Expansion joint covers are designed to accommodate building movement between structural elements, typically used in exterior or structural joints to prevent damage from thermal expansion, seismic activity, or load shifts. Interior joint covers, on the other hand, are primarily aesthetic and functional solutions for gaps within interior spaces, focusing on seamless finishes and minor movement accommodation. Choosing between expansion joint covers and interior joint covers depends on the location, movement requirements, and environmental exposure of the joint.
Table of Comparison
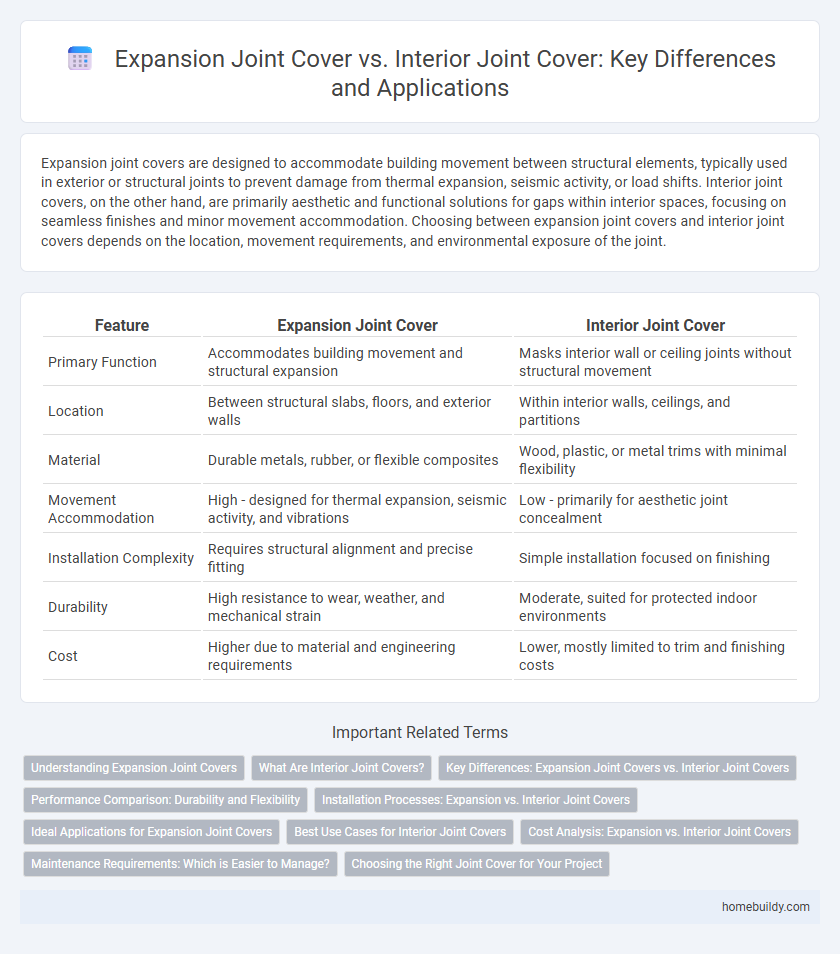
| Feature | Expansion Joint Cover | Interior Joint Cover |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Accommodates building movement and structural expansion | Masks interior wall or ceiling joints without structural movement |
| Location | Between structural slabs, floors, and exterior walls | Within interior walls, ceilings, and partitions |
| Material | Durable metals, rubber, or flexible composites | Wood, plastic, or metal trims with minimal flexibility |
| Movement Accommodation | High - designed for thermal expansion, seismic activity, and vibrations | Low - primarily for aesthetic joint concealment |
| Installation Complexity | Requires structural alignment and precise fitting | Simple installation focused on finishing |
| Durability | High resistance to wear, weather, and mechanical strain | Moderate, suited for protected indoor environments |
| Cost | Higher due to material and engineering requirements | Lower, mostly limited to trim and finishing costs |
Understanding Expansion Joint Covers
Expansion joint covers are designed to accommodate building movements caused by thermal expansion, seismic activity, and structural shifts, ensuring the integrity of structural joints in floors, walls, and ceilings. Interior joint covers, in contrast, primarily focus on aesthetic concealment and minor movement absorption within interior spaces but may not withstand significant structural displacement or environmental stress. Understanding expansion joint covers involves recognizing their critical role in preventing damage, maintaining safety, and prolonging the lifespan of architectural elements by allowing controlled movement in various construction materials.
What Are Interior Joint Covers?
Interior joint covers are specialized architectural elements designed to conceal expansion joints within building interiors, ensuring seamless aesthetics while accommodating structural movement caused by thermal expansion and contraction. Unlike exterior expansion joint covers exposed to environmental elements, interior joint covers prioritize materials that blend with interior finishes such as drywall, tiles, or carpet, providing both functional flexibility and visual integration. These covers play a critical role in maintaining building integrity by preventing interior surface damage while allowing movement flexibility in walls, ceilings, and floors.
Key Differences: Expansion Joint Covers vs. Interior Joint Covers
Expansion joint covers are designed to accommodate large movements caused by thermal expansion, seismic activity, or structural shifts, typically used in exterior and structural joints, while interior joint covers manage smaller movements within interior walls, floors, or ceilings. Expansion joint covers feature robust materials and flexible designs that resist weather, water infiltration, and heavy traffic, contrasting with interior joint covers that prioritize aesthetic integration and concealment. The selection depends on the joint's location, expected movement range, and environmental exposure, ensuring durability and functional performance in building infrastructure.
Performance Comparison: Durability and Flexibility
Expansion joint covers are engineered for superior durability and flexibility, accommodating significant structural movement and external environmental stresses, unlike interior joint covers which primarily focus on aesthetic integration and minor surface-level expansion. The robust materials and design of expansion joint covers enable long-term performance in demanding conditions such as thermal expansion, seismic activity, and heavy foot or vehicle traffic. Interior joint covers offer limited flexibility and wear resistance, making them less suitable for critical structural applications where movement accommodation and durability are essential.
Installation Processes: Expansion vs. Interior Joint Covers
Expansion joint covers require precise alignment and anchoring to accommodate structural movement, often involving heavy-duty materials like metal or rubber to withstand exterior conditions. Interior joint covers typically have simpler installation processes, using lighter materials such as vinyl or plastic, and focus on aesthetic integration within indoor environments. The installation of expansion joint covers demands more robust sealing and flexibility to handle thermal expansion and contraction compared to interior joint covers designed primarily for decorative and minor movement purposes.
Ideal Applications for Expansion Joint Covers
Expansion joint covers are designed to accommodate building movement in areas exposed to structural shifts, vibrations, and thermal expansion, making them ideal for exterior facades, ceilings, and floors in commercial or industrial buildings. Interior joint covers, by contrast, are best suited for controlled environments where minimal movement occurs, such as office partitions or interior walls. Expansion joint covers ensure durability, safety, and aesthetic continuity in high-traffic areas prone to dynamic loads and environmental stresses.
Best Use Cases for Interior Joint Covers
Interior joint covers are best suited for controlling building movement within interior spaces, such as office corridors, hospital hallways, and commercial lobbies, where aesthetic integration and durability are essential. These covers accommodate thermal expansion, seismic activity, and structural vibrations while maintaining a smooth, flush surface to prevent tripping hazards. Their design typically emphasizes fire resistance and ease of maintenance, making them ideal for locations with high foot traffic and strict safety requirements.
Cost Analysis: Expansion vs. Interior Joint Covers
Expansion joint covers generally incur higher initial costs due to their robust materials and ability to accommodate building movement, while interior joint covers are typically less expensive as they mainly address aesthetic and minor functional needs. Maintenance expenses for expansion joint covers tend to be higher given their exposure to structural stresses and environmental factors, whereas interior joint covers have lower upkeep requirements. Evaluating lifecycle costs reveals that investing in expansion joint covers reduces long-term repair risks, making them cost-effective for structural integrity despite the upfront price difference.
Maintenance Requirements: Which is Easier to Manage?
Expansion joint covers typically require more maintenance due to their exposure to external elements like weather, temperature fluctuations, and debris, which can cause wear and tear. Interior joint covers are easier to manage as they are protected from harsh environmental conditions, reducing the need for frequent inspections and repairs. Regular cleaning and periodic checks suffice for interior covers, whereas expansion joint covers demand rigorous maintenance schedules to ensure durability and functionality.
Choosing the Right Joint Cover for Your Project
Expansion joint covers are designed to accommodate larger movements between structural elements and are typically used in exterior applications where thermal expansion and seismic activity are factors. Interior joint covers, by contrast, prioritize aesthetics and surface continuity, often featuring materials that blend seamlessly with interior finishes. Choosing the right joint cover depends on the specific movement requirements, environmental exposure, and design intent of your project to ensure durability and performance.
expansion joint cover vs interior joint cover Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com