Gutter spike corrosion involves the gradual deterioration of metal due to chemical reactions with environmental elements, often accelerated by moisture and pollutants. Rust specifically refers to the red, flaky iron oxide that forms when iron or steel is exposed to oxygen and water over time. Understanding the difference helps in selecting materials and maintenance methods to prolong the lifespan of gutter spikes effectively.
Table of Comparison
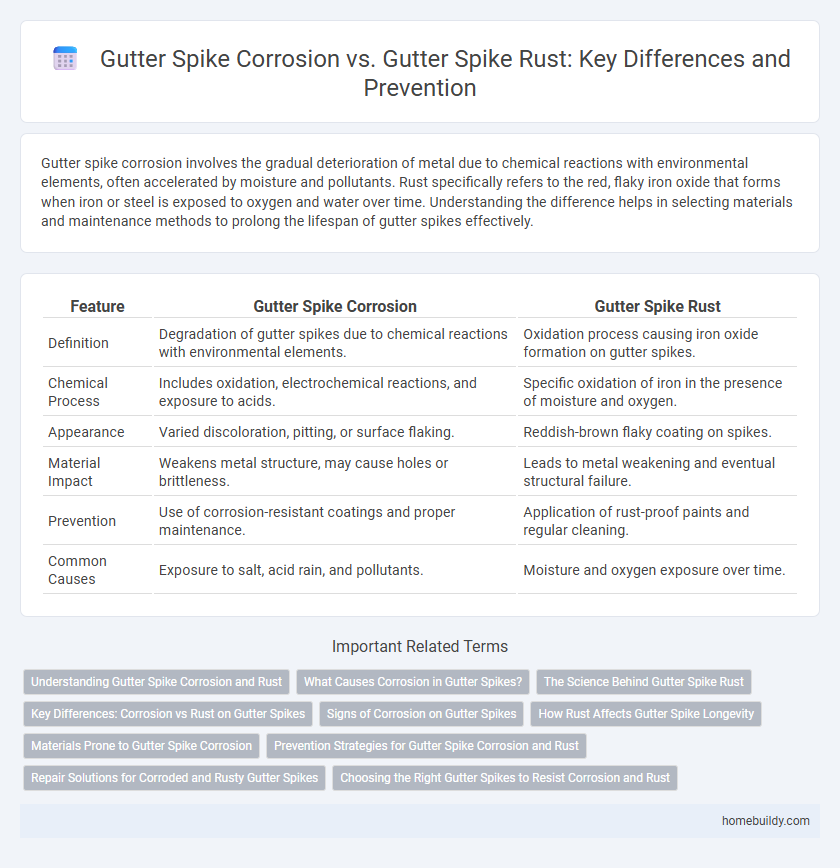
| Feature | Gutter Spike Corrosion | Gutter Spike Rust |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Degradation of gutter spikes due to chemical reactions with environmental elements. | Oxidation process causing iron oxide formation on gutter spikes. |
| Chemical Process | Includes oxidation, electrochemical reactions, and exposure to acids. | Specific oxidation of iron in the presence of moisture and oxygen. |
| Appearance | Varied discoloration, pitting, or surface flaking. | Reddish-brown flaky coating on spikes. |
| Material Impact | Weakens metal structure, may cause holes or brittleness. | Leads to metal weakening and eventual structural failure. |
| Prevention | Use of corrosion-resistant coatings and proper maintenance. | Application of rust-proof paints and regular cleaning. |
| Common Causes | Exposure to salt, acid rain, and pollutants. | Moisture and oxygen exposure over time. |
Understanding Gutter Spike Corrosion and Rust
Gutter spike corrosion occurs when metal degrades due to chemical reactions with environmental elements such as moisture, salt, and pollutants, leading to weakened structural integrity. Rust, a specific form of corrosion, is the oxidation of iron or steel gutter spikes resulting in reddish-brown flaky deposits that compromise the spike's durability. Understanding the distinction between general corrosion and rust is essential for selecting appropriate materials and protective coatings to extend the lifespan of gutter spikes.
What Causes Corrosion in Gutter Spikes?
Corrosion in gutter spikes occurs primarily due to prolonged exposure to moisture combined with environmental factors such as acid rain, salt, and pollutants that accelerate metal degradation. Unlike surface rust, corrosion involves electrochemical reactions breaking down the metal's structural integrity at a deeper level. Gutter spike materials with low corrosion resistance, such as untreated steel, are more susceptible to this process compared to galvanized or stainless steel spikes.
The Science Behind Gutter Spike Rust
Gutter spike rust occurs when iron in the metal reacts with oxygen and moisture, forming iron oxide, which weakens the spike's structural integrity. Corrosion, on the other hand, encompasses a broader range of chemical reactions, including rust, that degrade metal surfaces through electrochemical processes. Understanding the oxidation process specifically highlights how water exposure accelerates rust formation on gutter spikes, compromising their durability over time.
Key Differences: Corrosion vs Rust on Gutter Spikes
Gutter spike corrosion refers to the chemical degradation of metal caused by environmental exposure, leading to weakened structural integrity, while rust specifically denotes the formation of iron oxide on ferrous metals due to oxidation in the presence of moisture and oxygen. Corrosion encompasses a broader range of metal deterioration processes beyond just rust, affecting various types of metals used in gutter spikes. Rust is a specific type of corrosion limited to iron or steel gutter spikes, characterized by its reddish-brown flaky appearance and slower progression compared to other forms of corrosive damage.
Signs of Corrosion on Gutter Spikes
Signs of corrosion on gutter spikes include pitting, discoloration, and surface roughness, which indicate metal degradation beyond superficial rust. Unlike rust, which primarily appears as a flaky reddish-brown coating, corrosion often involves deeper structural damage compromising the spike's holding strength. Early detection of these symptoms is critical to prevent gutter instability and water damage.
How Rust Affects Gutter Spike Longevity
Rust, a form of corrosion, significantly reduces gutter spike longevity by weakening the metal structure through oxidative damage. The presence of rust causes gutter spikes to become brittle and prone to breaking, leading to compromised gutter stability and potential water damage. Preventing rust formation with coatings or stainless steel materials extends the functional lifespan of gutter spikes.
Materials Prone to Gutter Spike Corrosion
Gutter spike corrosion occurs primarily in metals such as galvanized steel, aluminum, and iron, which are commonly used due to their strength but are vulnerable to environmental factors like moisture and acidic rain. Rust, a specific type of corrosion, typically affects iron and steel gutters by forming iron oxide when exposed to oxygen and water, leading to material degradation. Understanding the specific metal composition of gutter spikes helps in selecting appropriate protective coatings or stainless steel alternatives to enhance longevity and reduce maintenance costs.
Prevention Strategies for Gutter Spike Corrosion and Rust
Effective prevention strategies for gutter spike corrosion and rust include applying protective coatings such as zinc or galvanized plating to inhibit oxidation. Regular maintenance involves inspecting and cleaning gutter spikes to remove debris and moisture buildup, which accelerates corrosion and rust formation. Using stainless steel or corrosion-resistant materials for gutter spikes enhances durability and minimizes the risk of both corrosion and rust over time.
Repair Solutions for Corroded and Rusty Gutter Spikes
Corrosion of gutter spikes results from chemical reactions between metal and environmental elements, leading to weakened structural integrity, while rust specifically refers to iron oxide forming on iron-based spikes due to oxidation. Repair solutions for corroded and rusty gutter spikes include replacing compromised spikes with stainless steel or galvanized alternatives to prevent future corrosion, applying rust-inhibitive primers and sealants, and performing routine maintenance to identify early signs of deterioration. Using corrosion-resistant materials and protective coatings enhances the longevity and stability of gutter systems, reducing maintenance costs and damage risks.
Choosing the Right Gutter Spikes to Resist Corrosion and Rust
Gutter spikes made from stainless steel or galvanized steel offer superior resistance to corrosion and rust compared to traditional iron spikes, ensuring longevity in various weather conditions. Choosing spikes with protective coatings such as zinc or ceramic layers further extends their durability by preventing oxidation and moisture damage. Properly selected corrosion-resistant gutter spikes minimize maintenance costs and protect gutter integrity, making them a cost-effective solution for long-term roofing system preservation.
Gutter spike corrosion vs Gutter spike rust Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com