards require more labor-intensive cutting and painting, increasing overall expenses. Choosing between threshold and baseboard costs depends on the project's size, complexity, and the materials selected.
Best Use Cases for Thresholds and Baseboards
Thresholds are ideal for separating different floor surfaces and preventing drafts or water intrusion at doorways, enhancing energy efficiency and accessibility. Baseboards provide protection for walls from impact and wear while offering a decorative finish, best suited for interior spaces to conceal gaps between floors and walls. Optimal use of thresholds is in entryways and transitions, whereas baseboards are most effective along perimeter walls inside rooms.
Choosing Between Threshold and Baseboard for Your Project
Selecting between threshold and baseboard depends on their specific functions and placement in your project. Thresholds serve as protective transition strips at doorways, preventing wear and accommodating floor height changes, while baseboards provide aesthetic finishing along wall-floor junctions and protect walls from damage. Prioritize thresholds for durability in high-traffic areas and baseboards for enhancing room appearance and wall protection.
Threshold vs Baseboard Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com