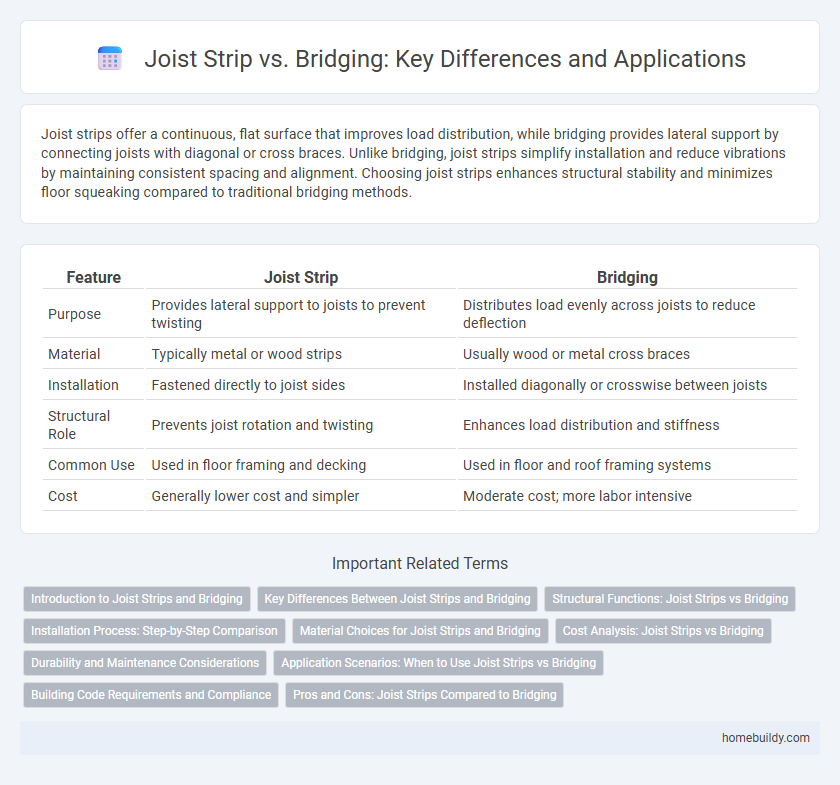
Joist strips offer a continuous, flat surface that improves load distribution, while bridging provides lateral support by connecting joists with diagonal or cross braces. Unlike bridging, joist strips simplify installation and reduce vibrations by maintaining consistent spacing and alignment. Choosing joist strips enhances structural stability and minimizes floor squeaking compared to traditional bridging methods.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Joist Strip | Bridging |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Provides lateral support to joists to prevent twisting | Distributes load evenly across joists to reduce deflection |
| Material | Typically metal or wood strips | Usually wood or metal cross braces |
| Installation | Fastened directly to joist sides | Installed diagonally or crosswise between joists |
| Structural Role | Prevents joist rotation and twisting | Enhances load distribution and stiffness |
| Common Use | Used in floor framing and decking | Used in floor and roof framing systems |
| Cost | Generally lower cost and simpler | Moderate cost; more labor intensive |
Introduction to Joist Strips and Bridging
Joist strips are narrow metal plates installed between joists to provide lateral support and prevent twisting, enhancing floor stability in wood-framed structures. Bridging consists of diagonal or cross braces fastened between joists to distribute loads evenly and reduce joist deflection. Both joist strips and bridging improve floor rigidity, but joist strips are typically easier to install in tight spaces while bridging offers greater load distribution.
Key Differences Between Joist Strips and Bridging
Joist strips are narrow metal or wood pieces installed perpendicular to floor joists to prevent twisting and provide lateral stability, while bridging consists of diagonal or cross-bracing members connecting joists to distribute loads evenly. Joist strips are primarily used to resist joist rotation and maintain alignment, whereas bridging enhances structural rigidity by transferring loads and minimizing deflection between joists. The key difference lies in their orientation and function: joist strips run perpendicular directly under the joist, focusing on torsional resistance, while bridging creates triangulation between joists, improving load distribution and floor stability.
Structural Functions: Joist Strips vs Bridging
Joist strips provide localized support by securing joists to adjacent framing elements, enhancing lateral stability and preventing twisting at specific points along the span. Bridging, typically installed between joists, distributes loads evenly and resists buckling by connecting joists in a continuous framework, improving overall floor rigidity. Structurally, joist strips reinforce connections primarily at bearing points, while bridging offers continuous mid-span stabilization to reduce deflection and increase load capacity.
Installation Process: Step-by-Step Comparison
Joist strip installation involves fastening strips of metal or wood perpendicular to joists, creating a continuous edge restraint that is simpler and quicker to install compared to bridging. Bridging requires fitting cross braces or diagonal supports between joists, demanding precise measurement and cutting for each brace to ensure structural stability. Joist strips reduce labor time by providing a uniform, repeatable installation process, whereas bridging necessitates increased skill and time for accurate placement.
Material Choices for Joist Strips and Bridging
Joist strips are typically made from galvanized steel or aluminum, offering corrosion resistance and lightweight durability, while bridging often uses steel or wood, depending on structural requirements and budget. Material choice for joist strips prioritizes ease of installation and long-term stability, whereas bridging materials are selected for load distribution and rigidity. Understanding these differences ensures optimal performance in floor framing systems through appropriate material selection.
Cost Analysis: Joist Strips vs Bridging
Joist strips typically offer a more cost-effective solution compared to bridging due to lower material and labor expenses, reducing overall project budgets. Bridging involves additional components and installation time, which can increase labor costs and extend project timelines. Choosing joist strips can streamline construction processes while maintaining structural stability, resulting in significant savings for contractors and developers.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Joist strips offer enhanced durability compared to traditional bridging due to their solid, continuous support that minimizes wood movement and reduces the risk of warping over time. Maintenance for joist strips is generally lower, as they require less frequent inspection and adjustment than bridging, which can loosen or shift. Selecting joist strips ensures long-term structural stability with minimal upkeep in flooring applications.
Application Scenarios: When to Use Joist Strips vs Bridging
Joist strips are ideal for securing floor joists in close-span applications where lateral stability is required without obstructing access for utilities. Bridging is more suitable in long-span or heavily loaded floors, distributing loads and reducing joist twisting to enhance structural integrity. Choosing between joist strips and bridging depends on floor design, load requirements, and space considerations for mechanical installations.
Building Code Requirements and Compliance
Joist strips must comply with specific building code requirements that ensure proper load distribution and structural stability, meeting standards outlined in the International Building Code (IBC) and local amendments. Unlike bridging, joist strips provide continuous lateral support, reducing joist rotation and maintaining alignment under load, which is critical for compliance in floor framing systems. Proper installation following code mandates also ensures fire resistance, vibration control, and adherence to minimum fastening schedules required for both residential and commercial construction.
Pros and Cons: Joist Strips Compared to Bridging
Joist strips provide enhanced stability by firmly securing joists and preventing lateral movement, making them ideal for minimizing floor vibrations and improving structural integrity. Unlike bridging, which relies on cross braces and can be harder to install in tight spaces, joist strips offer a simpler installation process and better adaptability to various joist layouts. However, joist strips may incur higher material costs and require precise positioning to be effective, whereas bridging often uses less expensive materials and can distribute loads more evenly across joists.
Joist strip vs Bridging Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com