A threshold strip creates a smooth transition between different flooring types, offering durability and protection against moisture and drafts. In contrast, a baseboard serves primarily decorative purposes, covering the joint between the wall and the floor while protecting the wall from damage. Threshold strips are essential for functional flooring transitions, whereas baseboards enhance the room's aesthetic and protect walls.
Table of Comparison
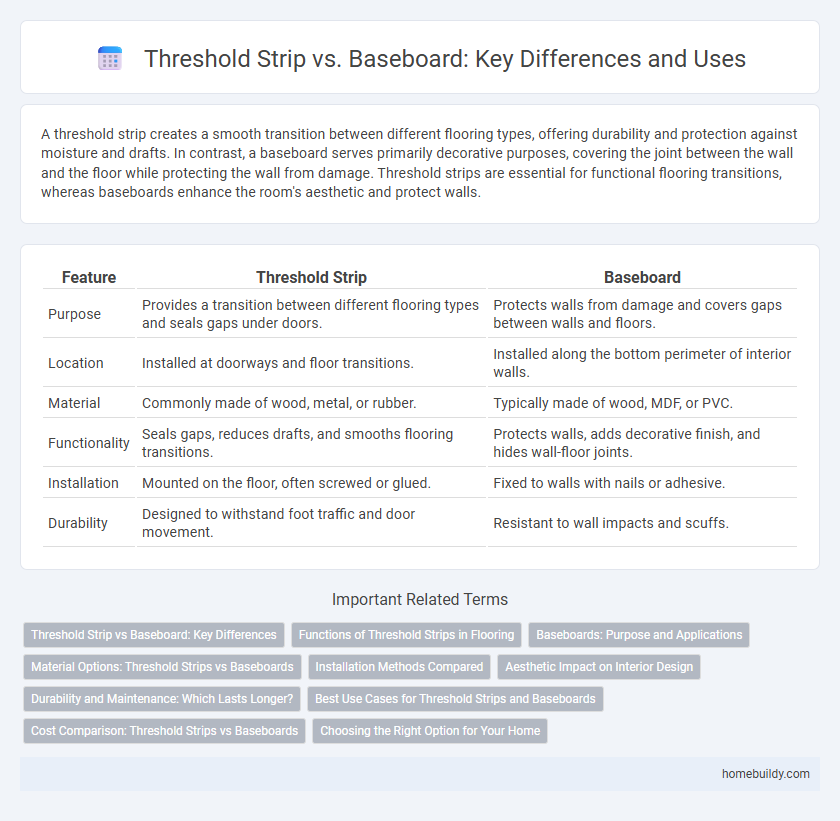
| Feature | Threshold Strip | Baseboard |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Provides a transition between different flooring types and seals gaps under doors. | Protects walls from damage and covers gaps between walls and floors. |
| Location | Installed at doorways and floor transitions. | Installed along the bottom perimeter of interior walls. |
| Material | Commonly made of wood, metal, or rubber. | Typically made of wood, MDF, or PVC. |
| Functionality | Seals gaps, reduces drafts, and smooths flooring transitions. | Protects walls, adds decorative finish, and hides wall-floor joints. |
| Installation | Mounted on the floor, often screwed or glued. | Fixed to walls with nails or adhesive. |
| Durability | Designed to withstand foot traffic and door movement. | Resistant to wall impacts and scuffs. |
Threshold Strip vs Baseboard: Key Differences
Threshold strips serve as transitional elements between flooring surfaces, providing a smooth, durable connection that prevents tripping hazards and masks floor height differences. Baseboards, on the other hand, protect walls from damage, cover gaps between walls and floors, and enhance interior aesthetics without addressing floor transitions. The primary difference lies in functionality: threshold strips manage floor-to-floor transitions while baseboards focus on wall-floor junctions and decorative finishing.
Functions of Threshold Strips in Flooring
Threshold strips provide a smooth transition between different flooring types, ensuring safety by reducing tripping hazards. They effectively cover expansion gaps in flooring, preventing dirt and moisture from penetrating beneath the floor surface. Unlike baseboards, threshold strips are specifically designed to bridge the gap between floors, enhancing durability and maintaining floor integrity.
Baseboards: Purpose and Applications
Baseboards serve as protective and decorative elements installed along the bottom of interior walls, covering the joint between the wall surface and the floor. Their primary purpose includes shielding walls from damage caused by furniture, foot traffic, and cleaning tools while also enhancing the room's aesthetic appeal with various materials such as wood, MDF, or vinyl. Unlike threshold strips, which transition between different flooring types or levels, baseboards are integral to wall finishing and interior design continuity.
Material Options: Threshold Strips vs Baseboards
Threshold strips are commonly made from durable materials like aluminum, vinyl, rubber, and wood, designed to withstand foot traffic and provide a seal between different flooring types. Baseboards primarily use wood, MDF, or PVC, focusing on aesthetic appeal and wall protection rather than durability against wear. Material choice for threshold strips emphasizes durability and functionality, while baseboards prioritize style and wall coverage.
Installation Methods Compared
Threshold strips typically install using adhesive backing or screws for secure placement at doorways, offering easy alignment and quick setup compared to baseboards. Baseboards require nailing or stapling to walls and often need additional caulking or painting, resulting in a more time-consuming installation process. The simpler and faster installation of threshold strips makes them ideal for transitional areas where durability and swift application are prioritized.
Aesthetic Impact on Interior Design
Threshold strips create seamless transitions between flooring types, enhancing spatial flow and visual harmony in interior design. Unlike baseboards that frame walls, threshold strips minimize visual interruptions, allowing flooring patterns and textures to stand out. Their slim profile supports a modern, clean aesthetic by preserving uninterrupted lines and emphasizing horizontal continuity.
Durability and Maintenance: Which Lasts Longer?
Threshold strips typically offer greater durability than baseboards due to their design for high foot traffic areas, resisting wear and moisture effectively. Baseboards, often made from wood or MDF, may require more frequent maintenance to prevent damage from impacts, moisture, or warping. Choosing a threshold strip can reduce long-term upkeep costs and extend the lifespan of the transition area between flooring surfaces.
Best Use Cases for Threshold Strips and Baseboards
Threshold strips are ideal for bridging gaps between different flooring types, such as hardwood and tile, providing a smooth transition that prevents tripping hazards. Baseboards excel in covering wall-floor junctions, protecting walls from damage and offering a finished look especially in living rooms and hallways. For doorways and high-traffic areas, threshold strips enhance durability and safety, whereas baseboards are best used for aesthetic enhancement and minor impact protection along interior walls.
Cost Comparison: Threshold Strips vs Baseboards
Threshold strips typically cost less than baseboards, with prices ranging from $1 to $5 per linear foot compared to baseboards, which can range from $3 to $10 per linear foot depending on material and style. Installation of threshold strips is generally quicker and less labor-intensive, resulting in lower overall labor costs compared to baseboards that require precise cutting and nailing. Maintenance expenses also favor threshold strips, as they are more durable in high-traffic areas and require less frequent replacement or repair than baseboards.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Home
Threshold strips provide a seamless transition between different flooring types while preventing drafts and moisture, making them ideal for doorways and high-traffic areas. Baseboards protect walls from damage and add a decorative finish but do not address floor-level gaps or transitions. Choose a threshold strip when floor protection and airtight sealing are priorities, whereas baseboards are preferable for wall protection and aesthetic enhancement.
threshold strip vs baseboard Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com