Balusters are vertical posts that provide support and aesthetic appeal to staircases, balconies, and terraces, while guardrails are horizontal safety barriers designed primarily to prevent falls. Balusters contribute to the structural integrity and decorative style of a railing system, whereas guardrails focus on safety compliance and height requirements. Understanding the distinction between balusters and guardrails is essential for selecting the appropriate components in architectural and construction projects.
Table of Comparison
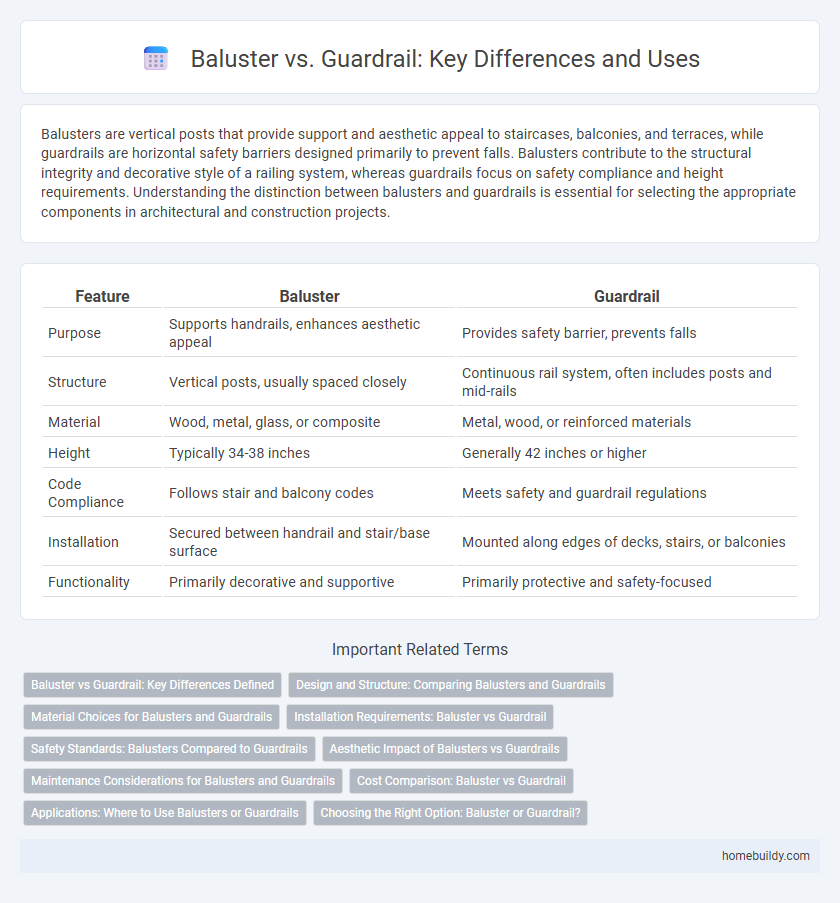
| Feature | Baluster | Guardrail |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Supports handrails, enhances aesthetic appeal | Provides safety barrier, prevents falls |
| Structure | Vertical posts, usually spaced closely | Continuous rail system, often includes posts and mid-rails |
| Material | Wood, metal, glass, or composite | Metal, wood, or reinforced materials |
| Height | Typically 34-38 inches | Generally 42 inches or higher |
| Code Compliance | Follows stair and balcony codes | Meets safety and guardrail regulations |
| Installation | Secured between handrail and stair/base surface | Mounted along edges of decks, stairs, or balconies |
| Functionality | Primarily decorative and supportive | Primarily protective and safety-focused |
Baluster vs Guardrail: Key Differences Defined
Balusters are vertical posts that support a railing, primarily designed for aesthetic appeal and minor safety functions, while guardrails are robust safety barriers intended to prevent falls from elevated surfaces. Balusters typically have smaller spacing and decorative designs, whereas guardrails are constructed to meet strict safety codes with stronger materials and higher load resistance. Understanding the key differences involves recognizing that balusters contribute to style and light visibility, whereas guardrails prioritize protection and structural integrity.
Design and Structure: Comparing Balusters and Guardrails
Balusters are typically slender, vertical posts that provide support to handrails and are often designed with decorative elements, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of staircases and balconies. Guardrails, on the other hand, are broader safety barriers engineered to prevent falls and can incorporate solid panels, glass, or metal bars for increased security and durability. The structural design of balusters emphasizes style and spacing for visibility, while guardrails prioritize strength and compliance with safety standards in residential and commercial buildings.
Material Choices for Balusters and Guardrails
Balusters and guardrails differ significantly in material choices, with balusters commonly crafted from wood, metal, glass, or composite materials to balance aesthetic appeal and structural support. Guardrails often utilize stronger, more durable materials like steel, aluminum, or reinforced concrete to ensure safety and withstand higher impact forces. Selecting the right material depends on factors such as desired style, environmental exposure, load requirements, and maintenance preferences.
Installation Requirements: Baluster vs Guardrail
Balusters require precise spacing and secure anchoring to comply with safety regulations, typically spaced no more than 4 inches apart to prevent falls. Guardrails demand sturdier installation with posts embedded deeply or secured to structural elements, supporting higher load capacities for safety compliance. Both installations must meet local building codes, but guardrails generally involve more robust materials and anchoring methods to provide enhanced protection.
Safety Standards: Balusters Compared to Guardrails
Balusters and guardrails serve distinct roles in fall protection, with guardrails typically meeting stricter safety standards due to their height and strength requirements set by OSHA and building codes. Balusters often focus on spacing to prevent small children or objects from falling through, adhering to maximum gap limits of 4 inches. Guardrails must withstand specific load pressures, usually 200 pounds of force applied outward and downward, to ensure effective fall prevention on elevated surfaces.
Aesthetic Impact of Balusters vs Guardrails
Balusters offer intricate designs that enhance the visual appeal of staircases and balconies, creating a more refined and elegant look compared to guardrails. Guardrails typically emphasize functionality and safety, often featuring simpler, more robust construction with fewer decorative details. The aesthetic impact of balusters lies in their ability to add architectural interest and complement interior styles, making them a preferred choice for enhancing visual character.
Maintenance Considerations for Balusters and Guardrails
Balusters require regular inspection for cracks, chips, and loose fittings to ensure structural integrity, with wood balusters needing periodic sealing or painting to prevent rot and weather damage. Guardrails, often made from metal or composite materials, typically demand less frequent maintenance but still require rust prevention treatments and checks for stability against impact. Both elements benefit from routine cleaning to maintain appearance and safety, with attention to local building codes impacting specific maintenance protocols.
Cost Comparison: Baluster vs Guardrail
Balusters typically cost between $15 to $50 per piece depending on material and design, while guardrails can range from $30 to $100 per linear foot due to their structural components and installation complexity. Balusters offer a more budget-friendly option for decorative railing, whereas guardrails require higher investment for safety compliance and durability. Comparing installation costs, balusters are quicker and less labor-intensive, reducing overall expenses compared to the more robust guardrail systems.
Applications: Where to Use Balusters or Guardrails
Balusters are ideal for decorative staircases, balconies, and interior railings where aesthetics and detailed design are prioritized, providing both support and ornamental appeal. Guardrails are essential in industrial settings, commercial buildings, and outdoor areas requiring robust safety measures to prevent falls, offering higher strength and durability. Choosing between balusters and guardrails depends on the application's safety requirements and design preferences, with balusters commonly used in residential architecture and guardrails in high-risk environments.
Choosing the Right Option: Baluster or Guardrail?
Balusters provide decorative support and are typically spaced closely to enhance aesthetic appeal and safety on staircases or balconies. Guardrails offer robust protection by serving as a barrier with a solid or continuous top rail, ideal for high-risk areas requiring maximum fall prevention. Selecting between balusters and guardrails depends on factors such as safety requirements, design preferences, and building code specifications for residential or commercial applications.
Baluster vs Guardrail Infographic
 homebuildy.com
homebuildy.com