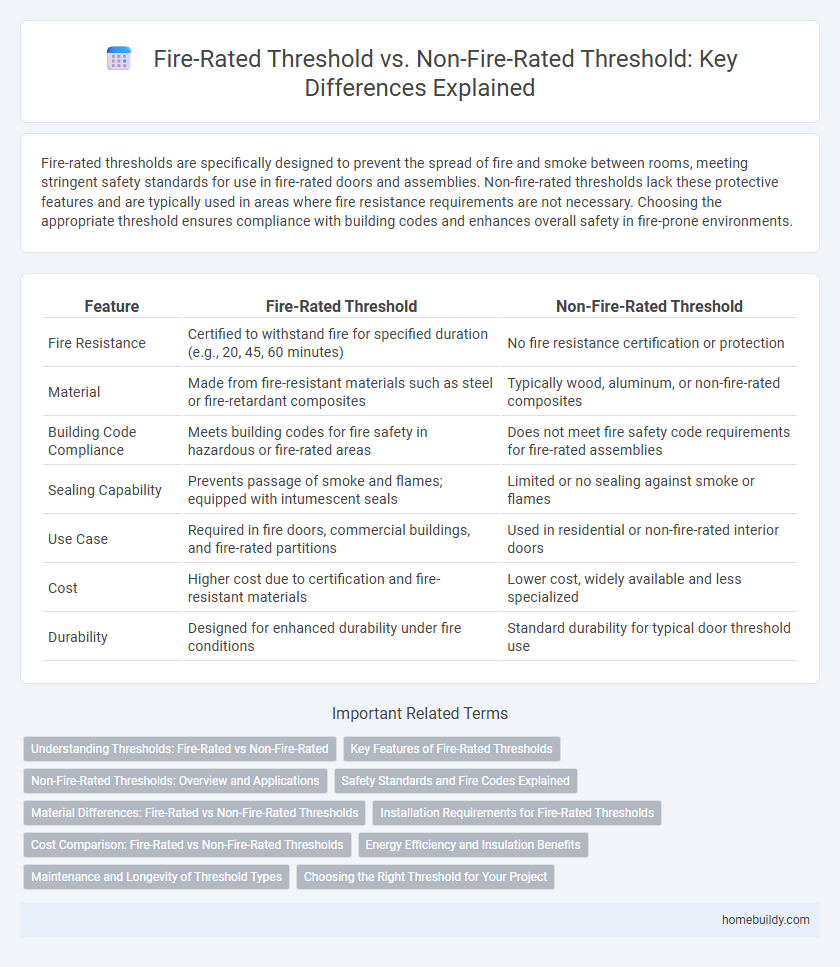
Fire-rated thresholds are specifically designed to prevent the spread of fire and smoke between rooms, meeting stringent safety standards for use in fire-rated doors and assemblies. Non-fire-rated thresholds lack these protective features and are typically used in areas where fire resistance requirements are not necessary. Choosing the appropriate threshold ensures compliance with building codes and enhances overall safety in fire-prone environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fire-Rated Threshold | Non-Fire-Rated Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Certified to withstand fire for specified duration (e.g., 20, 45, 60 minutes) | No fire resistance certification or protection |
| Material | Made from fire-resistant materials such as steel or fire-retardant composites | Typically wood, aluminum, or non-fire-rated composites |
| Building Code Compliance | Meets building codes for fire safety in hazardous or fire-rated areas | Does not meet fire safety code requirements for fire-rated assemblies |
| Sealing Capability | Prevents passage of smoke and flames; equipped with intumescent seals | Limited or no sealing against smoke or flames |
| Use Case | Required in fire doors, commercial buildings, and fire-rated partitions | Used in residential or non-fire-rated interior doors |
| Cost | Higher cost due to certification and fire-resistant materials | Lower cost, widely available and less specialized |
| Durability | Designed for enhanced durability under fire conditions | Standard durability for typical door threshold use |
Understanding Thresholds: Fire-Rated vs Non-Fire-Rated
Fire-rated thresholds are specifically designed to prevent the spread of fire and smoke between rooms, meeting strict building codes and safety standards such as UL 10C and NFPA 80. Non-fire-rated thresholds lack these protective features and are typically used in residential or non-hazardous environments where fire containment is not a critical concern. Choosing the appropriate threshold depends on the specific application, with fire-rated options essential for commercial buildings, hospitals, and areas requiring enhanced fire safety compliance.
Key Features of Fire-Rated Thresholds
Fire-rated thresholds provide enhanced protection by sealing gaps to prevent the spread of fire, smoke, and toxic gases between rooms, essential in maintaining fire compartmentalization. They are constructed with fire-resistant materials such as steel or intumescent seals that expand when exposed to heat, maintaining the barrier's integrity under fire conditions. Compliance with fire safety standards like UL 10C or NFPA 80 ensures these thresholds meet rigorous testing criteria for effective performance during emergencies.
Non-Fire-Rated Thresholds: Overview and Applications
Non-fire-rated thresholds are designed primarily for general use in residential and commercial buildings where fire resistance is not a critical requirement. These thresholds provide a smooth transition between different flooring surfaces and help contain drafts, dust, and moisture without the added barrier properties against heat or flames. Common applications include interior doorways, closets, and non-rated partitions where fire protection standards do not apply.
Safety Standards and Fire Codes Explained
Fire-rated thresholds meet stringent safety standards and comply with fire codes such as NFPA 80, designed to prevent the spread of fire and smoke between rooms. Non-fire-rated thresholds lack these certifications and do not provide the same level of fire resistance or protection in emergency situations. Installing fire-rated thresholds is essential for buildings requiring compliance with fire safety regulations to ensure occupant safety and property protection.
Material Differences: Fire-Rated vs Non-Fire-Rated Thresholds
Fire-rated thresholds typically utilize materials such as steel, aluminum with intumescent seals, or specially treated wood to withstand high temperatures and prevent fire spread for specified periods. Non-fire-rated thresholds often use standard wood, plastic, or aluminum without any fire-resistant coatings or seals, focusing mainly on durability and aesthetics rather than fire protection. The critical material difference lies in fire-rated thresholds being engineered to maintain structural integrity and slow ember passage during fires, while non-fire-rated variants lack these protective enhancements.
Installation Requirements for Fire-Rated Thresholds
Fire-rated thresholds require strict installation standards, including precise alignment with fire door assemblies to maintain integrity under fire conditions. These thresholds must be secured with specific fasteners and fire-resistant sealants to prevent smoke and flame penetration. Proper clearance gaps and compatibility with fire-rated door and frame assemblies ensure compliance with safety codes and certification standards.
Cost Comparison: Fire-Rated vs Non-Fire-Rated Thresholds
Fire-rated thresholds typically cost 30% to 50% more than non-fire-rated thresholds due to the specialized materials and testing standards required for fire resistance. Non-fire-rated thresholds offer budget-friendly options but lack the certification needed for fire safety compliance in commercial buildings. Investing in fire-rated thresholds ensures adherence to building codes and reduces potential liabilities, justifying the higher initial expense.
Energy Efficiency and Insulation Benefits
Fire-rated thresholds provide superior energy efficiency by incorporating materials designed to resist heat transfer and maintain airtight seals, significantly reducing thermal bridging compared to non-fire-rated thresholds. These thresholds enhance insulation performance by minimizing drafts and preventing heat loss, contributing to lower energy consumption for heating and cooling systems. Non-fire-rated thresholds typically lack these specialized properties, resulting in less effective insulation and higher energy costs over time.
Maintenance and Longevity of Threshold Types
Fire-rated thresholds require regular inspection and maintenance to ensure their fire-resistant properties remain effective over time, often involving checks for damage and integrity of intumescent seals. Non-fire-rated thresholds typically demand less rigorous maintenance, focusing primarily on wear and tear from daily use rather than compliance with fire safety standards. Longevity of fire-rated thresholds depends on adherence to fire code requirements and proper upkeep, while non-fire-rated thresholds may last longer with basic maintenance but offer no fire protection.
Choosing the Right Threshold for Your Project
When selecting a threshold for your project, understanding the difference between fire-rated and non-fire-rated thresholds is crucial to ensure safety compliance and building code requirements. Fire-rated thresholds are designed to withstand fire exposure for a specified duration, typically ranging from 20 to 90 minutes, providing essential protection in commercial and residential buildings. Non-fire-rated thresholds offer basic functionality without fire resistance, making them suitable for interior applications where fire protection is not mandated.
Fire-Rated Threshold vs Non-Fire-Rated Threshold Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com